Difference Between Molds and Yeasts
Table of Contents
The key difference between molds and yeasts is that the molds are multicellular filamentous fungi whereas the yeasts are unicellular round or oval fungi.
Kingdom fungi are one of the five kingdoms that include eukaryotic microorganisms such as yeasts, molds rusts, smuts, mildews and mushrooms. They are very vital and useful decomposers in the environment that help the recycling of nutrients within the many types of ecosystems. Moreover, fungi are a diverse group of organisms. Some are unicellular round fungi. Many are filamentous fungi.
Apart from these two types, some fungi are club-shaped while some are powdery forms. However, it is important to study different types of fungi since some are hazardous to our health while some cause different kinds of plant and animal diseases. But not all fungi are bad. Accordingly, there are very useful fungi in this kingdom which have different commercial applications in industries especially in antibiotic production, food production and extraction of secondary metabolites. Hence, this article targets two types of fungi; molds and yeasts especially their differences. Once you go down the article, you will find information regarding the difference between molds and yeasts.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Molds
3. What are Yeasts
4. Similarities Between Molds vs Yeasts
5. Side by Side Comparison – Molds vs Yeasts in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Molds?
Molds characteristically possess a multicellular filamentous mycelium called hyphae. Hyphae can have compartments or not. Based on that, some fungi are septate molds while others are aseptate molds. They are a type of fungi which includes various genera of important fungi such as Aspergillus and Penicillium. They reproduce mainly through spores asexually, but sometimes they reproduce sexually as well. A network of these molds such as the hyphae forming tubular branches comprises the same genetic information and hence, it is believed as a single organism.
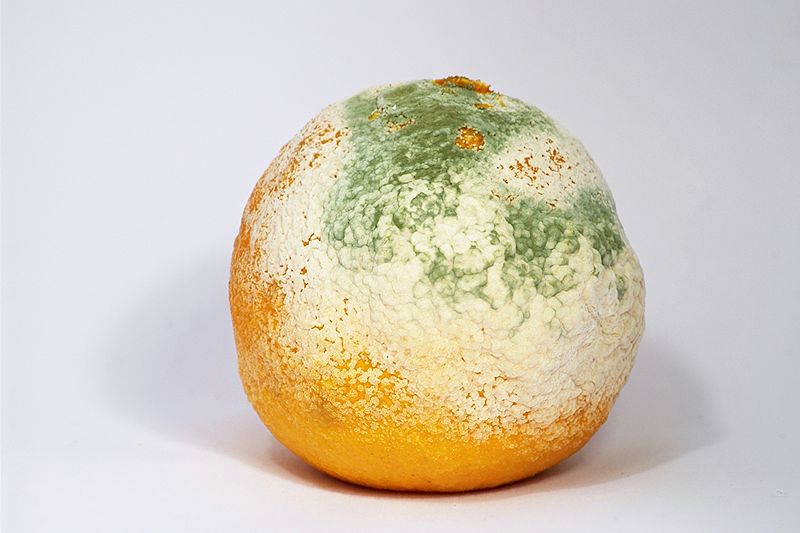

Figure 01: Mold
In food, molds grow giving a fuzzy appearance causing deterioration and discolouration. They cause biodegradation of natural materials while playing an important part in biotechnology. Molds become hazardous causing allergic reactions and respiratory problems if you inhale a high dose of spores of molds. In addition, some molds help with food production especially during the preparation of fermenting foods. Also, molds have immense use in medicine preparation such as antibiotics and extraction of organic acids.
What are Yeasts?
Yeasts are single-celled fungi that reproduce asexually by budding or by binary fission with over 1500 species described so far. We encounter them commonly in the ocean, soil and on plant surfaces. Yeasts are popular in food and beverage production, especially in the production of beer and other alcoholic beverages such as Japanese sake. The most commonly used yeast species is the Saccharomyces cerevisiae that converts carbohydrates to carbon dioxide and alcohol. The most common use of yeast, however, would be for bread as a leavening agent.
