Difference Between Total Cell Count and Viable Cell Count
Table of Contents
The key difference between total cell count and viable cell count is that total cell count estimates all cells including both living and dead microbial cells in a sample while viable cell count estimates only the living microbial cells in a sample.
Counting the number of organisms within a population is considered necessary for most experimental work. Therefore, we try to analyse the number of microbes within a sample using direct and indirect methods. Direct measurements involve methods that count cell numbers directly. Indirect measurements involve measuring some parameter that can be related to cell number such as cell density, dry weight, etc. Some methods quantify only the living microbial cells in a sample. Viable cell count is one such method. Direct microscopic counts quantify all cells in a known volume of medium/sample using a microscope. Therefore, it counts both living and dead cells. It is a type of a total cell count.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Total Cell Count
3. What is Viable Cell Count
4. Similarities Between Total Cell Count and Viable Cell Count
5. Side by Side Comparison – Total Cell Count vs Viable Cell Count in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Total Cell Count?
Total cell count is the method that involves counting all cells in a known volume of medium/sample using a microscope and a counting chamber (hemocytometer). Unlike viable counts, both living and dead cells are counted. Therefore, this is a total count unless a viability stain is applied during the observation. In microscopy, the cells are observed directly under the microscope and counted. It uses a cell suspension that consists of microbial cells. For the ease of counting and accurate measurements, dilution of the sample can be done. In very high/low concentrations of cells, obtaining the total cell count using a microscope is a difficult task.
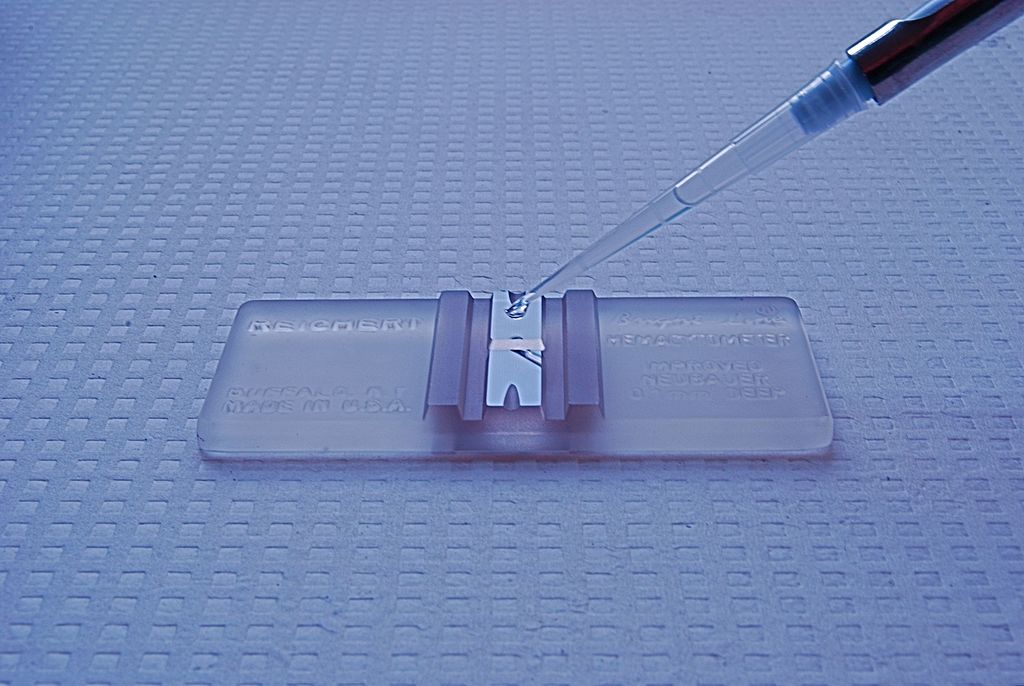
Figure 01: Counting Chamber – Hemocytometer
Counting chambers are easy, inexpensive, and quick in taking a total cell count. Most importantly, counting chambers are useful for counting both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. We count cells in selected squares of known volume to quantify total cell count.
What is Viable Cell Count?
Viable cell count is a method of counting living microbial cells in a sample. It only counts living cells in the sample. Viable plate count, membrane filtration, and most probable number are few viable cell count techniques. These approaches are growth-based. Viable plate count method is a powerful method used in many microbiological fields, including food and dairy microbiology, medical microbiology, environmental microbiology, microbial genetics, growth media development and biotechnology.
