Difference Between Slow and Fast Twitch Fibers
Table of Contents
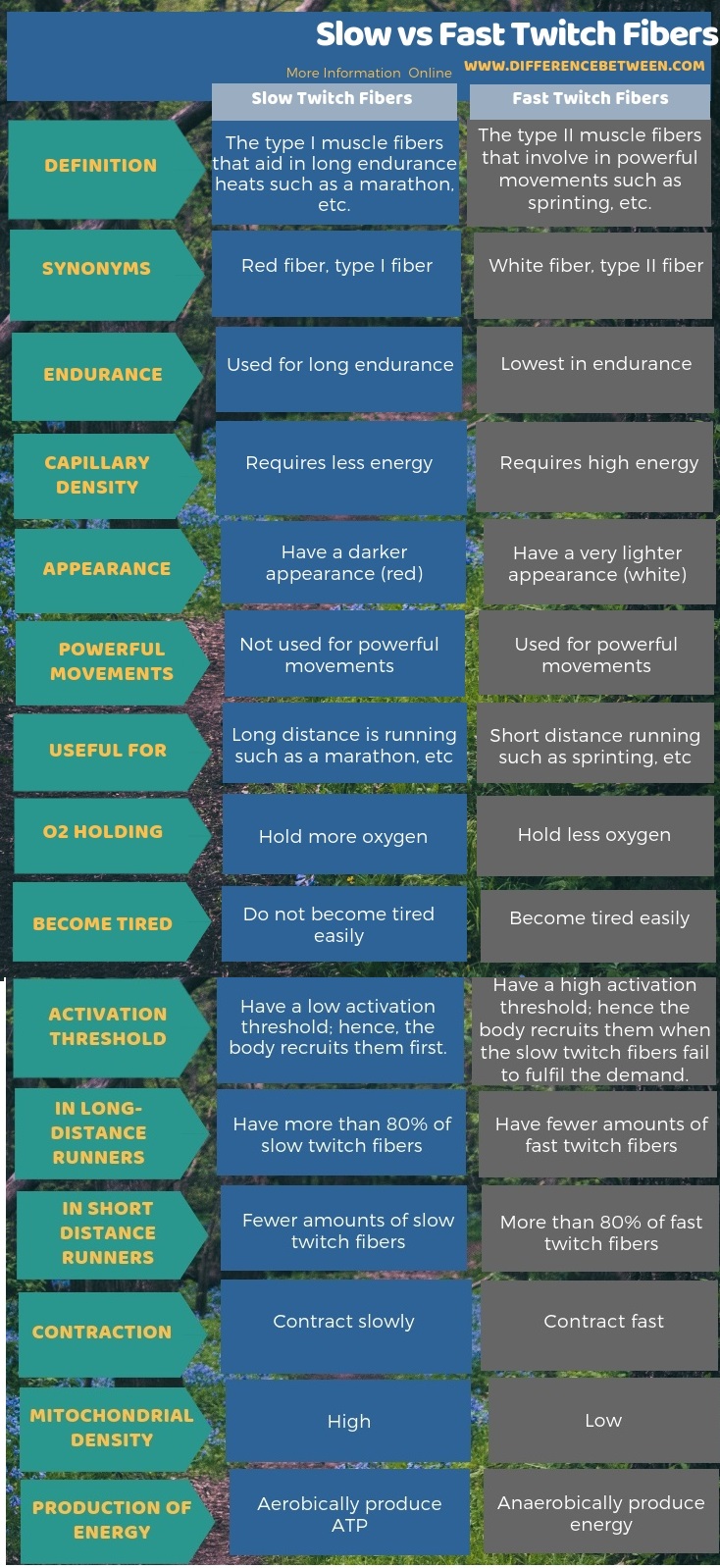
The key difference between slow and fast twitch fibers is that the slow twitch fibers are the muscle fibers mainly used for long endurance such as distance running and they do not become tired easily while fast twitch fibers are the muscle fibers used for a powerful burst of movements such as sprinting and they get tired quickly.
