What is the Difference Between Exteroceptors and Interoceptors
Table of Contents
The key difference between exteroceptors and interoceptors is that exteroceptors detect stimuli from the outside of the body and send information about the external environment, while interoceptors receive stimuli from internal organs (viscera) and blood vessels and send information about the internal state of the body to the central nervous system.
Sensory receptors respond to the changes occurring around them. In other words, sensory receptors are able to sense the changes in their environment. Their activation triggers nerve impulses. Based on the stimulus location of receptors, there are three main types of receptors as exteroceptors, interoceptors, and proprioceptors. Exteroceptors are located near the surface of the skin, and they respond to stimuli coming from the outside of the body. Interoceptors are located within the body, and they respond to stimuli coming from internal viscera and blood vessels. Proprioceptors respond to movements derived from muscular, tendon, and articular tensions and pressures.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Exteroceptors
3. What are Interoceptors
4. Similarities – Exteroceptors and Interoceptors
5. Exteroceptors vs Interoceptors in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Exteroceptors vs Interoceptors
What are Exteroceptors?
Exteroceptors are the sensory receptors that detect stimuli originating from the outside of the body. They are specialized to monitor the external environment of the body. Structurally, they are the afferent nerve endings (axons of sensory neurons). They are present near the surface of the skin and mediate vision, sound, smell, and cutaneous sensations such as touch, pain, vibration, temperature, itching, and tickling. Once after receiving an external stimulus, the exteroceptor converts it to a nerve impulse and sends it to the central nervous system in order to process and send it into the effector.
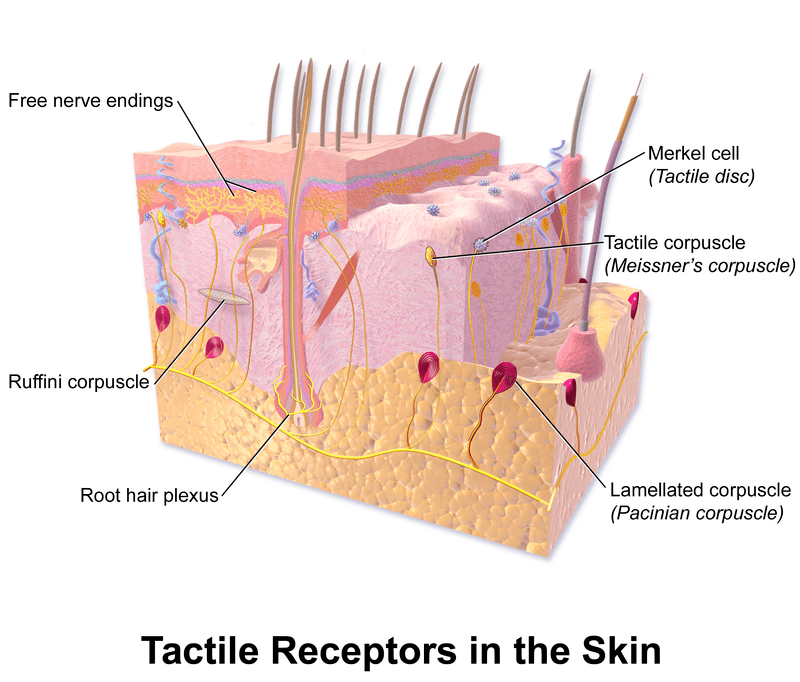
Figure 01: Mechanoreceptor
Mechanoreceptors are a type of exteroceptors specialized to sense a mechanical stimulus such as touch, pressure, stretch, and vibration, etc. Thermoreceptors are another type of exteroceptors that specifically respond to temperature changes.
What are Interoceptors?
Interoceptors are the sensory receptors that detect stimuli coming from the internal organs and blood vessels. Therefore, they respond to stimuli arising within the body. They are deep within the body in the viscera. Visceroceptors is another name of interoceptors. Interoceptors send information to the central nervous system about the internal state of the body. Hence, these receptors monitor viscera, especially cardiovascular, digestive, reproductive, respiratory, and urinary systems.