The commonest way to count viable bacteria is to use a sample capable of forming colonies on an agar medium. There are two main ways to perform a plate count: spread plate technique and pour plate technique. A known volume of sample can be either spread on the surface of an agar plate, or mixed into the agar. The plate is then incubated, and the arising colonies are counted. The number of colonies is related to the number of microorganisms within the original sample. Viable counts only measure those cells that are alive and growing.
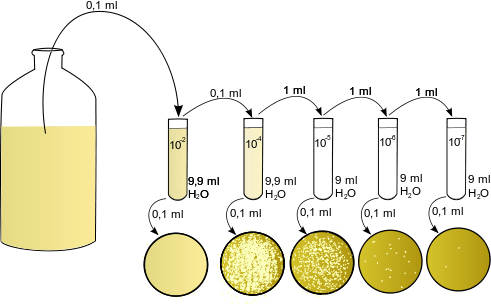
Figure 02: Viable Plate Count
Most probable number (MPN) is an alternative to plate count methods for estimating population density of viable cells. It counts organisms growing in liquid culture and is thus a predominantly bacteriological technique. It is particularly useful for low concentrations of organisms e.g. milk, potable water.
Membrane filtration technique is more suitable when microbes are very dilute as in a city’s water supply. It is done simply by passing a known volume of the liquid through a filter and incubating it on a nutrient medium. Colonies that develop on the filter are counted, and the bacteria per millilitre of the sample are calculated.
What are the Similarities Between Total Cell Count and Viable Cell Count?
- Total cell count and viable cell count are two types of microbial techniques that quantify cells.
- They are commonly used enumeration techniques in microbiology labs.
What is the Difference Between Total Cell Count and Viable Cell Count?
Total cell count enumerates all living and dead microbial cells in a sample. In contrast, viable cell count enumerates only the living cells in a sample. So, this is the key difference between total cell count and viable cell count. Total cell count is independent of the growth of colonies on agar plates while viable cell count is a growth-based technique and it depends on the growth of microbial colonies on agar plates.
The below info-graphic summarizes the difference between total cell count and viable cell count.
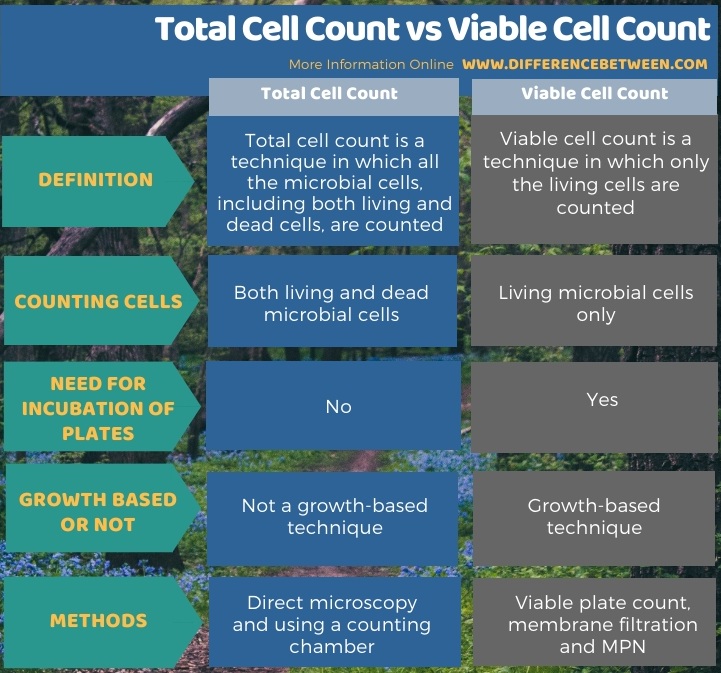
Summary – Total Cell Count vs Viable Cell Count
Total cell count enumerates both living and dead microbial cells while viable cell count enumerates only the living cells. Thus, this is the key difference between total cell count and viable cell count. Also, viable cell count is a growth-based technique, unlike total cell count. Moreover, it requires incubation of plates until getting the visible colonies. Viable plate count, MPN and membrane filtration are few techniques of viable cell count while direct microscopy and the use of hemocytometer are two techniques of total cell count.
Reference:
1. “Counting Bacteria.” Lumen, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Hemocytometer” By Todd – originally posted to Flickr as 0356 (CC BY-SA 2.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Verdünnungsreihe mit Ausplattieren” By Leberechtc – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau27Azq2YpWWTmrmtecKorKesXZa7pXnVopibpJVisKa4y2aaqK2eqXw%3D