Difference Between Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
Table of Contents
Key Difference – Lactobacillus vs Bifidobacterium
In the context of modern microbiology, different bacterial species with symbiotic associations with the human body are currently being investigated to identify different beneficiary factors. These bacterial species provide different benefits to the host that include the upregulation of host growth and development. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are such two bacterial species that are recognized as probiotics. Probiotics are beneficiary bacteria that are present in the gut microbiota that provides different benefits to the host. Lactobacillus is a facultative anaerobic bacterial species while Bifidobacterium is an obligate anaerobic bacterial species. This is the key difference between Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Lactobacillus
3. What is Bifidobacterium
4. Similarities Between Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
5. Side by Side Comparison – Lactobacillus vs Bifidobacterium in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Lactobacillus?
Lactobacillus belongs to the group of gram-positive bacteria that are facultative anaerobic organisms. Considering other features of Lactobacillus, they are rod-shaped microaerophilic bacteria. They do not form any spores during reproduction. This species of bacteria is considered as the major species that belongs to the group lactic acid bacteria. In the context of human gut microbiota, Lactobacillus is abundantly present. Not only in the human gut, but Lactobacillus also resided in places such as genital system and urinary system etc. In the context of females, but Lactobacillus is also present as a major microbial component in the vagina.
These bacteria have the ability to form biofilms in the gut and vagina and thereby prevail during harmful environmental condition. Lactobacillus present in the human body exists as mutualistic organisms that protect the body from different pathogenic intrusions. The human body provides ample of nutrients for the growth and development of the bacterial species and to reproduce successfully within the body. In the context of dairy products, Lactobacillus is considered as probiotics. These probiotics uplift human health and involve in the treatment of diarrhoea and different vaginal infections. Lactobacillus could also be used as a treatment strategy for skin infections such as eczema.
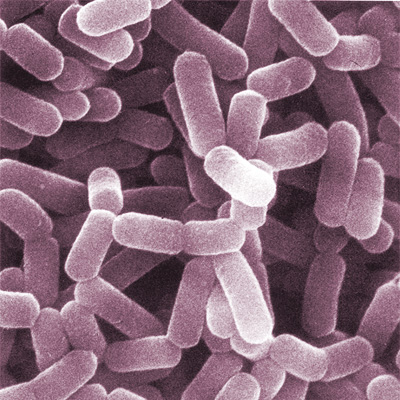
Figure 01: Lactobacillus
In the context of Lactobacillus metabolism, most of the species involved in homofermentative metabolism, and a minority of species involve in heterofermentative metabolisms. Homofermentative describes the production of only lactic acid from sugars whilst heterofermentative refers to the production of lactic acid or alcohols from sugars.
What is Bifidobacterium?
Bifidobacterium is a non-motile, gram-positive, rod-shaped (branched) obligate anaerobic bacterium that is primarily present in the intestines of animals and humans. These bacteria are considered as the major type of organisms that inhabits the colon of mammals. Similar to Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium is also used as a probiotic. In the context of fermentation of carbohydrates, Bifidobacterium utilizes the fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase pathway. These bacteria that present in the human gut involves in a symbiotic relationship with the host and provides beneficiary factors such as good digestion, production of lactic acid and acetic acid and promotes immunity through boosting up the immune system. It was revealed that Bifidobacterium has the ability to compete with other gut microorganisms actively and occupy a larger fraction of the gut microbiota.

Figure 02: Bifidobacterium
Out of the Bifidobacterium group, Bifidobacterium longum is the most common type of species. It has a genome which is circular that contains a length of 2,260,000 bp (base pairs) and with a GC (Guanine and Cytosine) content of 60 %. This species is currently under thorough research in order to identify the probiotic qualities. Bifidobacterium has a unique pathway for hexose metabolism that is driven by a phosphoketolase pathway. This unique pathway is referred to the as bifid shunt. During this pathway, the bacteria utilize the enzyme fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase. This is also used as a diagnostic tool since this phenomenon is not found in other species of gram-positive bacteria.
What are the Similarities Between Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium?
- Both Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are gram-positive.
- Both Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium produce lactate.
- Both Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium organisms are susceptible to antibiotics.
- Both Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium share a common habitat, which is the intestines of animals and humans.
- Both Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are utilized as probiotics.
What is the Difference Between Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium?
Lactobacillus vs Bifidobacterium | |
| Lactobacillus belongs to the group of gram-positive bacteria that are facultative anaerobic that converts sugars into lactic acid. | Bifidobacterium is a non-motile, gram-positive, rod-shaped (branched) obligate anaerobic bacterium that is primarily present in the intestines of animals and humans. |
| Habitat | |
| Milk and dairy products, animal and human intestines, fermented foods are the habitats of Lactobacillus. | Human and animal gastrointestinal tract (intestines) is the habitat of Bifidobacterium. |
| Cellular Morphology | |
| Lactobacillus can be cocci or rods. | Bifidobacterium is present as branched rods or club-shaped. |
| Major Metabolites | |
| Lactic acid is the major metabolite of Lactobacillus. | Lactic acid and acetic acid are the major metabolites of Bifidobacterium. |
| Oxygen Sensitivity | |
| Lactobacillus is a facultative anaerobe (has the ability to live even in the presence of oxygen). | Bifidobacterium is an obligate anaerobe (cannot live in the presence of oxygen). |
Summary – Lactobacillus vs Bifidobacterium
Lactobacillus belongs to the group of gram-positive bacteria that are facultative anaerobic that converts sugars into lactic acid. This species of bacteria is considered as the major species that belongs to the group lactic acid bacteria. Lactobacillus present in the human body exists as mutualistic organisms that protect the body from different pathogenic intrusions. Most of the species involve in homofermentative metabolism, and a minority of species involve in heterofermentative metabolisms. These probiotics uplift human health and involve during the treatment of diarrhoea and different vaginal infections. Bifidobacterium is a non-motile, gram-positive, rod-shaped (branched) obligate anaerobic bacterium that is primarily present in the intestines of animals and humans. Bifidobacterium has the ability to compete with other gut microorganisms actively and occupies a larger fraction of the gut microbiota.
Download the PDF of Lactobacillus vs Bifidobacterium
You can download the PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation note. Please download the PDF version here: Difference Between Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
Reference:
1.Ocallaghan, Amy, and Douwe Van Sinderen. “Bifidobacteria and Their Role as Members of the Human Gut Microbiota.” Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 7, 2016, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00925.
2.The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica. “Lactobacillus.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, inc., 29 Dec. 2017. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’8344600413’by AJC1 (CC BY-SA 2.0) via Flickr
2.’Bifidobacterium longum en microscopie électronique’By Julie6301 – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau264wJyrqJqRmLatuNSsZJqmlGLDtHnBop2inJ%2BXrqTAxKugrqVf