What is the Difference Between Isotopomer and Isotopologue
Table of Contents
The key difference between isotopomer and isotopologue is that an isotopomer is any organic compound differing only in the position of an isotope, whereas an isotopologue is any of a group of compounds that differ only in the isotopic composition.
The terms isotopomer and isotopologue are two important terms in organic chemistry. They describe the differences between two closely related organic compounds.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Isotopomer
3. What is Isotopologue
4. Isotopomer vs Isotopologue in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Isotopomer vs Isotopologue
What is an Isotopomer?
The term isotopomer refers to isomers with isotopic atoms consisting of the same number of each isotope of each element but differing in positions. This phenomenon is similar to constitutional isomerism. The isotopic location determines the stereoisomerism of the molecule. Stereoisomerism is a form of isomerism where isomers have the same composition (possessing the same parts) but there is a difference in the orientation of those parts in space. Furthermore, this term isotopomer was first introduced by Seeman and Paine in 1992 in distinguishing isotopic isomers from isotopologues.
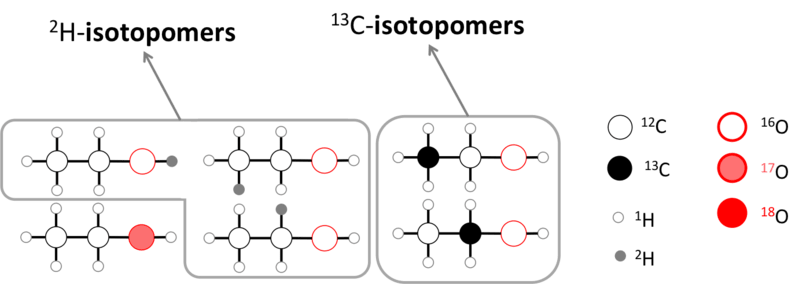
Figure 01: Hydrogen and Carbon Isotopomers of Ethanol
Moreover, in NMR spectroscopy, C-12 (the most abundant isotope) does not produce any signal, while C-13 (a less abundant isotope) can be easily detected. This results in carbon isotopomers of a compound to be studied by C-13 NMR to determine the different carbon atoms that occur in the compound.
What is an Isotopologue?
Isopologue molecules are molecules that differ only in the isotopic composition. These molecules have the same chemical formula and bonding arrangement of atoms. However, at least one atom has a different number of neutrons than the parent molecule.
For example, water has hydrogen-related isotopologues.
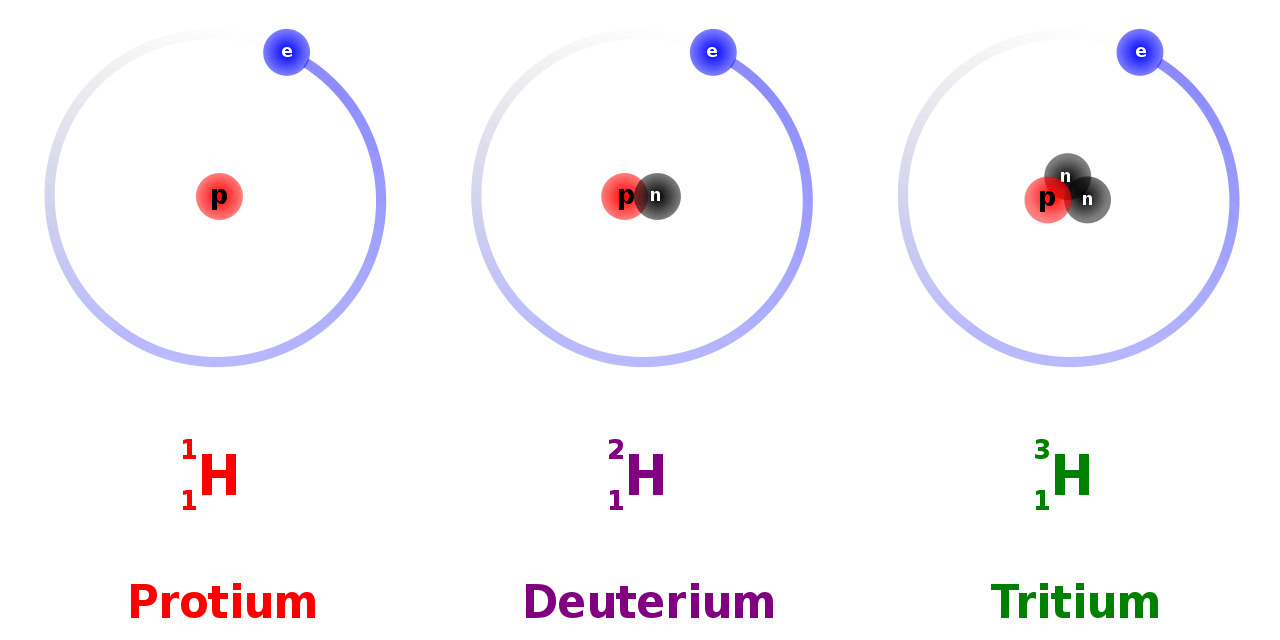
Figure 02: Protium, Deuterium, and Tritium
In isotopologues, the atoms of the different isotopes can occur anywhere on the molecule. Therefore, the difference is in the net chemical formula. If there are compounds with several atoms of the same element, it can have any of these atoms altered, and it still gives the same isotopologue.
What is the Difference Between Isotopomer and Isotopologue?
Isopologue molecules are molecules that differ only in the isotopic composition. Isotopomer are isomers with isotopic atoms, in which there is the same number of each isotope, but these isotopes are in different positions. Therefore, the key difference between isotopomer and isotopologue is that an isotopomer is any organic compound differing only in the position of an isotope whereas an isotopologue is any of a group of compounds that differ only in the isotopic composition.
The below infographic presents the differences between isotopomer and isotopologue in tabular form for side-by-side comparison.
Summary – Isotopomer vs Isotopologue
The terms isotopomer and isotopologue are two important terms in organic chemistry that describe the differences between two closely related organic compounds. The key difference between isotopomer and isotopologue is that an isotopomer is any organic compound differing only in the position of an isotope, whereas an isotopologue is any of a group of compounds that differ only in the isotopic composition.
Reference:
1. Gerber, Wilhelmus J., et al. “195PT NMR Isotopologue and Isotopomer Distributions of [Ptcln(h2o)6 − N]4 − N (n = 6,5,4) Species as a Fingerprint for Unambiguous Assignment of Isotopic Stereoisomers.” Dalton Transactions, The Royal Society of Chemistry, 18 June 2008.
2. “Isotopomers.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 26 Nov. 2021.
3. “Isotopologue.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 29 May 2022.
Image Courtesy:
1. “PSIA Wiki1” By Alexis Gilbert – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Hydrogen Deuterium Tritium Nuclei Schmatic-en” By Dirk Hünniger;Derivative work in english – Balajijagadesh – This file was derived from: Hydrogen Deuterium Tritium Nuclei Schmatic-de.svg (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyiqqisn6W8rrHRZpinnF2ewLDAzqmmpaeXqrJw