Difference Between Regulatory and Repressor Protein
Table of Contents
The key difference between regulatory and repressor protein is that regulatory protein can promote or inhibit the transcription of genes. Meanwhile, the repressor protein inhibits the expression of one or more genes.
Before going further into the discussion of the difference between regulatory and repressor protein, let’s briefly discuss gene regulation. Gene is a specific nucleotide sequence in which the genetic information is hidden in order to synthesize a protein. Gene expression can be regulated in different ways. Through different mechanisms, cells control the expression of genes and their levels of expression. Generally, gene regulation occurs at the transcription level. Regulatory protein and repressor protein are two types of proteins involved in gene regulation at the transcription level. These regulatory proteins and repressor proteins bind to a specific sequence near the gene and influence the transcription of the gene.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Regulatory Protein
3. What is Repressor Protein
4. Similarities Between Regulatory and Repressor Protein
5. Side by Side Comparison – Regulatory vs Repressor Protein in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Regulatory Protein?
Regulatory protein is a protein that regulates the transcription of genes. These proteins can induce or inhibit the transcription of genes. Bacterial genes exist as operons or clusters of genes operating under one promoter. Each operon has regulatory DNA sequences that provide sites for the binding of regulatory proteins. Once these regulatory proteins bind with the gene, they can inhibit or promote the transcription. Therefore, these regulatory proteins are capable of turning on or off the genes. Often, regulatory proteins act by helping or blocking the enzyme RNA polymerase which catalyzes the transcription.

Figure 01: Gene Regulation
Regulatory genes code for regulatory proteins. Generally, regulatory proteins bind with small molecules which can make them active or inactive by changing their ability to bind with DNA. In simple words, regulatory proteins get turned on or turned off themselves by binding with these small molecules. The binding of small molecules changes their shapes, enabling the binding with DNA.
Regulatory proteins and gene regulation differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, most regulatory proteins are specific to one gene.
What is Repressor Protein?
Repressor protein is a protein that binds with DNA or RNA and inhibits the expression of one or more genes. these repressor proteins often bind with the promoter region or associated silencers. DNA binding repressor proteins prevent the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter of the gene and stop the transcription of gene sequence into mRNA. On the other hand, RNA binding repressor proteins block the translation of mRNA into proteins.
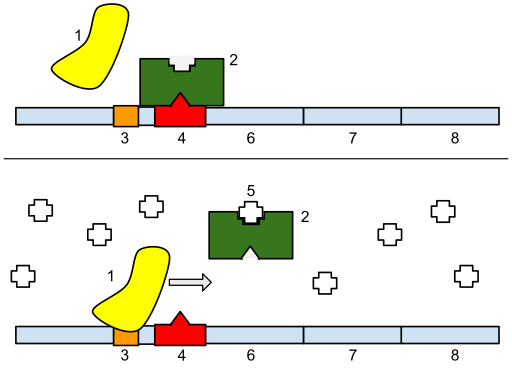
Figure 02: Repressor protein
Methionine repressor MetJ is an example of repressor protein. Moreover, the lactose repressor protein (LacI) is another example of repressor protein which controls expression of lactose metabolic genes.
What are the Similarities Between Regulatory and Repressor Protein?
- Both regulatory and repressor proteins bind with the specific regions of genes.
- They regulate gene expression.
- Some regulatory proteins are repressor proteins.
What is the Difference Between Regulatory and Repressor Protein?
Regulatory protein is a protein that induces or inhibits the expression of the gene. Repressor protein is a protein that suppresses the transcription of a gene. So, this is the key difference between regulatory and repressor protein. Moreover, repressor protein is a type of regulatory protein that involves in negative regulation of genes.
Summary – Regulatory vs Repressor Protein
Regulatory proteins are proteins that bind with regulatory sequences of genes and regulate the gene expression. Some regulatory proteins are activators, which increase the transcription of genes by helping RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. But, some regulatory proteins are repressors, which reduce transcription by blocking RNA polymerase from moving forward on the DNA. Meanwhile, repressor proteins are proteins that bind with DNA or RNA and suppress the gene expression. So, this summarizes the difference between regulatory and repressor protein.
Reference:
1. “Overview: Gene Regulation in Bacteria.” Khan Academy, Khan Academy, Available here.
2. “Gene Expression and Regulation.” Nature News, Nature Publishing Group, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Gene Regulatory Network” Dominio público) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Lac Operon” By T A RAJU – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26%2BxKCspZmkpL%2B6ecCnm2aqlaW%2Fpr%2FSqKlmqKKkwaa1zWg%3D