What is the Difference Between N-acetyl Tyrosine and L-tyrosine
Table of Contents
The key difference between N-acetyl tyrosine and L-tyrosine is that N-acetyl tyrosine has better absorption and stronger nootropic effects than L-tyrosine.
N-acetyl tyrosine is a derivative of L-tyrosine. L-tyrosine is the most common isomer of tyrosine amino acid. L-tyrosine is commonly known as tyrosine because it is the most abundant isomer of tyrosine. This article discusses the differences between N-acetyl tyrosine and L-tyrosine.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is N-acetyl Tyrosine
3. What is L-tyrosine
4. Similarities – N-acetyl Tyrosine and L-tyrosine
5. N-acetyl Tyrosine vs L-tyrosine in Tabular Form
6. Summary – N-acetyl Tyrosine vs L-tyrosine
What is N-acetyl Tyrosine?
N-acetyl tyrosine is a derivative of L-tyrosine that is promoted for its better absorption and efficacy. It is abbreviated as NALT or NAT. It is useful as a supplement for boosting physical and mental performance. This compound is a source of L-tyrosine but does not show the same health effect.
Typically, upon ingestion, a portion of N-acetyl tyrosine converts into L-tyrosine. This, in turn, helps in increasing the neurotransmitters known as catecholamines. These include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, which are produced with the help of L-tyrosine.
What is L-tyrosine?
L-tyrosine is the most common isomer of tyrosine amino acid. It is commonly known as tyrosine because it is the most abundant isomer of tyrosine. The chemical name of this compound is 4-hydroxyphenylalanine. In fact, it is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are useful for cells in synthesizing proteins. However, we can name it as a non-essential amino acid having a polar side group.
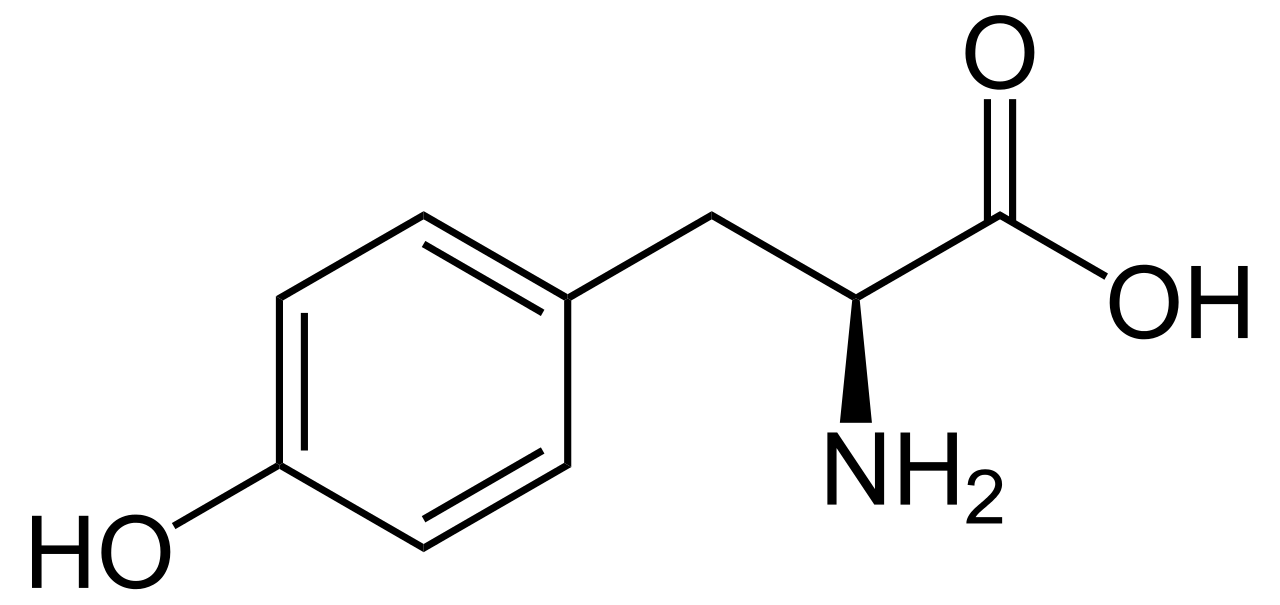
Figure 01: The Chemical Structure of L-tyrosine
Although it is common as a proteinogenic amino acid, it has a special role in phenol functionality as well. Sometimes, it exists in proteins as a part of the signal transduction process and can function as a receiver for phosphate groups that comes from protein kinases.
A standard dose of L-tyrosine, according to the Dietary Reference Intake, is 42 mg per kilogram of body weight. For instance, if the body weight is 70 kg, the intake is 2.31 g. Moreover, L-tyrosine is formed in the body from phenylalanine, which can be found in many high-protein food products, including chicken, turkey, fish, milk, sesame seeds, soy products, and lima beans.
There are several medical uses of L-tyrosine, which include the use of it as a precursor to neurotransmitters and increasing the plasma neurotransmitter level. However, it shows little effect on this. There are also studies that show L-tyrosine as a medication useful in conditions of stress, cold, fatigue, sleep deprivation, etc.
What are the Similarities Between N-acetyl Tyrosine and L-tyrosine?
What is the Difference Between N-acetyl Tyrosine and L-tyrosine?
N-acetyl tyrosine is a derivative of L-tyrosine, which is promoted for its better absorption and efficacy. L-tyrosine is commonly known as tyrosine because it is the most abundant isomer of tyrosine. The key difference between N-acetyl tyrosine and L-tyrosine is that N-acetyl tyrosine has better absorption and stronger nootropic effects than L-tyrosine.
Below is a summary of the difference between N-acetyl tyrosine and L-tyrosine in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – N-acetyl Tyrosine vs L-tyrosine
N-acetyl tyrosine is a derivative of L-tyrosine while L-tyrosine is the most common isomer of tyrosine amino acid. The key difference between N-acetyl tyrosine and L-tyrosine is that N-acetyl tyrosine has better absorption and stronger nootropic effects than L-tyrosine.
Reference:
1. Aleksa, Ristic. “N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine (NALT) Benefits, Side Effects & Dosage.” SelfDecode Supplements, 9 Sept. 2021.
Image Courtesy:
1. “L-Tyrosin – L-Tyrosine” By NEUROtiker – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoynZJqblanGrXnTsqmoq5mjsm6tzZ1kpWWkrr%2Bwv8innGg%3D