Difference Between Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fats
Table of Contents
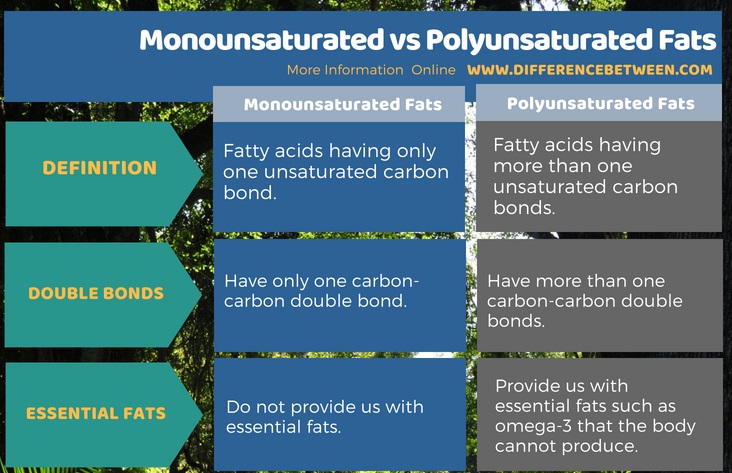
The key difference between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is that the monounsaturated fats have one unsaturated carbon bond whereas the polyunsaturated fats have more than one unsaturated carbon bonds. Another important difference between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is that the monounsaturated fats cannot provide us with essential fats whereas, the polyunsaturated fats provide us with essential fats that the body cannot produce; that is, omega-3 and omega-6.
Both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are forms of fatty acids. These fats have at least one double bond between two carbon atoms in their chemical structure. Moreover, these fats have health benefits because both these are forms of dietary fats.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Monounsaturated Fats
3. What are Polyunsaturated Fats
4. Side by Side Comparison – Monounsaturated vs Polyunsaturated Fats in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What are Monounsaturated Fats?
Monounsaturated fats are fatty acids that have only one unsaturated carbon bond (double bond between two carbon atoms). All other carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain have single bonds between them. Since the viscosity and melting temperature of a fatty acid increase with the decreasing number of double bonds, monounsaturated fats have higher viscosity and melting temperatures when compared with other fatty acids.
Some examples of monounsaturated fats include myristoleic acid, palmitoleic acid, vaccenic acid, oleic acid, etc. The health benefits of these fats include decreased risk for breast cancer, reduce cholesterol levels, lower risk for heart diseases and helpful for weight loss.
What are Polyunsaturated Fats?
Polyunsaturated fats are fatty acids having more than one unsaturated carbon bonds. An unsaturated carbon bond is a double bond between two carbon atoms. Therefore, these fats have many double bonds between the carbon atoms. The oils having these fatty acids are liquid at room temperature but solidifies when chilled. Ex: olive oil.

Figure 01: Sunflower Oil is a Polyunsaturated Fatty Compound
Eating a moderate amount of these fatty acids rather than eating saturated or trans fats give health benefits. Moreover, these fats provide us with essential fats that the body cannot produce, i.e. omega-3 and omega-6. Polyunsaturated fats can decrease the LDL cholesterol (we call it bad cholesterol). Therefore, the risk for heart diseases reduces. The foods that are high in these fats include grapeseed oil, mustardseed oil, and sunflower oil.
What is the Difference Between Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fats?
Monounsaturated fats are fatty acids that have only one unsaturated carbon bond whereas Polyunsaturated fats are fatty acids having more than one unsaturated carbon bonds. Moreover, Monounsaturated fats have only one carbon-carbon double bond. On the other hands, Polyunsaturated fats have more than one carbon-carbon double bonds.
Monounsaturated fats do not provide us with essential fats while Polyunsaturated fats provide us with essential fats such as omega-3 that the body cannot produce.
Summary – Monounsaturated vs Polyunsaturated Fats
Both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are liquids at room temperature. The difference between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is that monounsaturated fats have one unsaturated carbon bond whereas polyunsaturated fats have more than two unsaturated carbon bonds.
Reference:
1. “The 6 Benefits of Monounsaturated Fats (MUFAs).” All Body Ecology Articles, 28 Sept. 2016. Available here
2. “Monounsaturated Fat.” American Heart Association. Available here
3. “Facts about Polyunsaturated Fats: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.” MedlinePlus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’Sunflower oil and sunflower’By torange.biz (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau265zqemrqajlsG2vsCtnJ1lkaOxbrzOpbCupqOWwba%2BwK2cnWWWlsG0ew%3D%3D