Difference Between Trans Fat and Saturated Fat
Table of Contents
The key difference between trans fat and saturated fat is that trans fats are a type of unsaturated fats that have double bonds between carbon molecules while saturated fats are a type of fat molecules that have no double bonds between carbon molecules.
Lipids or fats are the fourth major group of molecules present in plants and animals. They are important in energy storage of both plant and animal bodies. Moreover, calories that we can obtain from 1g of lipids is higher than the calories from 1g of carbohydrates. Generally, fats are hydrophobic; hence, they are water insoluble. However, they can be extracted to organic solvents such as ether, chloroform, and benzene. Lipid molecule constitutes of a fatty acid and alcohol molecule. Fatty acids generally have the formula of R-COOH, and R may be a hydrogen or alkyl group such as CH2, C2H5 etc. Fatty acids may have an even number (14 to 22) of carbon atoms. Some fatty acid chains can have double bonds between carbon atom; accordingly, there are two types of fats as unsaturated fats and saturated fats.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Trans Fat
3. What is Saturated Fat
4. Similarities Between Trans Fat and Saturated Fat
5. Side by Side Comparison – Trans Fat vs Saturated Fat in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Trans Fat?
Trans fats or trans fatty acids are a type of unsaturated fats. Dehydrogenation is the process that yields trans fats. In the presence of a catalyst and hydrogen gas, trans fat forms when heating the liquid vegetable oil. The cis configuration of double bonds in fatty acids isomerizes into trans configuration by technological and microbiological techniques. Thus, trans fats are unsaturated trans-isomer fatty acids. These are partially hydrogenated oil, and they are less likely to spoil, so it increases the shelf life.
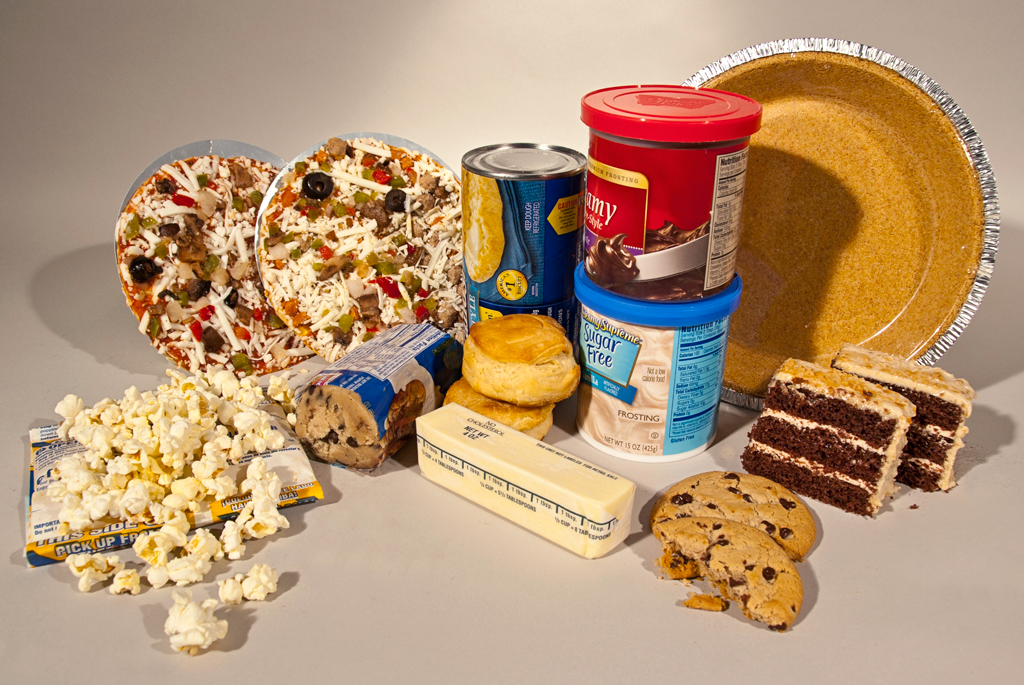

Figure 01: Food Containing Trans Fats
Hydrogenation converts oil into a solid state. When processing food, especially in fast foods, partially hydrogenated fats can form. Also, trans fat can naturally occur in beef fat and dairy fat in ruminants in small quantity. High intake of trans fat will increase the cholesterol level of the bloodstream. Thus, trans fat can adversely affect health than saturated fats since saturated fats increase the LDL in blood while decreasing in High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL).
What is Saturated Fat?
Saturated fats are a type of fats that do not have double bonds between carbon atoms in the fatty acid chains. Thus, these molecules are fully reduced or saturated with hydrogen bonds. Biochemically, these are highly flexible molecules, which can have numerous conformations having free rotations around the C-C bonds. Examples of saturated fatty acids are Lauric acid, Myristic acid, Palmitic acids, etc.
