Difference Between Tap Root and Fibrous Root
Table of Contents
The key difference between tap root and fibrous root is that tap root is the main thick root of the root system of dicotyledonous plants while fibrous root is one of the hair-like roots of the root system of monocotyledonous plants.
The root system is a vital system of land plants, especially in ferns and flowering plants. The root can simply be defined as an underground part of a plant body which has no leaves and nodes. The basic function of a root system is to absorb water and minerals. Furthermore, root system anchors the plant body to the ground. There are two main types of root systems as tap root system and adventitious root system based on the morphology and anatomy of the roots.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is a Tap Root
3. What is a Fibrous Root
4. Similarities Between Tap Root and Fibrous Root
5. Side by Side Comparison – Tap Root vs Fibrous Root in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is a Tap Root?
Tap root system is a unique feature of dicotyledonous plants. Tap root is the main thick root of the root system which grows vertically deep into the soil. It develops from the radical of the seed. Hence, a single plant has only one tap root in its root system. It is a persistent root. Moreover, dicot plants can withstand droughts due to their tap root system, which can explore the soil and absorb water from the deeper parts of the soil.
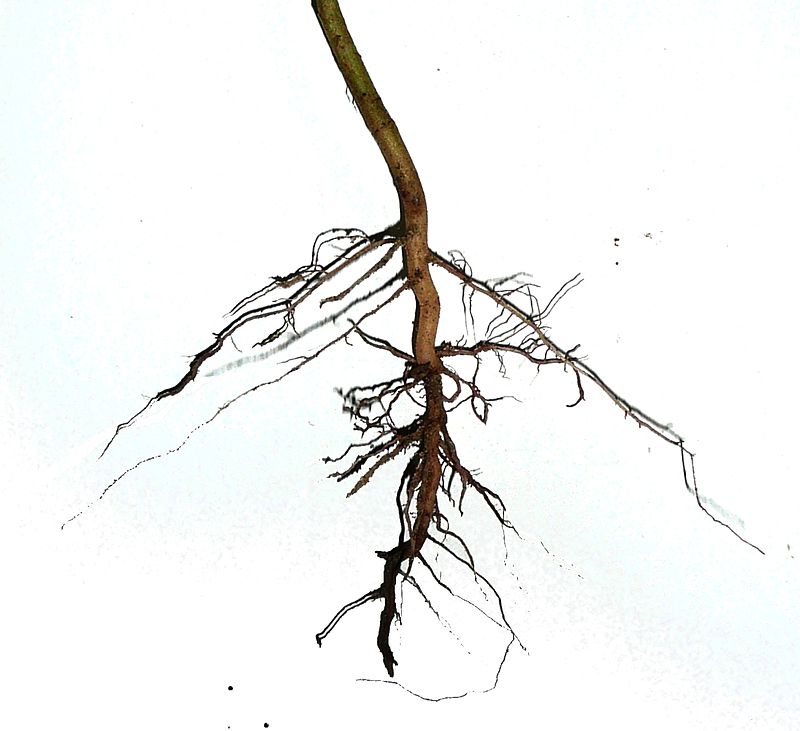

Figure 01: Tap Root
Secondary and tertiary roots originate from the tap root, and they grow horizontally and vertically. Some plants store foods in the tap root. In those plants, root is their main food storing space.
What is a Fibrous Root?
A fibrous root is one of the hair-like tiny roots of the fibrous root system. Fibrous roots originate from the base of the plant. This root system is available mainly in Monocotyledons, Gymnospermae (conifers) and Pteridophyta (ferns) plants. Most fibrous roots grow horizontally and very few percentages of roots grow vertically to anchor the plant. Most importantly, fibrous roots are short-lived. They grow near the surface of the soil, without growing deep into the soil.
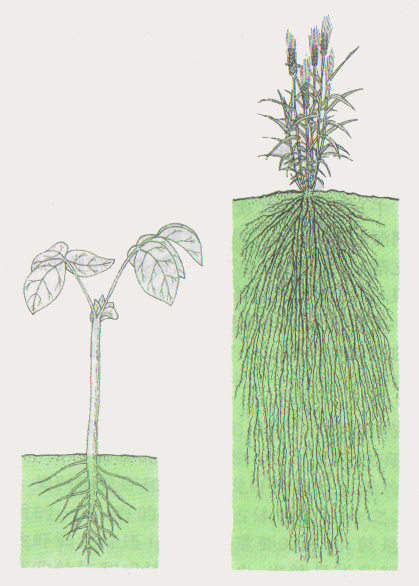
Figure 02: Fibrous Root System
Furthermore, all fibrous roots are morphologically similar. They don’t differentiate into the main root, secondary roots or tertiary roots. In addition, some fibrous roots are aerial.
What are the Similarities Between Tap Root and Fibrous Root?
- Both tap roots and fibrous roots are true root types.
- They absorb water and minerals from the soil
- Moreover, they facilitate anchoring of plants into the ground.
- They are underground plant parts.
What is the Difference Between Tap Root and Fibrous Root?
Tap root is the thick main root seen in the root system of dicotyledonous plants while fibrous root is a tiny hair-like root seen in the root system of the monocotyledonous plants. Thus, this is the key difference between tap root and fibrous root. Tap root develops from the radical of the seed. Therefore, a plant has only one tap root. On the other hand, fibrous root originates from the stem tissue, and a single plant consists of hundreds of fibrous roots. This is another difference between tap root and fibrous root. Furthermore, secondary and tertiary roots grow off from the tap root and construct the tap root system. Therefore, different size roots are available in the tap root system, and the tap root is the largest. At the same time, all the fibrous roots originate from the base of the plant, and they do not branch as tap root does. In addition, they are much similar in size, as well.
Moreover, tap root continuously grows deep into the soil vertically over a long period. Thus, it is much longer and has an extremely large surface area. It can also anchorage the plant well. However, fibrous roots do not deeply penetrate into the soil. They are small in size and their anchoring ability is comparatively low. This is another important difference between tap root and fibrous root.

Summary – Tap Root vs Fibrous Root
With the evolution of plants, fibrous roots originated first and they are available in ferns, conifers, and monocots. In contrast, tap root system is available only in dicots, and they evolved later. However, both these root types are true root types which aid plants in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Moreover, they facilitate anchoring of plants into the ground. Tap root system has a primary root, secondary and tertiary roots, which are morphologically distinct. But all fibrous roots are morphologically similar and there is no such differentiation. Furthermore, tap roots are persistent and grow very deep into the soil while fibrous roots are short-lived and grow near to the surface of the soil. Moreover, a single plant has only one tap root while a single plant has numerous fibrous roots. This is the summary of the difference between tap root and fibrous root.
Reference:
1. “Tap Roots.” Tap Roots – an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics, Available here.
2. “Fibrous Root System.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 14 May 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Dicotyledoneae Asteraceae herb – root system, primary root becomes tap root and lateral roots” By RoRo – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Tap Root & Fibrous Root” By CRCHF – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau27AwKlkq6efqXqiusNmraxllp6vs7vUrGSrp5%2BpfA%3D%3D