What is the Difference Between Hyperplastic and Adenomatous Polyp
Table of Contents
The key difference between hyperplastic and adenomatous polyp is that hyperplastic polyp is a type of colon polyp that has virtually no chance of becoming cancerous, while adenomatous polyp is a type of colon polyp that has the potential to become cancerous.
The diagnosing of polyps in the colon or rectum often raises questions for patients as well as their families. Polyps are very common in males and females of all races who live in industrialized countries. This suggests that dietary and environmental factors play a vital role in polyp development. The most common types of polyps are hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps. Other types of polyps can also be found in the colon, such as malignant polyps.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Hyperplastic Polyp
3. What is Adenomatous Polyp
4. Similarities – Hyperplastic and Adenomatous Polyp
5. Hyperplastic vs Adenomatous Polyp in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Hyperplastic vs Adenomatous Polyp
What is Hyperplastic Polyp?
A hyperplastic polyp is a type of small polyp normally located in the end portion of the colon (especially the rectum and sigmoid colon). Hyperplastic gastric polyps appear in the epithelium that lines the inside of the stomach. They have no potential to become malignant and are not worrisome. They are not always possible to distinguish from adenomatous polyps based upon appearance during a colonoscopy. Therefore, hyperplastic polyps have to be removed in order to allow microscopic examination. The symptoms of this condition may include stomach pain, vomiting, losing an unusual amount of weight, and blood in the stool.
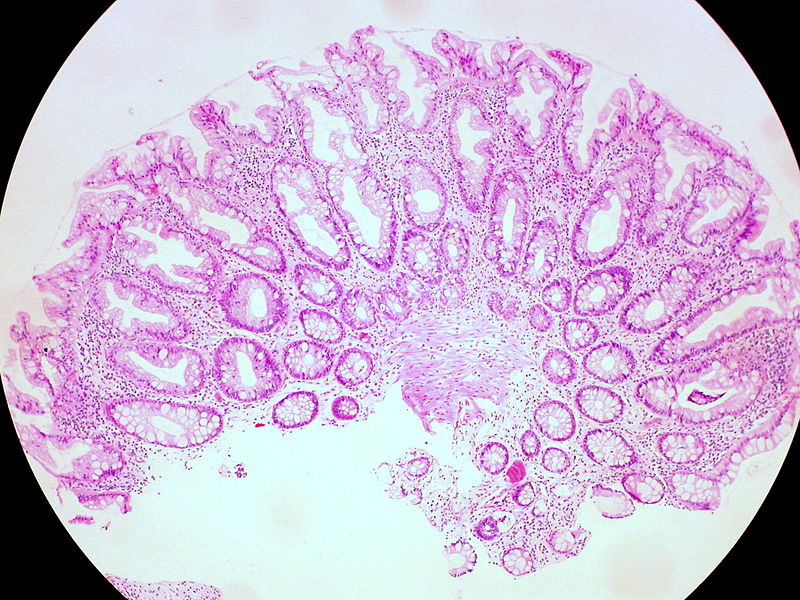
Figure 01: Hyperplastic Polyp
There are several types of hyperplastic polyps that vary according to their shape: pedunculated (long and narrow with a mushroom-like stalk), sessile (shorter and squat looking), and serrated (flat, short, and wide around the bottom). Developing multiple hyperplastic polyps in the colon is known as hyperplastic polyposis. Due to multiple mutations that affect DNA mismatch repair pathways, hyperplastic polyps may rarely convert to cancers. Moreover, hyperplastic polyposis can develop into colon cancer if people have certain risk factors such as being male, being obese, eating a lot of red meat, not getting enough exercise, frequent and long-term smoking, regularly drinking alcohol, having an inflammatory bowel condition like Crohn’s disease, and having polyps in the right colon.
A hyperplastic polyp is diagnosed through colonoscopy or stomach endoscopy. If suspected of cancer, blood tests or antibody tests can be performed. Furthermore, hyperplastic polyps can be treated by removing polyps. In case hyperplastic polyp is cancerous, partial or total colon removal, partial total stomach removal, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy can be performed.
What is Adenomatous Polyp?