There are many different types of body muscles. Among these different body muscles, some of them work involuntarily. Of these muscles, the skeletal muscles are the muscles that move bones, limbs and the body in general. These skeletal muscles have two general types of fibers. Namely, they are the slow twitch fiber (type I) and fast twitch fiber (type II). Generally, a human body contains a relatively equal amount of these two fibers. However, it is not surprising to note that sprint runners in Olympics have almost 80% of fast twitch fibers and marathon runners have almost 80% slow twitch fibers that aid them in their events. It is because we have different percentage makeup of slow and fast twitch fibers in our bodies due to our genetics. Therefore, even if you want to be a runner, whether that suits you depends on your fiber makeup on the basis of your genetics.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Slow Twitch Fibers
3. What are Fast Twitch Fibers
4. Similarities Between Slow and Fast Twitch Fibers
5. Side by Side Comparison – Slow vs Fast Twitch Fibers in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Slow Twitch Fibers?
Slow twitch fibers (type I) are a type of muscle fibers that contracts slowly. These fibers help in long endurance heats such as distance running since they are resistant to fatigue. Furthermore, these fibers are very efficient in utilizing oxygen for cellular respiration and in the production of ATP. For these purposes, slow twitch fibers have more mitochondria.

Figure 01: Muscle Fibers
As they can hold oxygen efficiently, they can produce energy easily without causing a buildup of lactic acid. Also, these fibers have great endurance despite being weak. Athletes running marathons make good use of these fibers to run long distances. Moreover, red fiber is another name for these fibers due to their color. That is; because of the high amount of blood-carrying myoglobin, they get this darker appearance.
What are Fast Twitch Fibers?
Fast twitch fibers are a type of muscle fibers that contract quickly. Because these fibers can generate more energy within a short time, they aid in powerful burst movements such as sprinting. Therefore, it gives them extra power, and they become active and explosive. However, they can easily become tired. In simple words, they fatigue faster than the slow twitch fibers when the force demand is higher, the body recruits or activates fast twitch muscle fibers. However, it happens only if the slow twitch fibers cannot fulfil the force demand.

Figure 02: A Sprinter Runner
Moreover, the fast twitch fibers appear in white since they do not contain much blood. Hence, they are lighter in appearance than the slow twitch fibers. Furthermore, fast twitch fibers are of two types; namely, they are the fast-twitch IIa and fast-twitch type IIb.
What are the Similarities Between Slow and Fast Twitch Fibers?
- Slow and Fast Twitch Fibers are two types of skeletal muscle fibers.
- Both types produce energy and help in movements.
- Also, both generate force.
- Furthermore, both types of fibers are present relatively in equal amounts in the human body.
What is the Difference Between Slow and Fast Twitch Fibers?
Slow twitch fibers are the muscle fibers that help long endurance while fast twitch fibers are the muscle fibers that facilitate powerful movements while having least endurance. Therefore, this is the key difference between slow and fast twitch fibers. Based on the endurance capacity, long-distance runners have a relatively high amount of slow twitch fibers while short distance runners who engage in sprinting etc., have a relatively high amount of fast twitch fibers.
A further difference between slow and fast twitch fibers is that the slow twitch fibers do not fatigue faster while the fast twitch fibers fatigue faster. Moreover, the capacity to hold oxygen is another difference between slow and fast twitch fibers. That is; the slow twitch fibers can hold more oxygen for cellular respiration than the fast twitch fibers.
The following infographic provides more information regarding the difference between slow and fast twitch fibers.
Summary – Slow vs Fast Twitch Fibers
Slow and fast twitch fibers are two types of skeletal muscle fibers. Slow twitch fibers contract slowly and are somewhat weaker muscle fibers. On the other hand, fast twitch fibers contract very quickly and are strong fibers. Hence, this is the key difference between slow and fast twitch fibers. Furthermore, the slow twitch fibres appear in red since they have a greater capillary density while fast twitch fibers appear in white since they have a very low capillary density. Also, slow twitch fibers are highly resistant to fatigue; hence, do not become tired quickly.
On the other hand, fast twitch fibers are quicker to fatigue, hence become tired easily. Moreover, the slow twitch fibers aid in long endurance while the fast twitch fibers have low endurance. Besides, the fast twitch fibers involve in powerful movements since they can generate a high amount of force within a short time. However, the slow twitch fibers have more mitochondria than the fast twitch fibers. The above is the summary of the difference between slow and fast twitch fibers.
Reference:
1.Author Pete McCall Health and Fitness Expert Pete McCall. “Slow-Twitch vs. Fast-Twitch Muscle Fibers.” ACE. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Fibers (28089113308)”By Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library – Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Fibers, (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”1488271″ by KeithJJ (CC0) via pixabay
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26%2Fy6iuZpmemXq3v4yfmKysXanEqsDCoWSfoZKav7R7