Difference Between Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids
Table of Contents
The key difference between glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids is that the glucogenic amino acids produce pyruvate or any other glucose precursors during their catabolism while ketogenic amino acids produce acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA during their catabolism.
Amino acids are the fundamental molecules, which make up the chemical structure of proteins and polypeptides. Though there are different classifications for amino acids, we can classify them as glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids depending on the intermediates that they form during their catabolism. As mentioned above, the end product of the catabolism of amino acids gives two types of intermediate products; either pyruvate (or to other glucose precursors) or acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Glucogenic Amino Acids
3. What are Ketogenic Amino Acids
4. Side by Side Comparison – Glucogenic vs Ketogenic Amino Acids in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What are Glucogenic Amino Acids?
Glucogenic amino acids are the class of amino acids that produce pyruvate or other glucose precursors during the catabolism of the amino acid. These molecules convert into glucose via gluconeogenesis. Also, the intermediate products of these amino acids may include pyruvate, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate or oxaloacetate.
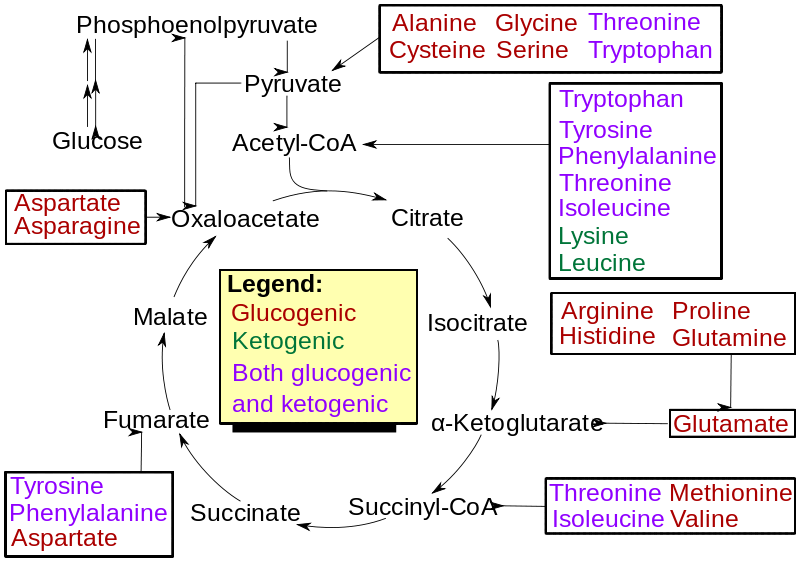
Figure 01: Different Amino Acids in the Amino Acid Catabolism Process
Moreover, almost all the essential and non-essential amino acids are glucogenic amino acids except for lysine and leucine.
Some common examples for these amino acids are as follows:
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartic
- Cysteine
- Glutamic
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Histidine
- Methionine
- Proline
- Serine
- Valine
What are Ketogenic Amino Acids?
Ketogenic amino acids are the class of amino acids that produce acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism of the amino acid. These are the intermediate products of their catabolism. Also, these products can further convert into ketone bodies. However, unlike the glucogenic amino acids, these amino acids cannot produce glucose. Because, the ketone body that they produce degrades into carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle ultimately.
Figure 02: Lysine
The most common ketogenic amino acids in our body are lysine and leucine, which are essential amino acids for us. Moreover, there are some amino acids that can act as both glucogenic or ketogenic forms.
The five major amino acids that can act in both these roles are as follows:
- Phenylalanine
- Isoleucine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
Also, these five amino acids can give rise to either glucose precursor (role of glucogenic amino acids) and to fatty acid precursors (role of ketogenic amino acids). Apart from that, our body uses the ketogenic amino acids for the production of lipids or for ketogenesis.
What is the Difference Between Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids?
Glucogenic amino acids are the class of amino acids that produce pyruvate or other glucose precursors during the catabolism of the amino acid whereas ketogenic amino acids are the class of amino acids that produce acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism of the amino acid. These two classes of amino acids are different from each other according to the intermediate products that they form during their catabolism. Hence the key difference between glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids is that glucogenic amino acids produce pyruvate or any other glucose precursors during their catabolism while ketogenic amino acids produce acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA during their catabolism.
Another difference between glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids is that the glucogenic amino acids involve in the production of glucose whereas the ketogenic amino acids cannot produce glucose.
The below infographic outlines the difference between glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids in tabular form.
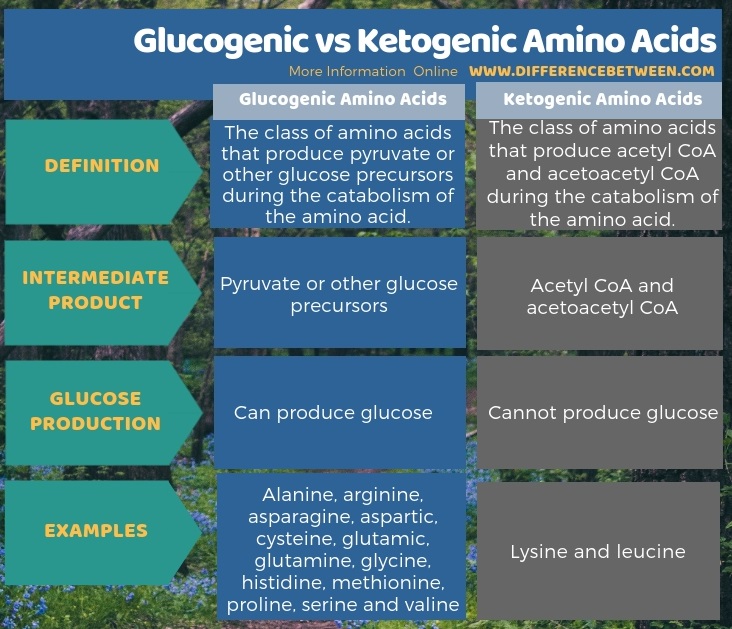
Summary – Glucogenic vs Ketogenic Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Furthermore, there are two types of amino acids depending on the intermediate products that they produce during their catabolism. They are glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids. The key difference between glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids is that the glucogenic amino acids produce pyruvate or any other glucose precursors during their catabolism while ketogenic amino acids produce acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA during their catabolism.
Reference:
1. “Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids.” Khan Academy, Khan Academy. Available here
2. “Ketogenic Amino Acid.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 24 Feb. 2018. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Amino acid catabolism revised”By Mikael Häggström (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”6062776253″ by Bioreg images (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26zy66aqJ%2BVo7akecCnm2ajlam8qLHNoppmmZ2eu7B5wJygnatf