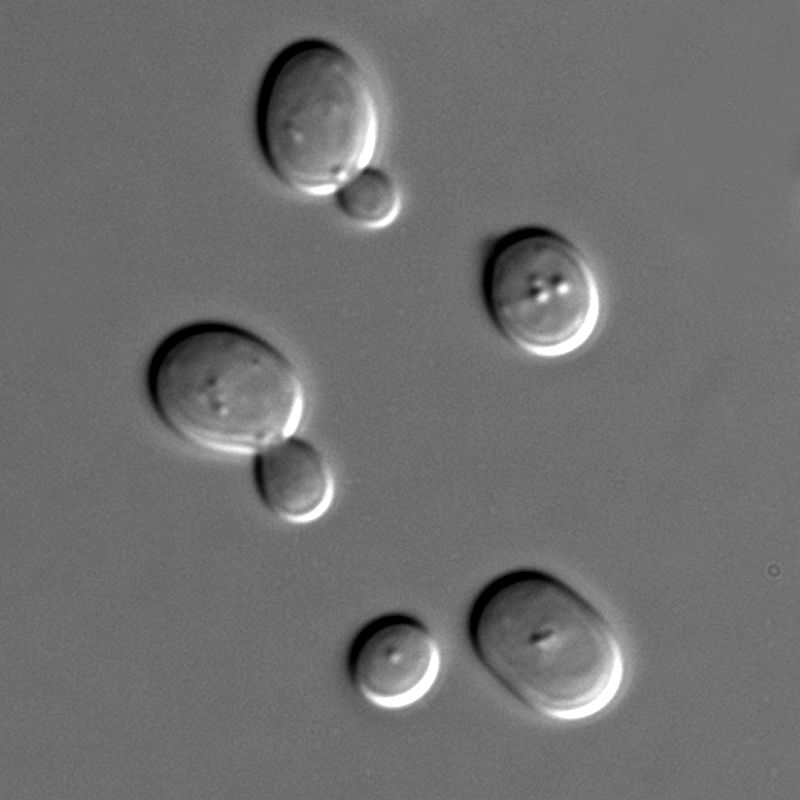
Figure 02: Yeasts
Apart from the use of yeasts in food and beverage production, some yeasts are pathogenic. Candida is one of the disease-causing fungi that come under the group yeasts. But, they only affect people with compromised immune systems.
What are the Similarities Between Molds and Yeasts?
- Molds and yeasts are fungi.
- Furthermore, they are both eukaryotes and saprophytes.
- Also, they are important decomposers in the soil.
- Moreover, they share a similar cell structure.
- Besides, their cell walls contain chitin as the main compound.
- Both molds and yeasts are opportunistic pathogens in immune compromised people.
What is the Difference Between Molds and Yeasts?
Molds and yeasts are two groups of fungi that share similarities as well as differences. Molds are multicellular microorganisms with some being colourful. They become pathogenic when consumed. Moreover, they cause a myriad of health issues such as allergic reactions and respiratory problems as a result of inhaling their spores. On the other hand, yeasts are unicellular, colourless, round or oval-shaped fungi. Typically, yeasts are harmless. But, they still spoil food, usually those with low pH levels and those with high sugar content, and could cause harm to people with weak immune systems. Therefore, the major difference between molds and yeasts is the cellular structure. Molds are multicellular filamentous fungi while the yeasts are single-celled round fungi.
Furthermore, another difference between molds and yeasts is that yeasts do not form hyphae, unlike molds. The below infographic provides further information on the difference between molds and yeasts.

Summary – Molds vs Yeasts
Kingdom fungi include eukaryotic microorganisms such as molds, rusts, yeasts, mushrooms, etc. Among the different groups of fungi, molds and yeasts are commercially important. Molds are a multicellular thread like fungi which form hyphae. On the other hand, yeasts are single-celled fungi with round or oval shapes. Therefore, this is the major difference between molds and yeasts. Furthermore, molds reproduce via both asexual and sexual reproduction methods while yeasts reproduce mainly through asexual methods such as budding and binary fission.
Reference:
1.“Yeast.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 25 Oct. 2018. Available here
2.Editors. “Fungi – Definition, Types, Examples, Characteristics & Reproduction.” Biology Dictionary, Biology Dictionary, 28 Apr. 2017. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Mouldy Clementine”By NotFromUtrecht – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”S cerevisiae under DIC microscopy”By Masur – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau265zqWbrGWRo7FuxcSaqq2rXw%3D%3D