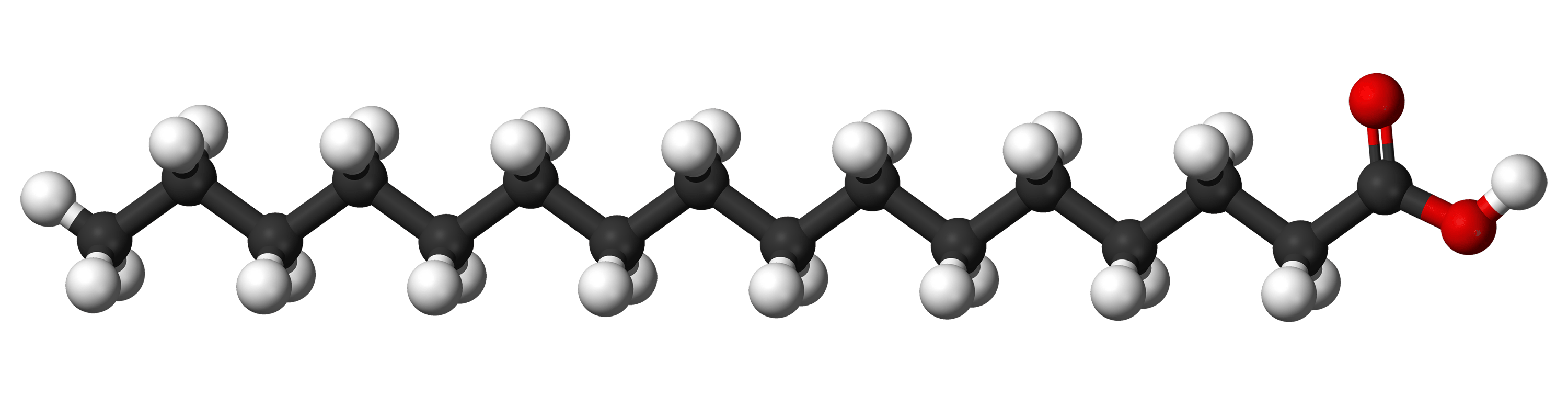
Figure 02: Saturated fat – Palmitic Acid
Saturated fats are available naturally in animal products such as meat, eggs and dairy product and in plant oils such as coconut oil, palm oil. Saturated fats raise the Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL) in the bloodstream, which carries cholesterol from the liver to the rest of the body. Thus, saturated fat intake increases many health problems including cardiovascular diseases.
What are the Similarities Between Trans Fat and Saturated Fat?
- Both trans fat and saturated fat are types of fat.
- They are dietary fats.
- Also, both are unhealthy fats.
- They can raise bad cholesterol.
- Furthermore, both can increase the risk of heart diseases and strokes.
- They exist as solid at room temperature.
What is the Difference Between Trans Fat and Saturated Fat?
Both trans fats and saturated fats are bad fats. The key difference between trans fat and saturated fat is that the trans fats contain double bonds between carbon atoms of their fatty acid chains while saturated fats do not contain double bonds. Trans fats are the worst fats as they increase the risk of heart diseases, diabetes, and strokes. Saturated fats also raise the risk of heart diseases and strokes. However, trans fats are unhealthier than saturated fats. Thus, this is a significant difference between trans fat and saturated fat.
Furthermore, trans fats can be formed during food processing like fast foods while saturated fats cannot be produced through such processing. Hence, this is also a difference between trans fat and saturated fat.
Below infographic summarizes the difference between trans fat and saturated fat.
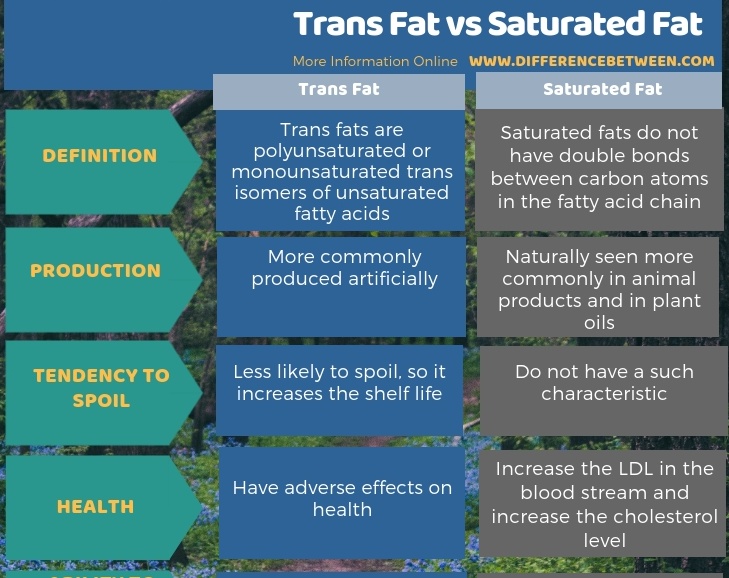
Summary – Trans Fat vs Saturated Fat
There are two main types of fats as saturated fats and unsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats are generally considered as good fats or healthy fats. However, trans fat is a type of unsaturated fats that is worse for our health. Saturated fats also come under bad fats since they can lower good cholesterol and increases the cholesterol level in blood similar to trans fats. However, trans fats are unhealthier than saturated fats. Thus, this is a summary of the difference between trans fat and saturated fat.
Reference:
1. “Trans Fats.” About Heart Attacks, Available here.
2. Harvard Health Publishing. “The Truth about Fats: the Good, the Bad, and the in-Between.” Harvard Health Blog, Harvard Health Publishing, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Avoiding Trans Fat” By The U.S. Food and Drug Administration – (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Palmitic-acid-3D-balls” By Jynto and Ben Mills – Derived from File:Caproic-acid-3D-balls.png. (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau27A0ZqlrGWWlsFurc2dZK%2BrXaiutcHRmquenF2brrV7