Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genome
Table of Contents
The key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome is that the prokaryotic genome is present in the cytoplasm while eukaryotic genome confines within the nucleus.
Genome refers to the entire collection of DNA of an organism. In other words, the genome is the genetic material of an organism that contains the total genetic information. Most of the organism has a genome made from DNA. However, some genomes are RNA based. As an example, certain viruses have RNA genomes. When considering the total genetic material of an organism, it does not include only the genes or the coding sequences. It includes both genes and non-encoding sequences of DNA.
Since the genetic information lies within the genome in the form of genes, genes undergo transcription and translation in order to produce proteins. There is a difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome expression processes. Furthermore, the storage and replication of both genomes are also different among the prokaryotes and eukaryotes. But the structure of the DNA remains the same (Double Helix) in both organisms. The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome goes with the cellular organization of organisms and where the genome resides.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Prokaryotic Genome
3. What is Eukaryotic Genome
4. Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genome
5. Side by Side Comparison – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Genome in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Prokaryotic Genome?
Prokaryotes are the simple unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles. Furthermore, they have small bodies and small genomes. Usually, prokaryotic genomes consist one or more DNA molecule. Simply they have a single chromosome that floats in the cytoplasm. Apart from this single chromosome, some bacteria have extra-chromosomal DNA called plasmids. Plasmids are not genomic DNA. They are accessory DNA molecules. However, plasmids provide additional advantages to bacteria such as antibiotic resistance, herbicide resistance, etc. They are small circular DNA molecules that have the ability to self-replicate. Hence, plasmids serve as important vectors in the recombinant DNA technology.
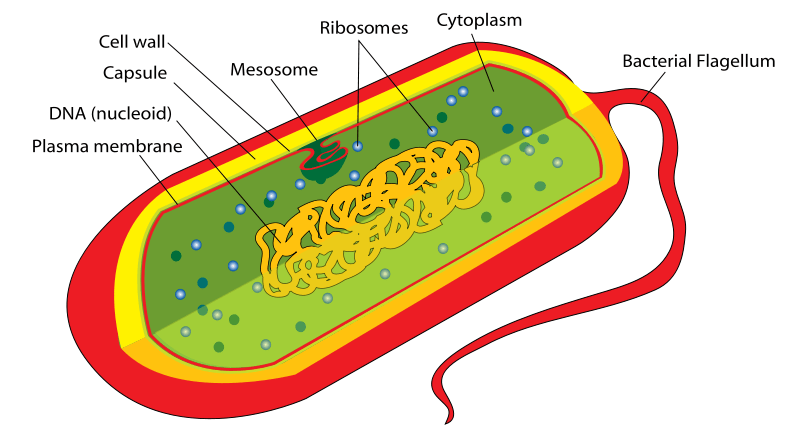
Figure 01: Prokaryotic Cell and Genome
Due to their small sizes, prokaryotic genome mainly contains coding sequences (exons). But, it does not contain introns and repetitive sequences. Furthermore, prokaryotic genes exist as clusters that regulate by a single promoter. And also, this single chromosome is circular and touches with the cell membrane from some points. Structurally, prokaryotic genome is more compact than eukaryotic genome. Moreover, it does not contain spaces between genes.
What is Eukaryotic Genome?
Eukaryotes are the organism that has a nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles. They have extensive cellular compartments that carry out distinct functions. Within the nucleus of eukaryotes, we can find the eukaryotic genome that contains the whole genetic information of the organism. Mainly, eukaryotic genome exists as linear chromosomes. Furthermore, DNA molecules together with the histone proteins make these chromosomes. In the human genome, there is a total of 46 chromosomes in each cell. Nuclear membrane encloses all these chromosomes. Hence, they can’t come to the cytoplasm of the cell unless they become mRNA molecules. Also, in eukaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts contain some DNA molecules. However, they are not genomic DNA.
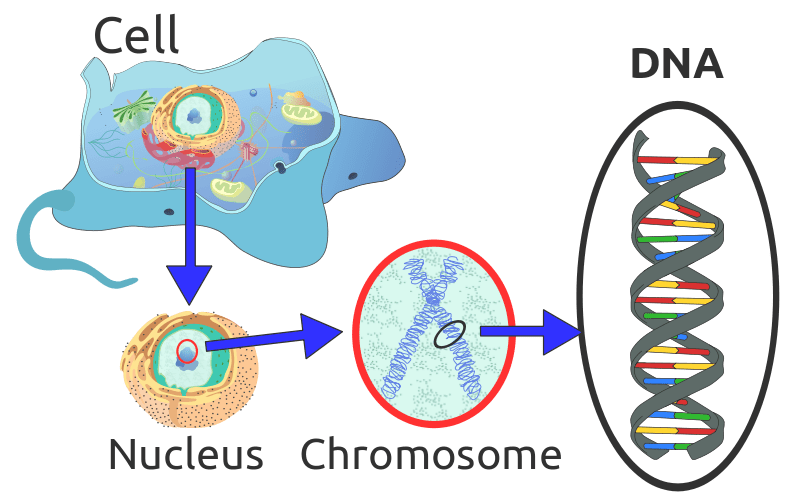
Figure 02: Eukaryotic Genome
Eukaryotic genome is less compact, and it contains repetitive sequences as well as many non-coding sequences such as introns and spacer DNA. With comparison to the prokaryotic genome, the eukaryotic genome is bigger and has billions of base pairs. Furthermore, it contains many genes with multiple copies.
