Difference Between Hydrometallurgy and Pyrometallurgy
Table of Contents
The key difference between hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy is that in hydrometallurgy, we use an aqueous solution to extract metals from the ore, whereas in pyrometallurgy, we use high temperatures to extract metals from the ore.
Hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are two main branches in industrial chemistry. Both these processes are important in extracting metals from their naturally occurring metal ores. Therefore, these techniques are also called extractive metallurgical processes.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Hydrometallurgy
3. What is Pyrometallurgy
4. Side by Side Comparison – Hydrometallurgy vs Pyrometallurgy in Tabular Form
5. Summary
Hydrometallurgy is a branch in industrial chemistry where we use an aqueous solution to extract a metal from its ore, concentrates, recycled or residual material, etc. There are three general areas in hydrometallurgy: leaching, concentration and purification, and recovery of the metal.
The leaching process can be done in different ways such as in situ leaching, heap leaching, vat leaching, tank leaching, and autoclave leaching. These are the five basic types of leaching. The leaching process uses an aqueous solution to extract metal from the ore. The solution that is used specifically in hydrometallurgy is named as the lixiviant solution. It may have different pH values, oxidation-reduction potentials, chelating agent composition, temperature and other properties depending on the type of metal we are going to extract. These reaction conditions are changed according to the need of optimization of the rate of the reaction, extent and selectivity of the dissolution, etc.
Figure 01: Hydrometallurgy for Copper Extraction
The next step of hydrometallurgy is the solution concentration and purification. This step involves the concentration of the metal ion in the leached liquor and removal of undesirable metal ions. The major steps included in this stage are precipitation, cementation, solvent extraction, ion exchange, and electrowinning.
The stage of metal recovery is the final step of hydrometallurgy. The metal obtained from this step is suitable for direct sale. However, further refining is a must when we need ultra-high purity metal. The metal recovery can be done in two ways: electrolysis and precipitation.
Pyrometallurgy is the branch of science and technology concerned with the use of high temperatures to extract and purify metals. Therefore, it is a branch of extractive metallurgy. This process can produce pure metals that are suitable for direct selling and alloys suitable as feed for further processing. Pyrometallurgical processes can be categorized based on the technique as follows: calcining, roasting, smelting, and refining.
