What is the Difference Between Elementary and Complex Reaction
Table of Contents
The key difference between elementary and complex reactions is that elementary reactions essentially have a single step, whereas complex reactions essentially have multiple steps.
We can categorize chemical reactions in different ways. But there are two basic categorizations as elementary reactions and complex reactions. Elementary reactions only include a single sub-step, while complex reactions have a series of steps and different transition states with different intermediates.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is an Elementary Reaction
3. What is a Complex Reaction
4. Elementary vs Complex Reaction in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Elementary vs Complex Reaction
What is Elementary Reaction?
An elementary reaction can be defined as a chemical reaction that includes a single sub-step. In these reactions, one chemical species undergoes a direct change to give the final product in one step. Here, a single transition state is observed. If we cannot experimentally detect any intermediate products during a chemical reaction, we can categorize that reaction as an elementary reaction.
Types of Elementary Reactions
There are several types of elementary reactions as follows:
In a unimolecular reaction, a single reactant undergoes a reaction such as a decomposition to give the final product(s). Some examples of unimolecular reactions include cis-trans isomerization, racemization, ring-opening, radioactive decay, etc.
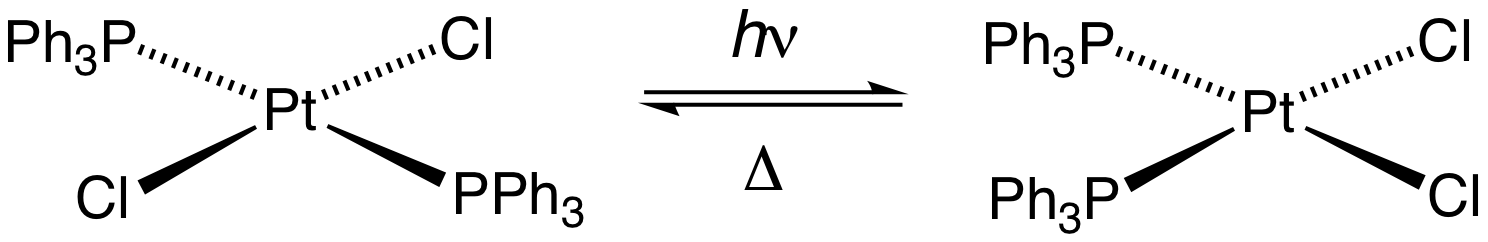
Figure 01: A Type of Cis-trans Isomerization
In bimolecular reactions, two particles undergo collision to give the product(s). These are second-order reactions because the rate of the reaction depends on both reactants. Nucleophilic substitution reactions are an example.
In a trimolecular reaction, three particles undergo collision at the same time to give the product(s). However, this type of reaction is rare since it is difficult for three reactants to collide at the same time.
What is a Complex Reaction?
A complex reaction can be defined as a chemical reaction that includes multiple sub-steps. In other words, these reactions have a series of steps as well as different transition states with different intermediates. Hence, these reactions are very complex in nature.
Unlike in elementary reactions, the order of the reaction does not agree with the stoichiometric coefficients of the reaction. In addition, the order of these reactions can be either an integer or a fraction.
A common example of this type of reaction is the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, where there are two different steps from which we can obtain the overall decomposition reaction.
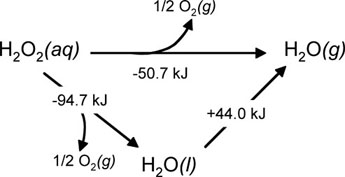
Figure 02: The Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
Types of Complex Reactions
There are three major types of complex reactions:
This type of reaction includes a series of first-order irreversible reactions.
Parallel reactions include multiple steps regarding the same net reaction, and the stepwise reactions occur parallel to each other at the same time.
Reversible reactions are chemical reactions in which the reactants form products that react together, forming the reactants back, which involve at least two steps of elementary reactions to give the same net reaction.
What is the Difference Between Elementary and Complex Reaction?
The key difference between elementary and complex reactions is that elementary reactions essentially have a single step, whereas complex reactions essentially have multiple steps. In addition, elementary reactions directly form the products, whereas complex reactions form one or more intermediates before giving the final product.
The below infographic presents the differences between elementary and complex reactions in tabular form for side-by-side comparison.
Summary – Elementary vs Complex Reaction
We can divide chemical reactions into different types. But there are two basic categorizations as elementary reactions and complex reactions. The key difference between elementary and complex reactions is that elementary reactions essentially have a single step, whereas complex reactions essentially have multiple steps.
Reference:
1. “9.4: More Complex Reactions.” Chemistry LibreTexts, Libretexts, 14 July 2020.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Cis-trans-PtCl2P2” By Smokefoot – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Chemical Principles Fig2-5” By Charles A. Wight – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyeo56llaPBor7YZpinnF2YvK68y56vZqqVlrC1tc6nZg%3D%3D