An adenomatous polyp is a type of colon polyp that has the potential to become cancerous. Two-thirds of the polyps are adenomatous polyps. Adenomatous polyps are classified by their size, general appearance, and specific features as observed under a microscope. The larger the adenomatous polyp, the more likely it is to eventually become cancer. Therefore, larger adenomatous polyps (larger than 5 millimeters) are usually removed completely to prevent cancer and for microscopic examination to guide follow-up testing.
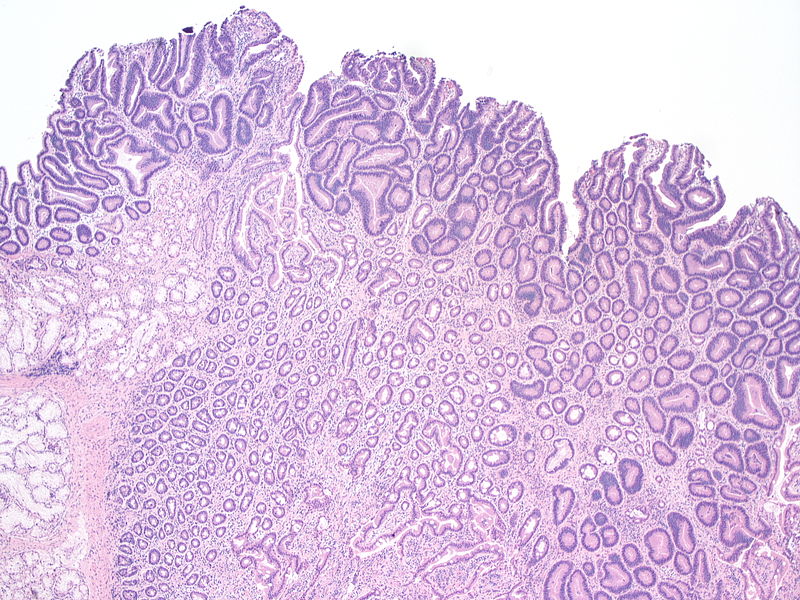
Figure 02: Adenomatous Polyp
Symptoms of adenomatous polyp include abdominal pain, change in stool colour, constipation or diarrhoea, and rectal bleeding. There are few things that can increase the risk of developing these polyps and colorectal cancer, including age (over 50 years), inflammation, drinking alcohol, race, ethnicity (African American, Jewish Eastern European descent), family history, personal history, smoking, and type 2 diabetes.
Adenomatous polyp can be diagnosed through colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, stool test, and virtual colonoscopy. Furthermore, treatments for adenomatous polyp may include polypectomy and laparoscopic surgery.
What are the Similarities Between Hyperplastic and Adenomatous Polyp?
- Hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps are the most common types of colon polyps.
- Both polyps can be located in the colon as well as in the stomach.
- Family history and food may influence this polyp development in the colon.
- They can be removed through surgeries.
What is the Difference Between Hyperplastic and Adenomatous Polyp?
The hyperplastic polyp is a type of colon polyp that has virtually no chance of becoming cancerous, while adenomatous polyp is a type of colon polyp that has the potential to become cancerous. Thus, this is the key difference between hyperplastic and adenomatous polyp. Furthermore, the hyperplastic polyp is comparatively smaller than the adenomatous polyp.
The below infographic presents the differences between hyperplastic and adenomatous polyp in tabular form for side-by-side comparison.
Summary – Hyperplastic vs Adenomatous Polyp
Hyperplastic and adenomatous polyp are two types of colon polyps. Hyperplastic polyp has no chance of becoming cancerous, while adenomatous polyp has the potential to become cancerous. So, this is the key difference between hyperplastic and adenomatous polyp.
Reference:
1. Jewell, Tim. “Hyperplastic Polyp in Colon or Stomach: Follow-up and Treatment.” Healthline, Healthline Media.
2. “Adenomatous Polyps: Causes, Risk Factors, and Treatment.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Hyperplastic Polyp of the Rectum (14060044206)” By Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA – (CC BY 2.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Duodenum Adenomatous Polyp 4×1” By Tissuepathology – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyhsKmdoqW5or%2FToppmmZ6ZeqKwxKemppmkpMK0ec%2Boo7KoXw%3D%3D