Difference Between Oxidases and Oxygenases
Table of Contents
The key difference between oxidases and oxygenases is that the oxidases are the enzymes that catalyze the oxidation-reduction reactions by transferring the hydrogen from a substrate to oxygen, and thus, forming water or hydrogen peroxide while, the oxygenases are the enzymes that catalyze direct incorporation of the oxygen from the molecular oxygen (O2) to a substrate during the oxidation of a particular substrate.
Enzymes are protein molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions occurring in the cells of living organisms. Accordingly, they increase the rate of reaction by reducing the activation energy of the reaction. Hence, the reactions occur at high speeds. Also, some enzymes catalyze the breakdown of complex molecules into their monomers while some enzymes catalyze the formation of biomolecules from their monomers. Likewise, oxidases and oxygenases are two types of enzymes present in all living organisms.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Oxidases
3. What are Oxygenases
4. Similarities Between Oxidases and Oxygenases
5. Side by Side Comparison – Oxidases vs Oxygenases in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Oxidases?
Oxidases are a type of oxido-reductases that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions. These enzymes involve in the oxidation-reduction reactions by transferring the hydrogen from a substrate to oxygen. Then the oxygen becomes water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
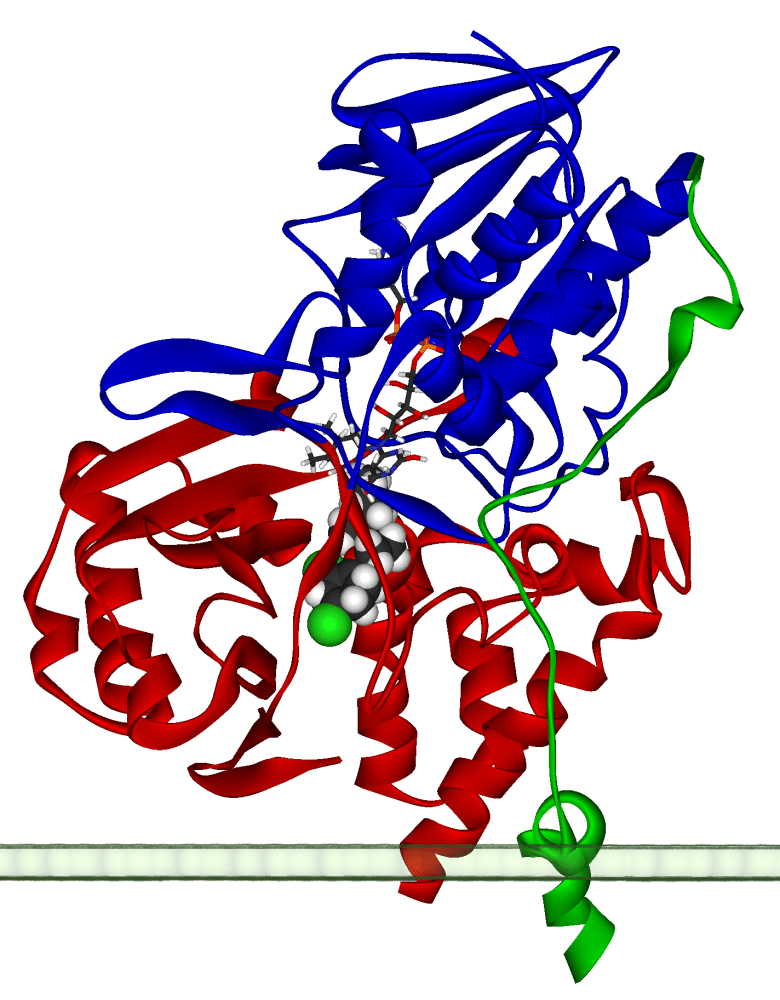
Figure 01: Monoamine Oxidase A
Generally, oxidases are present in many parts of the human body, and they act as catalysts in oxidizing many types of substrates. As a result, many complex molecules like amines, glucose, and xanthenes are oxidized into simpler molecules that are easily metabolized by the body.
Furthermore, there are different types of oxidases, and their names vary according to the molecule that they catalyze. Some examples of oxidases are cytochrome oxidase, ascorbic acid oxidase, uricase and monoamine oxidase. The following reaction illustrates the action of oxidase in an oxidation-reduction reaction,
AH + O2 + 2H+ + 2e– = AOH + H2O
What are Oxygenases?
