Difference Between Sodium Phosphate Monobasic and Dibasic
Table of Contents
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic vs Dibasic | Sodium Phosphate Dibasic vs Sodium Phosphate Monobasic | Monosodium Phosphate vs Disodium Phosphate| Monosodium vs Disodium Phosphate
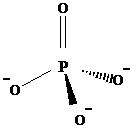
One phosphorus atom is bonded with four oxygens, to form a -3 polyatomic anion. Because of the single bonds and double bond, between P and O, phosphorus has a +5 oxidation state in here. It has a tetrahedral geometry. Following is the structure of phosphate anion.
PO43-
Phosphate anion can combine with different cations, to form numerous ionic compounds. Sodium phosphate is a salt like that where three sodium ions are electrostatistically bonded with one phosphate anion. Trisodium phosphate is a white colored crystal, which highly dissolve in water. When soluble in water, it produces an alkaline solution. Sodium phosphate monobasic and sodium phosphate dibasic are two other compounds of sodium and phosphate. For an acid, we define the term monobasic as “an acid, which possesses only one proton that can be donated to a base during an acid- base reaction.” Likewise, dibasic for an acid means having two protons, which can be donated to a base. But when consider these two terms regarding a salt, the meaning is completely different. A monobasic salt refers to a salt, which has only one atom of an univalent metal. And dibasic salt means having two univalent metal ions. In this case, the univalent metal ion is the sodium cation. Since these are salts, they readily dissolve in water and produce alkaline solutions. These compounds are commercially available in hydrous and anhydrous forms. Monobasic and dibasic sodium phosphate together are very important in biological systems as a buffer. Further, medically these two are used as a saline laxative, to treat constipation.
Sodium phosphate monobasic
Sodium phosphate monobasic or monosodium phosphate has the molecular formula of NaH2PO4. The molar mass of the compound is 120 g mol-1. The anion in this molecule is not the trivalent phosphate anion, but the H2PO4– anion. This anion has derived from the phosphate ion where two hydrogens are bonded with two negative oxygens. Alternatively, on the other side it has derived from the removal of one proton from the phosphoric acid (H3PO4). The phosphate anion and H2PO4– anions are in equilibrium, in aqueous media. Sodium phosphate monobasic is available as colorless crystals or white powder. It readily dissolve in water, but do not dissolve in organic solvents like alcohol. The pKa of this is between 6.8-7.20. This compound can be made when phosphoric acid reacts with a sodium salt like sodium halide.
Sodium phosphate dibasic
This compound is also known as disodium phosphate and has the molecular formula of Na2HPO4. The molar mass of the compound is 142 g mol-1. When two sodium cations replace the hydrogen atoms in the phosphoric acid, sodium phosphate dibasic is obtained. So in the laboratory we can make this compound by reacting two equivalents of sodium hydroxide with one equivalent of phosphoric acid. The compound is a white crystalline solid, and it readily dissolves in water. The pH of this aqueous solution is a basic value, which is between 8 and 11. This salt is used for cooking purposes, and as a laxative.
What is the difference between Sodium phosphate monobasic and sodium phosphate dibasic? • Sodium phosphate monobasic has the chemical formula of NaH2PO4, and the sodium phosphate dibasic has the chemical formula of Na2HPO4. • The molecular weight of sodium phosphate dibasic is higher than that of sodium phosphate monobasic. • When sodium phosphate dibasic dissolves in water, the basicity is higher in the medium than when sodium phosphate monobasic dissolves in water. |
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26%2Fzp2grqVdpbWwv8%2BhmK2dXaK8r7vBmqqim12Wu6V51axknaGSlsCqr44%3D