Difference Between Myxomycota and Eumycota
Table of Contents
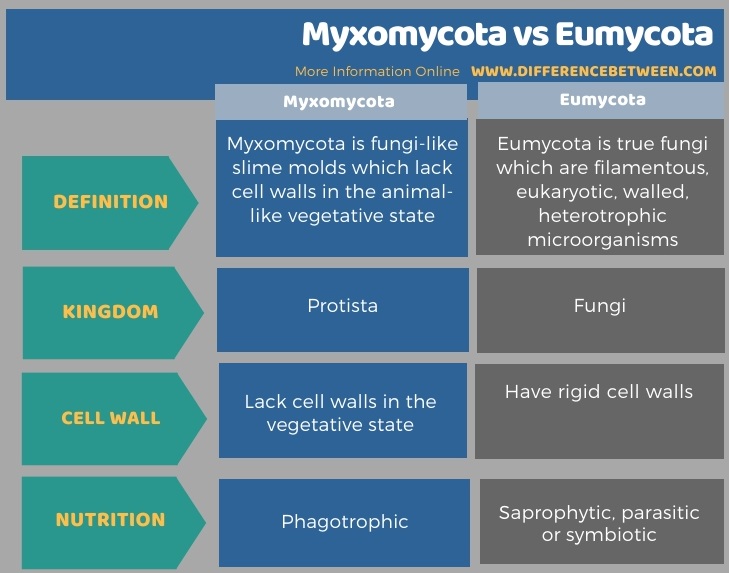
The key difference between Myxomycota and eumycota is that Myxomycota consists of fungi-like slime molds which lack cell walls in the vegetative state while eumycota consists of true fungi which are filamentous eukaryotic heterotrophic microorganisms consisting rigid cell walls.
Myxomycota and eumycota are two major divisions of organisms. Myxomycota belongs to Kingdom Protista while eumycota belongs to Kingdom Fungi. Myxomycota comprises fungi like organisms. They lack cell walls made up of chitin in the vegetative state. But eumycota is true fungi which have chitin cell walls. True fungi have mycelia, and they are heterotrophic aerobic microorganisms.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Myxomycota
3. What is Eumycota
4. Similarities Between Myxomycota and Eumycota
5. Side by Side Comparison – Myxomycota vs Eumycota in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Myxomycota?
Myxomycota, also known as slime molds, belong to the Kingdom Protista. They are similar to fungi as they produce spores and sporangia. Slime molds live on decaying plants, organic matter and microorganisms. The main unique feature of slime mold is the presence of the plasmodium. The plasmodium makes it easy for the identification process. Formation of plasmodium takes place under harsh conditions, especially during food shortages. The Slime molds swim and merge together to form a multinucleated cell. This cell is called the plasmodium. There is no cell wall in the plasmodium structure. Therefore, it receives less protection.
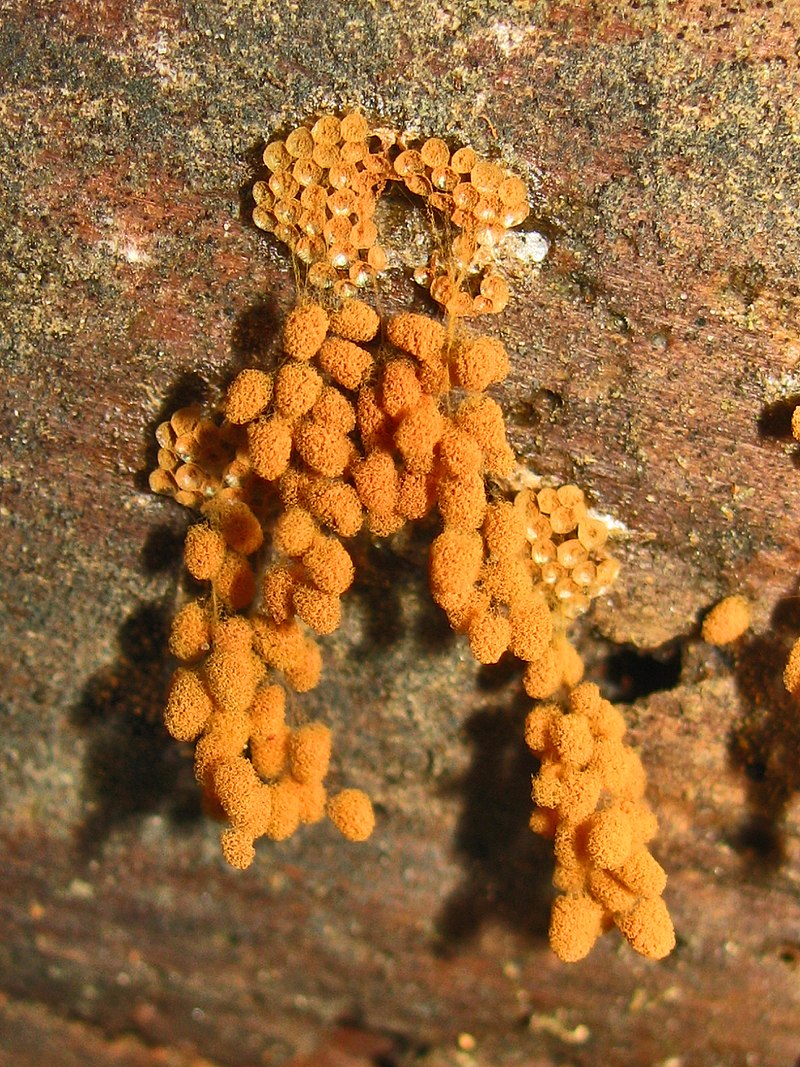

Figure 01: Myxomycota
The life cycle of Slime molds begins as an amoeboid cell. After engulfing bacteria and other food, the amoeboid cell becomes larger in size and multiplies. Under harsh conditions, these amoeboid cells can reach a dormant stage. During these stages, they form a hard outer covering which protects the cell until optimum conditions are reached. Upon maturation, these nuclei grow in size. Reproduction takes place through spores which are embedded in the sporangia as well as gametes. The reproductive cells are sometimes flagellated.
