Difference Between Fibrin and Slough
Table of Contents
The key difference between fibrin and slough is that fibrin is a tough protein that generates from fibrinogen and should be left in a wound for healing to take place, while slough is a dead necrotic tissue that needs to be removed from the wound for healing to take place.
Wound healing is the replacement of damaged or destroyed tissue by newly produced tissue. This process is usually divided into several stages, such as hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodelling. The wound healing process is a complex and fragile process. It is also susceptible to failure, which leads to the formation of non-healing chronic wounds. Therefore, wound assessment and management are very important. Fibrin and slough are two substances that can be observed in wounds during the healing process.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Fibrin
3. What is Slough
4. Similarities – Fibrin and Slough
5. Fibrin vs Slough in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Fibrin vs Slough
What is Fibrin?
Fibrin is a tough protein which generates from fibrinogen and should be left in the wound for healing to take place. It is a fibrous non-globular protein involved in the clotting process of blood. It forms due to the protease action of thrombin on fibrinogen. This causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin and platelets together form a hemostatic clot over the wound. It is yellow and gelatinous. Fibrin makes long strands of tough insoluble proteins that are bound to the platelets. The factor XIII generally competes with the cross linking of fibrin. Therefore, it hardens and contracts. The cross linked fibrin makes a mesh on the top of the platelet plug, which completes the clot.
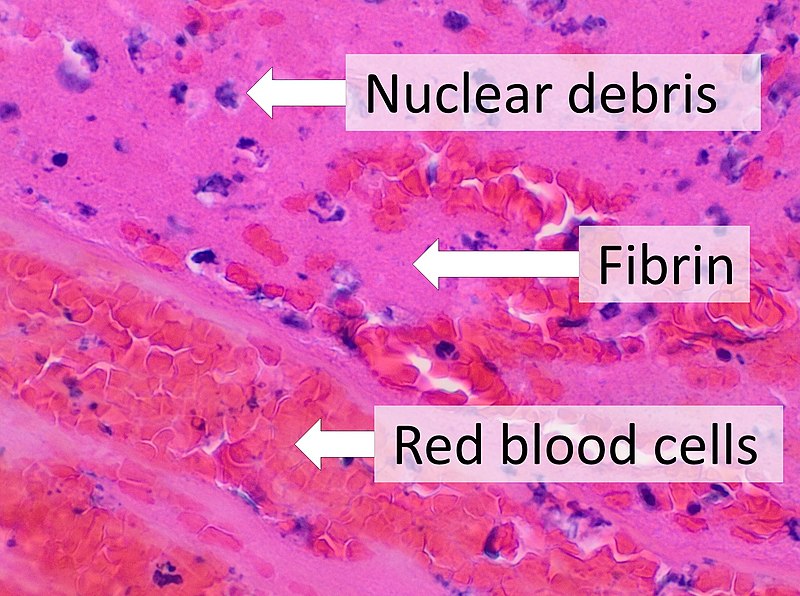
Figure 01: Fibrin in a Wound
Fibrin has different roles in diseases. The excessive generation of fibrin due to the activation of the coagulation cascade ultimately leads to thrombosis. Moreover, the ineffective generation of fibrin (premature lysis) increases the likelihood of a hemorrhage. On the other hand, the dysfunction of the liver can lead to a decrease in the production of fibrin precursor molecule fibrinogen. This causes dysfibrinogenaemia. Furthermore, reduced or dysfunctional fibrin is likely to make patients haemophiliacs. The fibrin coating is a normal consequence of the natural wound healing process, and attempting to remove it may damage healthy tissues. Therefore, it should be left in place in the wound.
What is Slough?
Slough is a dead necrotic tissue that needs to be removed from a wound for healing to take place. Slough refers to the yellow or white material in the wound bed. It is normally wet but can also be dry. Slough generally has a soft texture. It presents in the wound bed as a thin coating or patchy over the surface of the wound.
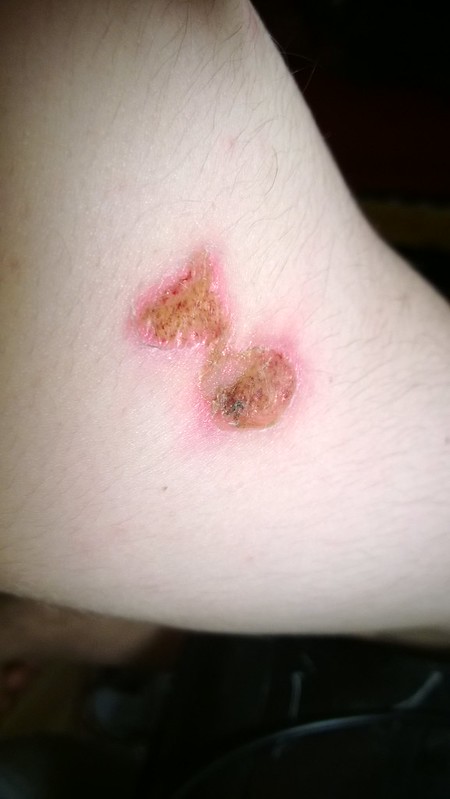
Figure 02: Slough
Slough consists of dead cells that accumulate in the wound exudates. During the inflammatory phase of healing, neutrophils gather to fight infection and clear away the debris. This devitalizes the tissue. They often die faster than they can be removed by the macrophages. Hence, this dead necrotic tissue accumulates in the wound as slough. Slough appears as a yellow or gray wet stringy substance on the wound. Moreover, it impairs the natural healing process. Therefore, it should be removed from the wound for healing to take place.
What are the Similarities Between Fibrin and Slough?
- Fibrin and slough are present in the wound bed.
- Both develop during the natural wound healing process.
- They can appear yellow.
- Both are present in acute and chronic wounds.
What is the Difference Between Fibrin and Slough?
Fibrin is a tough protein that originates from fibrinogen and should be left in the wound for healing to take place. On the other hand, slough is a dead necrotic tissue that needs to be removed from the wound for healing to take place. Thus, this is the key difference between fibrin and slough. Furthermore, fibrin forms in the blood clotting (hemostasis) stage of the wound healing process while slough forms in the inflammatory stage of the wound healing process.
The below infographic tabulates the differences between fibrin and slough for side by side comparison.
Summary – Fibrin vs Slough
Wound healing is a normal biological process in the human body. It is achieved through precisely programmed stages such as hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodelling. Fibrin and slough are two substances that can be observed in wounds in the healing process. Fibrin is a tough protein that should be left in a wound for healing to take place, while slough is a dead necrotic tissue that needs to be removed from a wound for healing to take place. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between fibrin and slough.
Reference:
1. Litvinov, Rustem I, and John W Weisel. “What Is the Biological and Clinical Relevance of Fibrin?” Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Composition of a fresh thrombus” By Mikael Häggström- Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Burning Blister Wound Scab Slough Crust Eschar Scurf” By I G (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26yyJupoqZdlruledKlpq6fmGQ%3D