Oxygenases are a subgroup of oxido-reductases. These enzymes catalyze the incorporation of oxygen atoms from molecular O2 to substrates during the oxidation of a substrate. Some reactions incorporate two oxygen atoms while some reactions incorporate one oxygen atom. Thus, based on the number of oxygen atoms incorporated during the reaction, the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction differs.
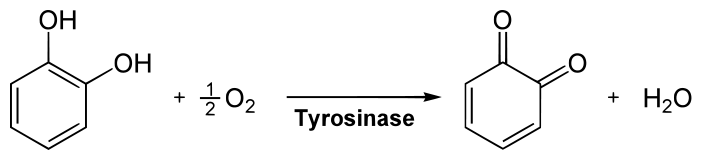
Figure 02: Oxygenase
Mono-oxygenases catalyze the incorporation of one oxygen atom as a hydroxyl group to a substrate. The second oxygen atom involves in the making of water molecule. Some examples of monooxygenases are tryptophan pyrrolase and carotenase. On the other hand, dioxygenases catalyze the incorporation of two atoms of oxygen to a substrate. Some examples of dioxygenases are phenylalanine hydroxylase and tyrosinase.
The following reaction illustrates the catalysis of mono-oxygenase in an oxidation-reduction reaction,
AH + XH2 + O2 = AOH + X+ H2O
What are the Similarities Between Oxidases and Oxygenases?
- Both oxidases and oxygenases are proteins that work as biocatalysts.
- Furthermore, they are oxido-reductases that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions.
What is the Difference Between Oxidases and Oxygenases?
The key difference between oxidases and oxygenases is the oxidation-reduction reaction that they catalyze. Oxidases catalyze the transfer of hydrogen from a substrate to an oxygen while oxygenases catalyze the transfer of the atomic oxygen from O2 to a substrate. Furthermore, oxygenases are of two types; monooxygenases and dioxygenase, while oxidases are one type. Thus, this is another difference between oxidases and oxygenases.
Moreover, a further difference between oxidases and oxygenases is that the oxidases are generally found in cell membranes and are responsible for the building of ATP that store cell energy while oxygenases are responsible for breaking down iron that is distributed to the whole body.
The below infographic gives more details on difference between oxidases and oxygenases .
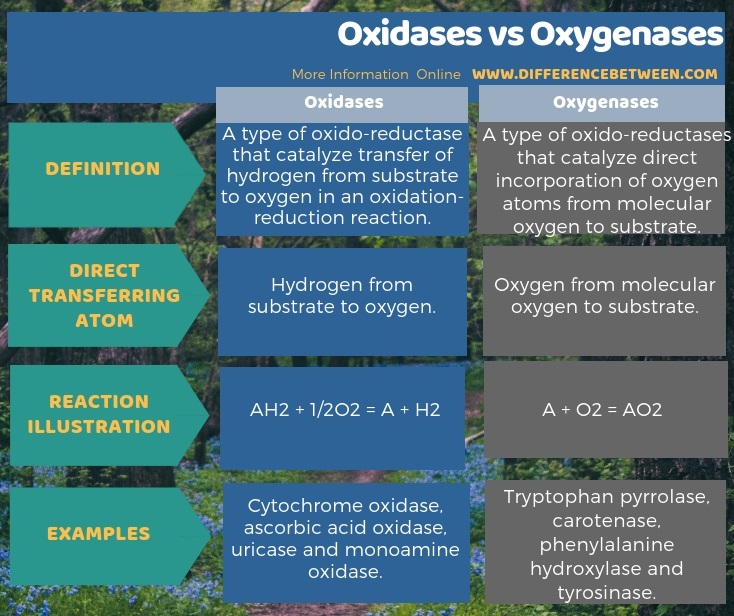
Summary – Oxidases vs Oxygenases
Oxidases and oxygenases are two types of oxido-reductases that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions. Oxidases catalyze the transferred hydrogen from the substrate to an oxygen during the oxidation-reduction reaction. On the other hand, oxygenases catalyze the direct incorporation of the oxygen atoms from O2 to a substrate. Therefore, this is the key difference between oxidases and oxygenases.
Reference:
1.“Oxygenase.” NeuroImage, Academic Press. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Monoamine oxidase A 2BXS”By Fvasconcellos, De Colibus L, Li M, Binda C, Lustig A, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2005). “Three-dimensional structure of human monoamine oxidase A (MAO A): relation to the structures of rat MAO A and human MAO B”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (36): 12684–9. PMID 16129825. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505975102., (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Reaction Tyrosinase”By Yikrazul – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26716KbmquVqHqiusNmraxln63GqLHNmqqeq18%3D