What is Eumycota?
Eumycota is a division consisting of true fungi. They are eukaryotic heterotrophic walled organisms. Their cell wall is made up of chitin. The fungal body consists of thread-like structures called hyphae. Eumycota has five subdivisions as Mastigomycotina, Zygomycotina, Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina and Deuteromycotina (imperfect fungi). Mastigomycotina comprises of fungi which produce zoospores or flagellated cells. Zygomycotina fungi produce unique zygospores while Ascomycotina fungi are sac fungi which produce asci bearing ascospores. Basidium is unique to Basidiomycotina. Deuteromycotina fungi show only asexual reproduction.
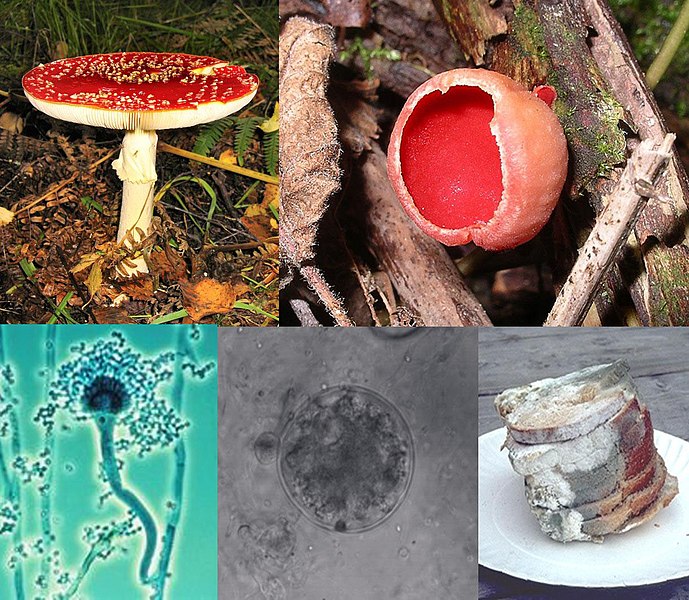

Figure 02: Eumycota
Eumycota fungi can be parasitic, saprophytic and symbiotic. Symbiotic fungi make an association with algae/cyanobacteria (lichens) or with roots of higher plants (mycorrhiza). Saprophytes feed on dead organic matter. Parasitic fungi infect plants, animals and other organisms.
What are the Similarities Between Myxomycota and Eumycota?
- Myxomycota members are fungi-like.
- Both myxomycota and eumycota members produce spores.
- They both have sporangia.
What is the Difference Between Myxomycota and Eumycota?
Myxomycota is fungi-like slime mold which lacks cell walls in the animal-like vegetative state while eumycota is true fungi that are filamentous eukaryotic heterotrophic walled microorganisms. So, this is the key difference between myxomycota and eumycota. Myxomycota belongs to Kingdom Protista while eumycota belongs to Kingdom Fungi.
Moreover, myxomycota organisms lack a cell wall in their vegetative state while eumycota fungi have a rigid cell wall made up of chitin. Also, another difference between myxomycota and eumycota is their nutrition. Myxomycota members are phagotrophic while fungi can be saprophytic, parasitic or symbiotic.
Below is a summary of the difference between myxomycota and eumycota.
Summary – Myxomycota vs Eumycota
Myxomycota is fungi-like organisms that are known as slime moulds. They belong to Kingdom Protista. In contrast, eumycota is true fungi belonging to Kingdom Fungi. They have cell walls made up of chitin. However, myxomycota members lack cell walls in their vegetative state. This summarizes the difference between myxomycota and eumycota.
Reference:
1. “Myxomycota: Features And Occurrence | Fungi”. Biology Discussion, 2020, Available here.
2. “Eumycota – An Overview | Sciencedirect Topics”. Sciencedirect.Com, 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Myxomycota” By Одинець Сергій – Own work (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Fungi collage” By BorgQueen – Sources clockwise from top left: File:Amanita muscaria tyndrum.jpg, File:Scarlet elf cap cadnant dingle.jpg, File:Mouldy bread alt.jpg, File:Spizellomycete.jpg, File:Aspergillus.jpg (CC BY-SA 2.5) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2652LGmprGTpMGiecCnm2adpaLGpLvTmmY%3D