What is the Difference Between Colorimetric and Fluorometric Assay
Table of Contents
The key difference between colorimetric and fluorometric assay is that colorimetric assay determines the concentration of colored compounds in a solution while fluorometric assay determines the kinetic mechanism of a solution.
A biochemical assay is a technique that detects or quantifies the activity of a biological molecule or substance analytically. It is an in vitro process. Colorimetric assay and fluorometric assay are two types of common biochemical assays carried out in laboratories. Multiple techniques such as ELISA and western blotting are also complex biochemical assays for the quantification of metabolic activity and measurement of the functional behavior of biomolecules such as proteins, enzymes, and other small molecules. These types of assays are used for the identification of protein-DNA, protein-RNA, and protein-protein interactions.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is a Colorimetric Assay
3. What is a Fluorometric Assay
4. Similarities – Colorimetric and Fluorometric Assay
5. Colorimetric vs Fluorometric Assays in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is a Colorimetric Assay?
A colorimetric assay is a technique that determines the concentration of colored compounds in a solution. In other words, colorimetric assay is a reaction that leads to a color change due to an enzymatic or chemical reaction between reagents and analytes. Colorimetric assays are practiced in biochemistry to test for enzymes, specific compounds, hormones, antibodies and other analytes. They use colorimeters or spectrophotometers. Colorimeters are instruments that characterize colored samples in order to provide an objective measure of color characteristics. A spectrophotometer is a device that measures light intensity as a function of the color or wavelength of the light.

Figure 01: Colorimetric Assay
How Does a Colorimetric Assay Work?
In a colorimetric assay, a plate is prepared with a particular antibody bound to wells. Then the sample is added. This may allow the sample to bind to the antibody. Then a detection antibody and a substrate are added to the wells to react with the detection probe. Stop solution is added at the end before the reading. An empty well called the blank is left without the sample. In the colorimetric assay, the darker the color, the greater the analyte concentration. Usually, only one wavelength is needed to take the reading. But if there is a reference measurement, two or more wavelengths are used.
What is a Fluorometric Assay?
The fluorometric assay is a technique that determines the kinetic mechanism of enzyme reactions. A fluorometric assay takes place with a formation of a fluorescent product from a nonfluorescent substrate or vice versa. This assay also makes use of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) where, the enzymatic reaction changes the position of two fluorophores in the substrate thus, changing the fluorescence intensity.
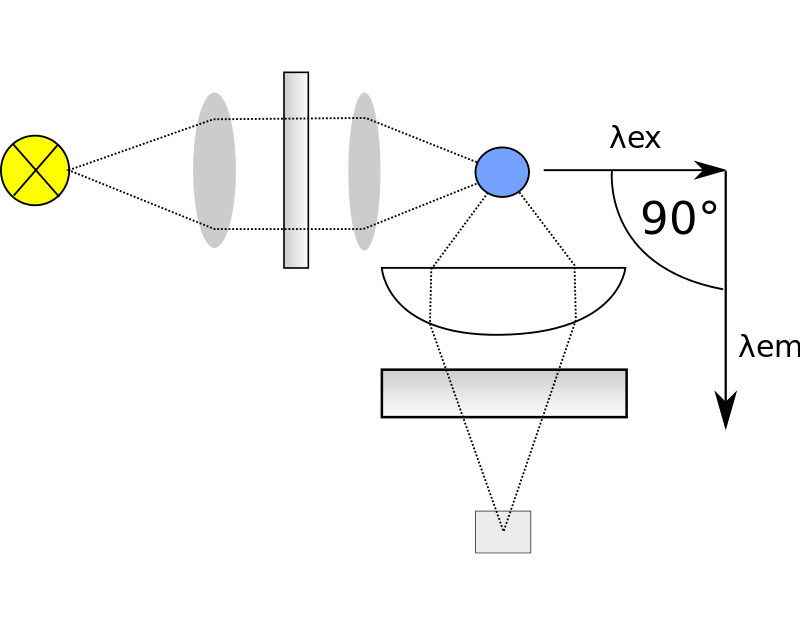
Figure 02: Fluorometric Assay
Fluorometric assays are generally much more sensitive than other assays. The diagnostic enzyme estimations in tissue, cell, or fluid samples of patients increase due to its higher sensitivity.
How Does a Fluorometric Assay Work?
In a fluorometric assay, a substrate is added to the sample in the plate, and the fluorescence response is taken using the plate reader. Here, each cell is measured separately. Opaque plates are used in fluorometric assays. This reduces the scattering of light. Two wavelengths are necessary for this type of assay. One wavelength is to detect the excitation and the other wavelength is for the emission.
What are the Similarities Between Colorimetric and Fluorometric Assay?
- Colorimetric assay and fluorometric assay are two types of biochemical assays.
- Both assays are carried out for medical diagnostics.
- These assays involve an enzymatic reaction.
- Both assays involve a substrate and analytes.
What is the Difference Between Colorimetric and Fluorometric Assay?
A colorimetric assay is a technique that determines the concentration of colored compounds in a solution, while fluorometric assay is a technique that determines the kinetic mechanism of enzyme reactions. So, this is the key difference between colorimetric and fluorometric assay. Moreover, the fluorometric assays are more sensitive than the colorimetric assays; thus, fluorometric assays have the ability to detect more analytes. Thus, this is another important difference between colorimetric and fluorometric assay. Furthermore, fluorometric assays require two wavelengths, while colorimetric assays are carried out with one wavelength.
The below infographic tabulates more differences between colorimetric and fluorometric assay.
Summary – Colorimetric vs Fluorometric Assay
A biochemical assay is an analytical process used to determine and quantify cellular metabolic reactions. Colorimetric assay and fluorometric assay are two types of biochemical assays. Colorimetric assay is a reaction that leads to a color change due to an enzymatic or chemical reaction between reagents and analytes while fluorometric assay is a technique that is used to determine the kinetic mechanism of enzyme reactions. Both assays depend on an enzymatic reaction that involves a substrate and an analyte. Fluorometric assays are more sensitive than colorimetric assays. Most importantly, fluorometric assays require two wavelengths, while colorimetric assays can be carried out with only one wavelength. Thus, this summarizes the difference between colorimetric and fluorometric assay.
Reference:
1. “Colorimetric assays.” Experimental Biosciences.
2. “Fluorometric enzyme assays.” Creative Enzymes.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Colorimetric assay” By Sepehr Ehsani (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0) via Flickr
2. “Fluorimeter” By Matthias M. – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoycpqWnop66psDRoppmmZ6Zeqe41KipqKWVqb%2Bqr4yaqqyZqWQ%3D