Difference Between Inductive Effect and Resonance Effect
Table of Contents
The key difference between inductive effect and resonance effect is that inductive effect occurs due to the polarization of chemical bonds whereas resonance effect occurs due to the presence of single bonds and double bonds together.
The terms inductive effect and resonance effect are related to atoms. The inductive effect occurs due to the induced electrical charges in atoms of a molecule. However, the resonance effect occurs when there are single bonds and double bonds in a molecule in an alternating pattern.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Inductive Effect
3. What is Resonance Effect
4. Side by Side Comparison – Inductive Effect vs Resonance Effect in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Inductive Effect?
Inductive effect occurs due to the transmission of an electrical charge throughout a chain of atoms. Finally, this transmission results in a fixed electrical charge on atoms in the molecule. Moreover, this effect happens when the electronegativity of atoms in the same molecule are different from each other.
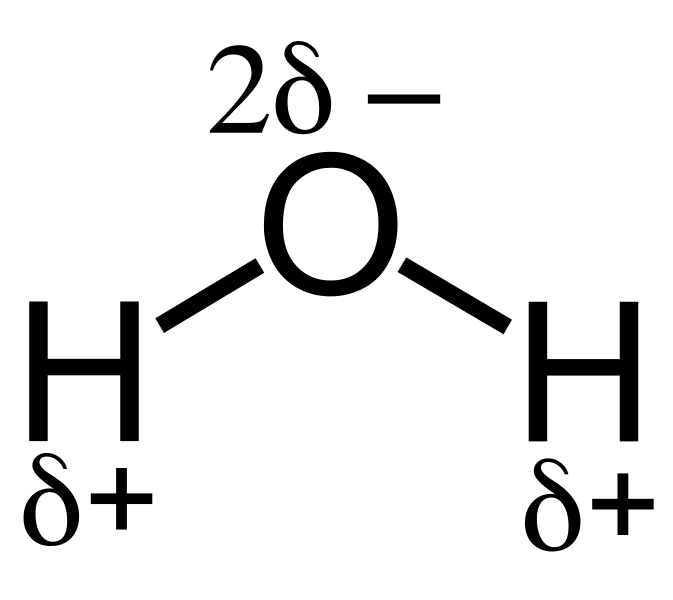
Figure 01: Charge Separation
Basically, atoms with high electronegativity values tend to attract bond electrons towards them than atoms with low electronegativity values. Therefore, when there are two atoms in a covalent bond that have a high difference between their electronegativity values, this induces the low electronegative atom to get a partial positive electrical charge. In contrast, the other atom gets a negative charge, which leads to the bond polarization. And, this whole process results in inductive effect. Furthermore, there are two types of effects; they are the electron withdrawing effect and electron releasing effect.
Moreover, this inductive effect has a direct effect on the stability of molecules. Thus, it is especially important in organic molecules. For instance, if there is a partial positive charge on a carbon atom in an organic molecule, then the electron releasing groups such as alkyl group can donate or share its electrons with this carbon atom, resulting in a reduction in the positive charge on it. Then, the stability of the organic molecule increases.
What is Resonance Effect?
Resonance effect is an effect on the stability of molecules with both single and double bonds. A double bond means that there is a pi bond along with the sigma bond. The pi bond electron delocalization is the basis of the resonance effect. Here, not only pi electrons, but also lone electron pairs may contribute.
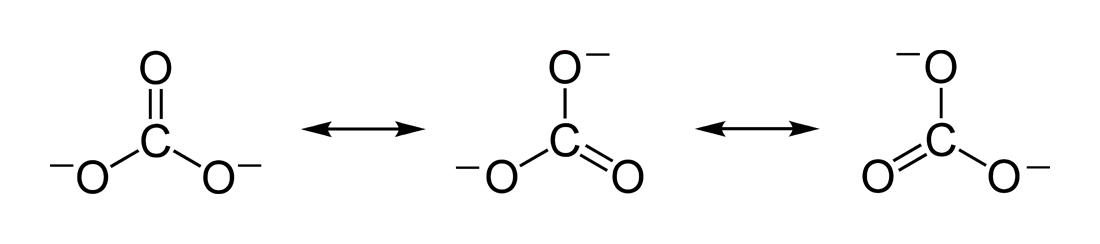
Figure 02: Resonance Stabilization of Carbonate Ion
The molecules with double bonds in an alternating pattern show resonance and we can use the resonance structures in order to determine the exact chemical build up of a certain molecule. It is because the molecule gets stabilized through resonance stabilization; thus, the actually occurring structure of a molecule is different from that of the molecule with alternating double bonds.
What is the Difference Between Inductive Effect and Resonance Effect?
Inductive effect is an effect that occurs due to the transmission of an electrical charge throughout a chain of atoms. Resonance effect is an effect on the stability of molecules with both single and double bonds. Therefore, the key difference between inductive effect and resonance effect is that inductive effect occurs due to the polarization of chemical bonds whereas resonance effect occurs due to the presence of single bonds and double bonds together.
Moreover, the electronegativity values of atoms in a molecule affect the inductive effect and number of double bonds and the pattern of their positions affect the resonance effect. So, this is also a significant difference between inductive effect and resonance effect.
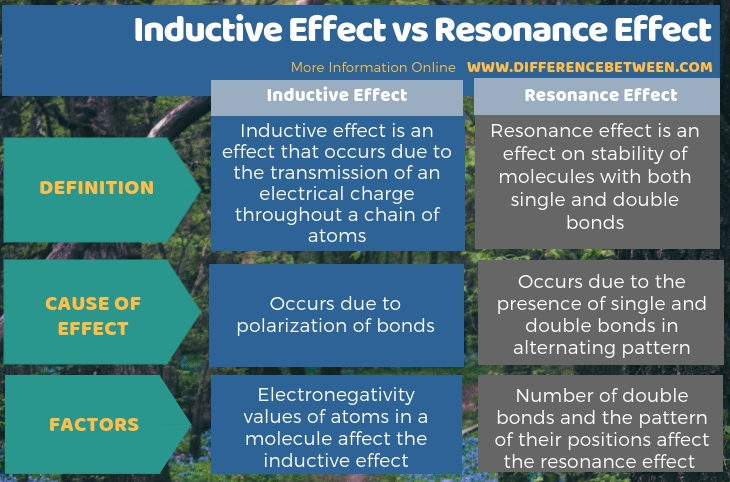
Summary – Inductive Effect vs Resonance Effect
Inductive effect and resonance effect are two important phenomena of chemical compounds. The key difference between inductive effect and resonance effect is that inductive effect occurs due to the polarization of chemical bonds whereas resonance effect occurs due to the presence of single bonds and double bonds together.
Reference:
1. James S. Panek, in Comprehensive Organic Synthesis, 1991
Image Courtesy:
1. “Water V.1” By Jü – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Carbonate-ion-resonance-2D” By Ben Mills – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau261zZ2snKyZq7JuscWfnJysXZa7pXnRnqqoppGjsKZ5xJ%2BdnpukZA%3D%3D