What is the Difference Between Iodide and Triiodide
Table of Contents
The key difference between iodide and triiodide is that iodide is a single iodine atom having a -1 charge whereas triiodide is a combination of three iodine atoms having a -1 overall charge.
Iodide and triiodide are two types of anions of iodine. These two ions usually exist together in aqueous solutions, having an equilibrium with the diiodide anion.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Iodide
3. What is Triiodide
4. Similarities – Iodide and Triiodide
5. Iodide vs Triiodide in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Iodide vs Triiodide
What is Iodide?
Iodide is an anion of iodine. This anion forms when an iodine atom obtains an electron from the outside. Accordingly, the chemical symbol of iodide is I–, and the molar mass of this ion is 126.9 g/mol. We name the chemical compounds consisting of this anion commonly as “iodides”. Above all, iodide is the largest monatomic anion because it forms from the iodine atom that has a large atomic size comparatively. Moreover, iodide forms comparatively weak bonds with opposite ions since it’s a large ion. Due to the same reason, iodide is less hydrophilic than other small anions.

Figure 01: Iodide Anion
Most of the time, compounds containing iodide ions such as iodide salt are water-soluble but not as water-soluble as chlorides and bromides. In addition, the aqueous solutions containing this anion can increase the solubility of iodine molecules (I2) better than pure water.
What is Triiodide?
Triiodide is the anion containing three iodine atoms bonded to each other with a -1 negative charge. The chemical formula of this compound is I3–. It is one of the polyhalogeno ions formed through the combination of aqueous solutions of iodide salts and iodine. In the aqueous solution, this ion creates a red-brown colour.
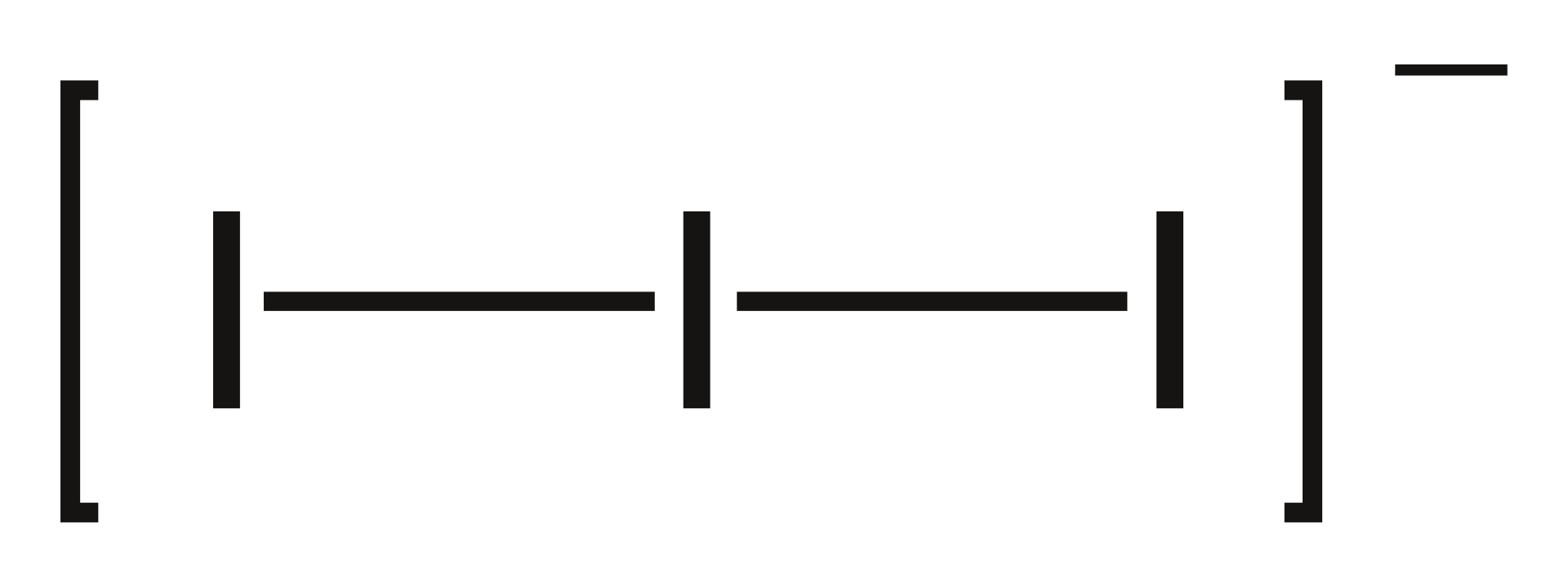
Figure 02: Chemical Structure of Triiodide Anion
The term triiodide is used to name other chemical compounds containing the triiodide anion as a common name. Moreover, this term can be used for compounds that contain three iodide centres that are not bound to each other but exist as separate iodide ions. E.g. Nitrogen triiodide and phosphorous triiodide contain nitrogen and phosphorous centres, respectively, where there are three iodine atoms attached to each centre, so we can name them as triiodide compounds.
Triiodide anion is linear. It is also symmetrical. There are three equatorial lone electron pairs on the central iodine atom of this anion. In this anion, the I-I bond length is longer than the I-I bond in the diatomic iodine compound. However, when the triiodide anion is in ionic compounds, this bond length may vary accordingly.
When the triiodide ion is in low concentration in some aqueous solutions, the solution appears in yellow colour. If the concentration is high, the solution appears in red-brown colour. Moreover, this anion is responsible for the blue-black colour that occurs when starch reacts with iodine solution.
When considering other solutions containing triiodide anion, Lugol’s iodine solution and tincture of iodine solution contain a considerable amount of triiodide anion.
Similarities Between Iodide and Triiodide
Difference Between Iodide and Triiodide
Iodide and triiodide are two types of anions of iodine. The key difference between iodide and triiodide is that iodide is a single iodine atom having a -1 charge, whereas triiodide is a combination of three iodine atoms having a -1 overall charge. Moreover, while iodide forms light orange-brown aqueous solutions, triiodide forms red-brown aqueous solutions at high concentrations and yellow colour solutions at low concentrations.
The following figure summarizes the difference between iodide and triiodide in tabular form.
Summary – Iodide vs Triiodide
Iodide and triiodide are two types of anions of iodine. The key difference between iodide and triiodide is that iodide is a single iodine atom having a -1 charge, whereas triiodide is a combination of three iodine atoms having a -1 overall charge.
Reference:
“Triiodide.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “I-” By NEUROtiker – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Triiodide” By Leyo – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyipp2hlJp6orrDZquroZmksaqwxGg%3D