Calcining or calcination is the thermal decomposition of material. This process is carried out in chambers that can withstand high energy input. For example, furnaces such as shaft furnaces, rotary kilns, and fluidized bed reactors.
Roasting includes thermal gas-solid reactions. This process uses techniques such as oxidation, reduction, chlorination, and sulfonation. Moreover, this method is mainly suitable for metal sulfide ores. Here, the metal sulfide is heated in the presence of air to a high temperature; this temperature can cause oxygen in the air to react with the sulfide, forming sulfur dioxide, which leaves the metal oxide.
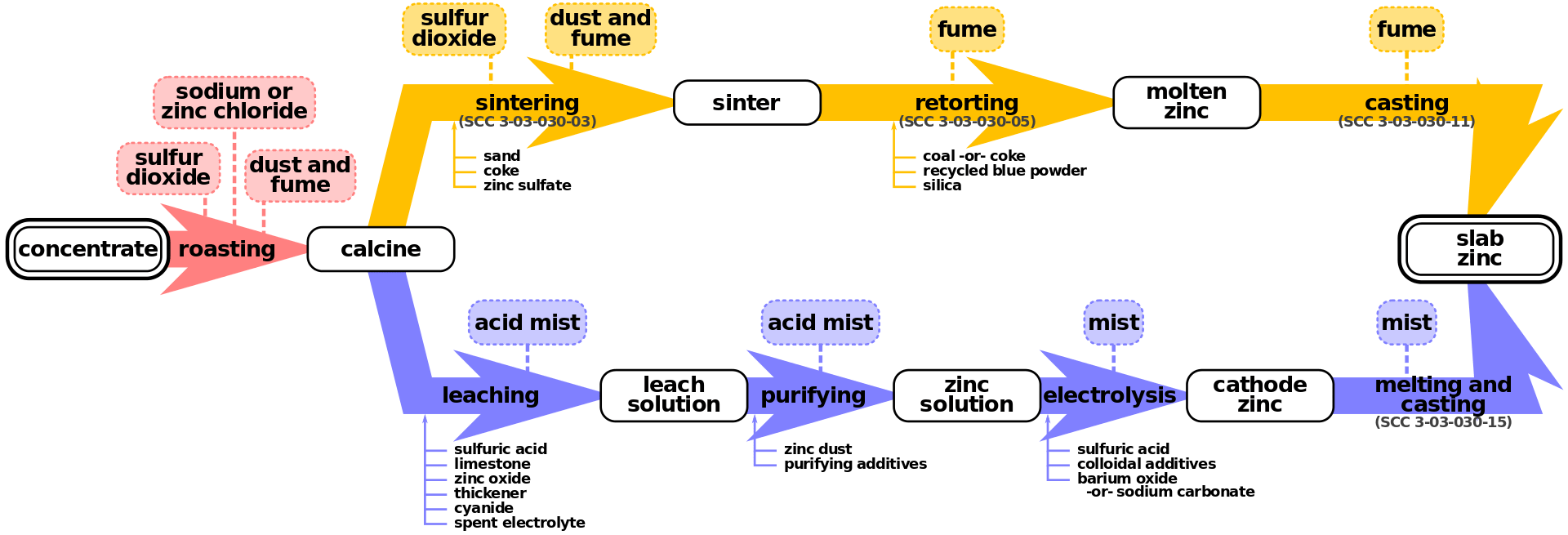
Figure 02: Zinc Smelting Process
Smelting is a thermal process in which at last one product is in the molten state. Then the metal oxides are smelted by heating along with coke (or charcoal), which allows releasing carbon dioxide. This leaves the refined mineral. Refining is the removal of impurities from the ore using thermal processes.
Hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are two main branches in industrial chemistry. The key difference between hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy is that in hydrometallurgy, we use an aqueous solution to extract metals from the ore, whereas in pyrometallurgy, we use high temperatures to extract metals from the ore.
Below infographic summarizes the difference between hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy.
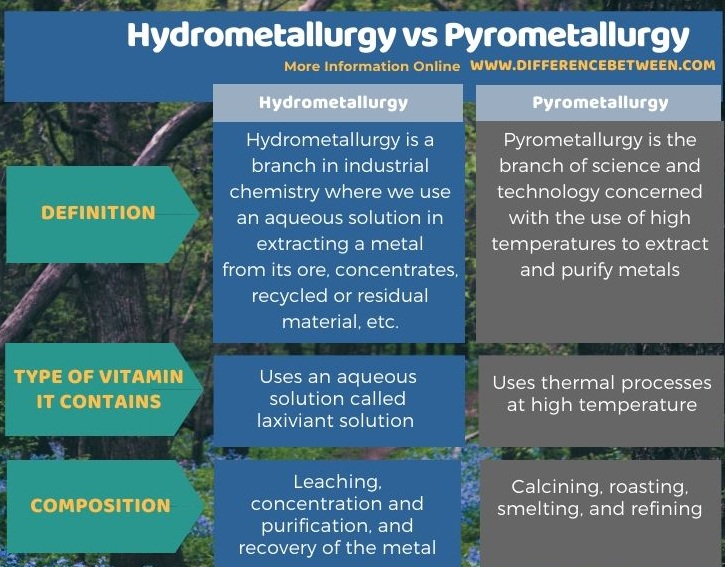
Summary – Hydrometallurgy vs Pyrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are two main branches in industrial chemistry. The key difference between hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy is that in hydrometallurgy, we use an aqueous solution to extract metals from the ore, whereas in pyrometallurgy, we use high temperatures to extract metals from the ore.
Reference:
1.“Hydrometallurgy.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 20 July 1998, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Image from page 443 of “The hydrometallurgy of copper” (1912) By Internet Archive Book Images (No known copyright restrictions) via Flickr
2. “Primary zinc smelting flowchart -vector” By raster: US Environmental Protection Agencyvector: Mliu92 – raster: US Environmental Protection Agency, figure 12.7-1vector: Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2602J2pqKWVqa6tuNSrnrJlkaOxbrzYq6amnaSWua3B0aCwaA%3D%3D