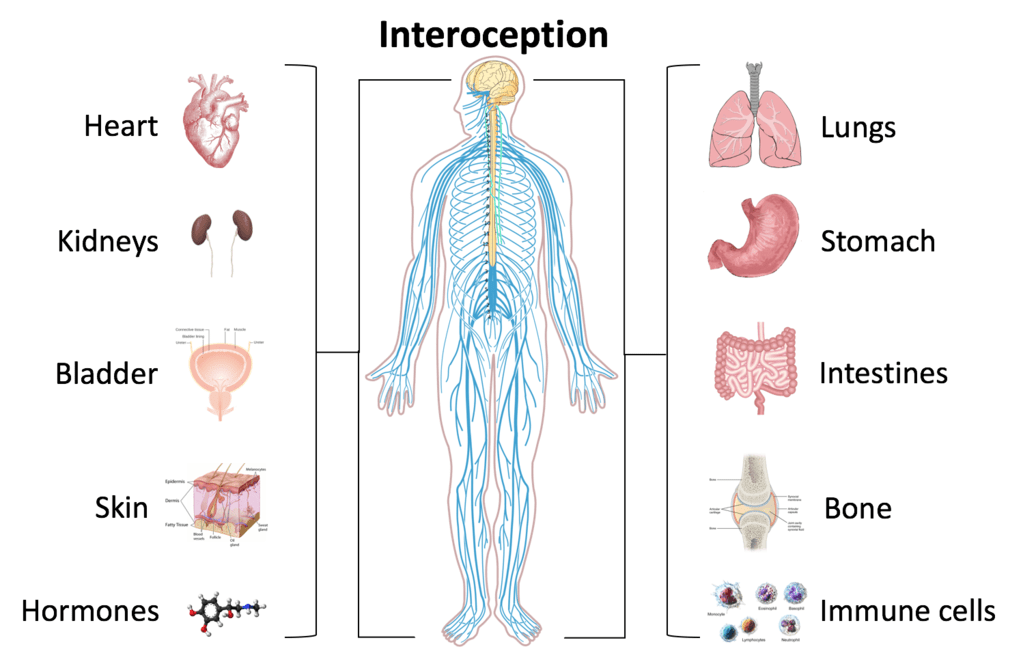
Figure 02: Interoception
Among the several types of interoceptors, chemoreceptors, nociceptors, and stretch receptors are three types. The carotid body is a chemoreceptor that detects CO2 levels in the blood and sends information to CNS. Stretch receptors, on the other hand, detect increased arterial pressure.
What are the Similarities Between Exteroceptors and Interoceptors?
- Exteroceptors and interoceptors are two types of sensory receptors found in our bodies.
- They belong to the peripheral nervous system.
- They can respond to stimuli and send information to the central nervous system.
- These receptors are able to convert stimuli into nerve impulses.
- They are transducers.
What is the Difference Between Exteroceptors and Interoceptors?
Exteroceptors are the sensory receptors that respond to stimuli originating from the outside of the body. In contrast, interoceptors are the sensory receptors that respond to stimuli arising within the body from internal organs and blood vessels. So, this is the key difference between exteroceptors and interoceptors. Exteroceptors monitor the external environment, while interoceptors monitor the internal environment. This is another difference between exteroceptors and interoceptors.
Moreover, exteroceptors are located near the surface of the body, while interoceptors are located deep within the body, in the viscera. Exteroceptors detect mainly touch, smell, temperature, pain, sound, vibration, etc., while interoceptors detect blood pressure, blood oxygen level, blood CO2 level, etc.
The following figure presents the differences between exteroceptors and interoceptors in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Exteroceptors vs Interoceptors
Sensory receptors respond to stimuli. Exteroceptors and interoceptors are two of the three main types of sensory receptors. Exteroceptors respond to stimuli arising from the outside of the body, while interoceptors respond to stimuli coming from internal organs or viscera (within the body). Exteroceptors are found near the surface of the body, while interoceptors are found deep within the body. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between exteroceptors and interoceptors.
Reference:
1. “Interoceptor.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
2. Marzvanyan, Anna. “Physiology, Sensory Receptors.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 27 Oct. 2020.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Blausen 0809 Skin TactileReceptors” By Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436. – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Interoception and the body” By Schappelle – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyer62doqSwprzTqKmsZZGjsW61za2cq6eTmr21u9GsZg%3D%3D