What are the Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genome?
- Both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genome consist of DNA molecules.
- Genomes serve as the storages of genetic information of both types of organisms.
- Also, both genomes contain genes.
- Furthermore, both undergo transcription and translation.
- Besides, both genomes duplicate and inherit to next generations.
What is the Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genome?
Organisms are two types either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have a simple cell organization while eukaryotes have a complex cell organization. Similar to that, prokaryotic genome is small and less complex compared to eukaryotic genome. Structurally, prokaryotic genome restricts to a single chromosome while eukaryotic genome has multiple chromosomes. This is one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome. Furthermore, one other difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome is that the prokaryotic genome is present in the cytoplasm while the eukaryotic genome is present inside the nucleus. Also, when considering the size of the genome, the prokaryotic genome is much smaller than the eukaryotic genome. Moreover, with regard to the composition, the eukaryotic genome has many repetitive DNA, introns, and spacer DNA that are absent in prokaryotic genome.
The below infographic illustrates more facts regarding the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome.
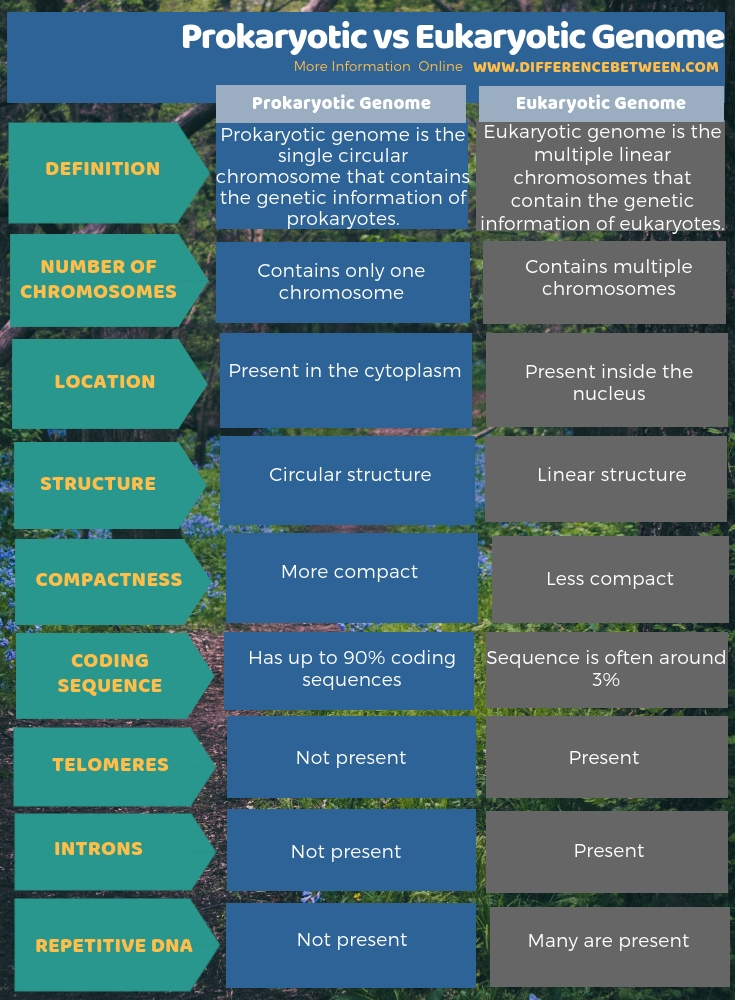
Summary – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Genome
Prokaryotes are two types such as bacteria and archaea. On the other hand, eukaryotes include plants, animals, fungi, algae and protozoa. Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, etc. In contrast, eukaryotes have extensive internal compartments that separate by membranes. According to these differences in the cellular organization, prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes also differ from each other. Thus, the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome is that the prokaryotic genome floats in the cytoplasm while the eukaryotic genome protects inside the nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotic genome is more compact and has no repetitive DNA, introns, and spacer DNA compared to eukaryotic genome. In contrast, eukaryotic genome has many genes, more repetitive DNA and introns. Hence, this is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genome.
Reference:
1.Brown, Terence A. “Genome Anatomies.” Genomes. 2nd Edition., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1 Jan. 1970. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Prokaryote cell diagram”By Mariana Ruiz LadyofHats – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Eukaryote DNA-en”By LadyofHats (Mariana Ruiz) (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2680aiimqqppMGqr4yapZ1lpqh6psHKmqmyp6SesG6zxKempp1f