Difference Between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic
Table of Contents
The key difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic is that hydrophilic means water-loving while hydrophobic means water-resistant.
“Hydro” means water. From the initial stages of earth’s evolution, water has been a major part of the earth. Today, water covers more than 70% of the earth surface. Since water is a universal solvent, it participates in most reactions. It is the most abundant inorganic compound in living matter. More than 75% of our body is composed of water. It is a component of cells and acts as a solvent and reactant. Water is the medium for almost all biological reactions. Therefore, the capacity of compounds to interact with water is crucial. The degree of this capacity is explained by the two terms hydrophilic and hydrophobic.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Hydrophilic
3. What is Hydrophobic
4. Side by Side Comparison – Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Hydrophilic?
Hydrophilic means water-loving. Water is a polar molecule. Hydrophilic substances are water-loving substances; therefore, they like to interact with water or they are dissolved in water. As the phrase “like dissolves like” says, to interact or dissolve in a polar molecule like water, the hydrophilic substance should also be polar. If there is even a part of a big molecule which is polar, that end can attract water. For example, the phospholipid molecules, which forms the membrane of the cell, has a hydrophilic phosphate group. Though the whole molecule is not hydrophilic (the large lipid part of the molecule is hydrophobic), that phosphate head is hydrophilic; thus it interacts with water.
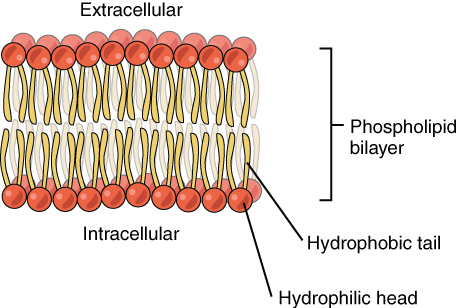
In contrast to molecules like this, some substances are very hydrophilic. For example, salts and sugar attract water so easily. They even have the ability to attract moisture from the air, so when they are exposed to air they tend to dissolve over time. This happens spontaneously because it is thermodynamically favourable. The substances tend to dissolve in water because they form hydrogen bonds with water. Usually, hydrophilic substances have a charge separation, which makes them polar and capable of hydrogen bonding with water. Hydrophilic substances are used to draw water and keep material dry.
What is Hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic is the opposite of hydrophilic. As the name suggests, “hydro” means water, and “phobic” means fear. Hence, substances that don’t like water are known as hydrophobic. Therefore, they repel water molecules.
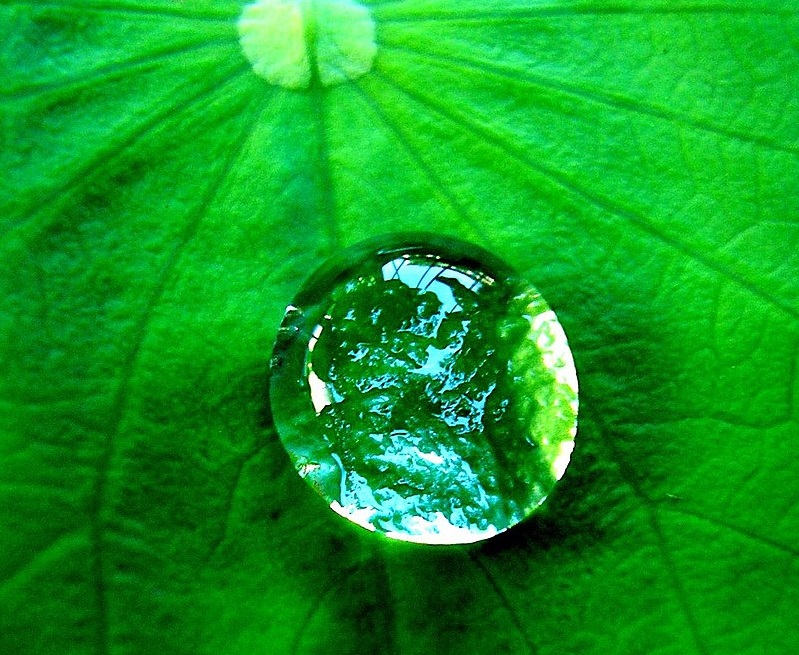

Non-polar substances show this kind of behaviour. In other words, hydrophobic substances like to interact with or dissolve in non-polar solvents like oil, hexane etc. Thus, hydrophobic substances are also known as lipophilic (fat-loving). When hydrophobic substances are in the water, they combine together and repel water molecules. Hydrophobic solvents are important to separate water-immiscible substances from water.
What is the Difference Between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic means water-loving while hydrophobic means fear of water or water-resistant. Therefore, hydrophilic substances interact with and dissolve in water, whereas hydrophobic substances do not show such behaviour. This is the key difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic. Moreover, hydrophilic substances are polar, and hydrophobic substances are non-polar.

Summary – Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic
The key difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic is that hydrophilic means water-loving while hydrophobic means water-resistant. Therefore, hydrophilic substances interact with and dissolve in water, whereas hydrophobic substances do not.
Image Courtesy:
1. “0302 Phospholipid Bilayer” By OpenStax – (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Water drop on a leaf” By Flickr user tanakawho – Flickr (CC BY 2.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2602J2pqKiYnrmqr4yapZ1lpqh6qcXDq6apoJ%2BXtqR7