Difference Between Ionic and Molecular Solids
Table of Contents
Key Difference – Ionic vs Molecular Solids
Solid substances are compounds that exist in a solid state at a given temperature and pressure. Solid state means, the atoms, molecules or ions in that substance are tightly packed, avoiding the movement of those chemical species (unlike in liquids or gases). There are two main types of solid substances; ionic solids and molecular solids. Ionic compounds contain ions that are held together via ionic chemical bonds. Ionic bonds are electrostatic attraction forces between oppositely charged ions. Molecular solids are solid substances that contain discrete molecules held together via Van der Waal forces. The key difference between ionic solids and molecular solids is that ionic solids contain ionic chemical bonds whereas molecular solid contain Van der Waal forces.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Ionic Solids
3. What are Molecular Solids
4. Side by Side Comparison – Ionic vs Molecular Solids in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What are Ionic Solids?
Ionic solids are solid compounds composed of oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic attractions. The ions are positively charged ions that are cations and negatively charged ions which are called anions. The chemical bond between these ions is known as an ionic bond. the overall charge of the ionic solid is neutral. That is because the cations are surrounded by anions and vice versa.
Ionic solids can contain either simple ions such as Na+ and Cl– or complex ions such as ammonium ion (NH4+). Ionic solids containing H+ ions are termed as acidic compounds because these solids release H+ ions when dissolved in water (it reduces the pH of the aqueous medium). Ionic solids containing OH– ions are termed as basic compounds because they release OH– ions (it increase the pH).
Ionic solids typically have high melting points and boiling points. These solids are hard and brittle. When ionic solids are melted, it becomes highly conductive because the molten form of ionic compounds contains ions that can conduct electricity. Ionic solids can be formed via different processes such as evaporation, precipitation, freezing, etc.
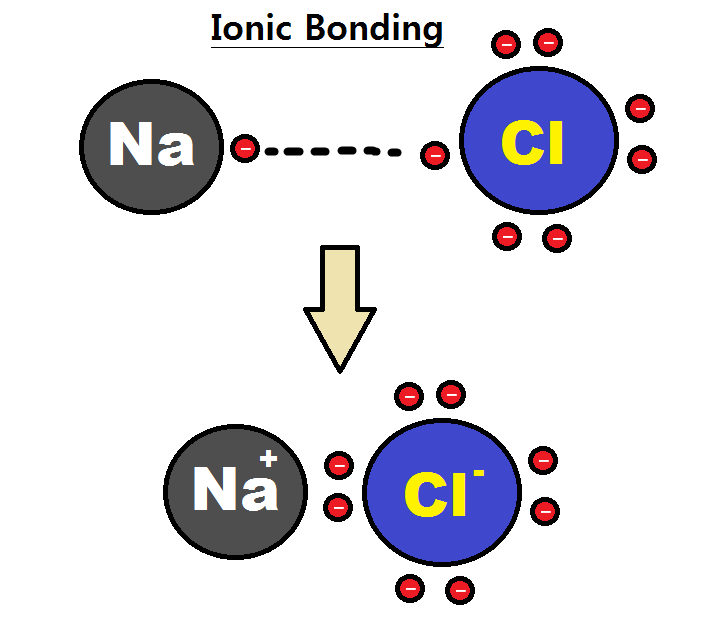
Figure 01: Formation of an Ionic Bond
Typically, ionic solids have regular crystalline structures. There, the ions are tightly packed in such a way that the lattice energy is minimized. Lattice energy is the amount of energy required to form a lattice from completely separated ions.
What are Molecular Solids?
A molecular solid is a type of solid in which molecules are held together by van der Waals forces rather than by ionic or covalent bonds. A molecular solid contains discrete molecules. The van der Waal forces that bind these molecules with each other are weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. The molecules present in these molecular solids can be monoatomic, diatomic or even polyatomic.
Since the intermolecular forces in the molecular solids are very weak, these solid compounds have lower melting points (often it is less than 300◦C). and also these molecular solids are relatively soft and have lower densities. However, there can be hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, London forces, etc. as well (instead of Van der Waal forces).
Van der Waal forces can be observed between nonpolar molecules. dipole-dipole interactions can be observed in polar molecules. hydrogen bonds are present between molecules containing functional groups such as O-H, N-H and F-H.
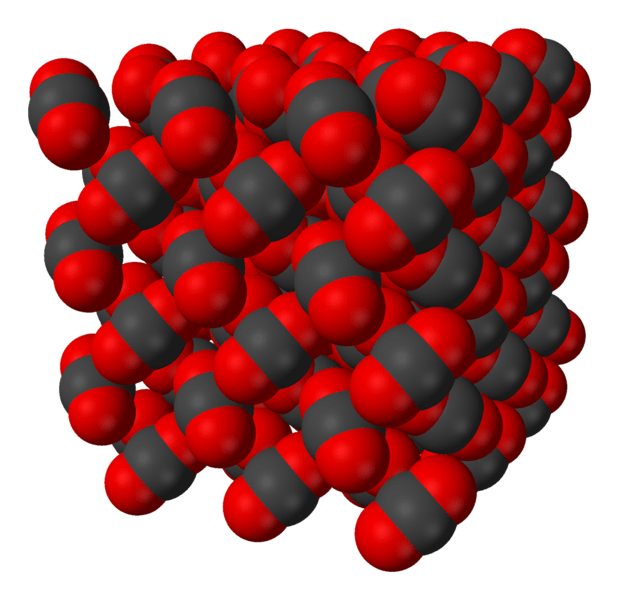
Figure 02: A Diagram Showing Carbon Dioxide Molecules in Solid Form
The weak Van der Waal forces between the molecules in molecular solids determine the properties of the solid. Some of these properties include low melting and boiling points, low mechanical strength, low electrical conductivity, low thermal conductivity, etc.
What is the Difference Between Ionic and Molecular Solids?
Ionic vs Molecular Solids | |
| Ionic solids are solid compounds composed of oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic attractions. | A molecular solid is a type of solid in which molecules are held together by van der Waals forces rather than by ionic or covalent bonds. |
| Chemical Bonds | |
| Ionic solids have ionic bonds. | Molecular solids have mainly Van der Waal forces, and there can be hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, London forces, etc. as well. |
| Bond Strength | |
| Ionic solids have strong bonds. | Molecular solids have weak bonds. |
| Components | |
| Ionic solids have cations and anions. | Molecular solids have polar or nonpolar molecules. |
| Melting and Boiling Points | |
| Ionic solids have high melting and boiling points. | Molecular solids have low melting and boiling points. |
| Density | |
| The density of ionic solids is very high. | The density of molecular solids is very low. |
| Nature | |
| Ionic solids are hard and brittle. | Molecular solids are relatively soft. |
Summary – Ionic vs Molecular Solids
Ionic solids are solid compounds made of cations and anions. There are electrostatic attraction forces between these oppositely charged ions. Molecular solids have molecules that have intermolecular forces between them. They are weak chemical interactions. The difference between ionic solids and molecular solids is that ionic solids contain ionic chemical bonds whereas molecular solid contain Van der Waal forces.
Reference:
1.Helmenstine, Anne Marie, D. “Molecular Solid – Definition and Examples.” ThoughtCo, Feb. 19, 2017. Available here
2.“Ionic Solids.” Chemistry LibreTexts, Libretexts, 21 July 2016. Available here
3.“Molecular solid.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 27 Feb. 2018. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’IonicBondingRH11’By Rhannosh – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.’Carbon-dioxide-crystal-3D-vdW’By Ben Mills – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau261zqegnGWRo7FuwtJmpKiklZjCra3RZqqopJmZwHA%3D