Difference Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
Table of Contents
The key difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms is that the eukaryotic organisms have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles while the prokaryotic organisms lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
All living organisms belong to two categories namely prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Prokaryotic organisms exhibit a simple cell organization while eukaryotic organisms show a complex cell organization. Moreover, prokaryotes are unicellular, and they lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. On the other hand, eukaryotes are generally multicellular and contain a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as chloroplasts, mitochondria and Endoplasmic reticulum, etc. Prokaryotes include bacteria and Archaea while eukaryotes include protists, fungi, plants and animals. Other than those above-mentioned differences, there are more differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Therefore, understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms is very important. The aim of this article is to discuss the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Eukaryotic
3. What is Prokaryotic
4. Similarities Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
5. Side by Side Comparison – Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic organisms have organized cells with membrane-bound organelles with defined nuclei. All plants, animals, fungi, protozoa and algae are eukaryotic organisms. They have 80S large ribosomes in the cytoplasm that act as the sites for proteins synthesis. And also they have mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ER, and chloroplast, etc. Hence, the nuclear envelope is the most defining characteristic of all eukaryotic organisms. Nuclear membrane encloses the nucleus of eukaryotes. The genome of the eukaryotes is tightly bound with histone proteins and packaged into chromosomes which are highly organized complex structures.
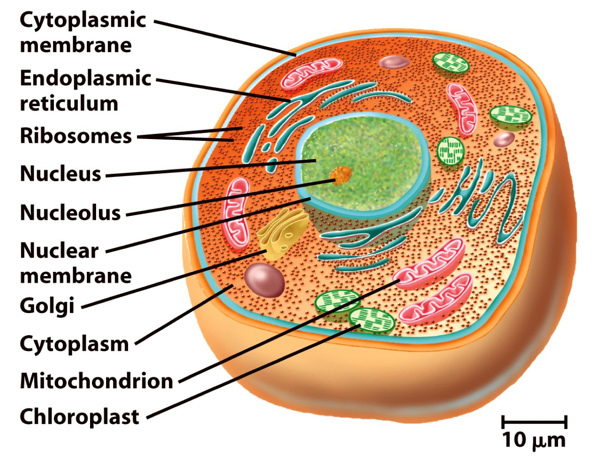
Figure 01: Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes include both simple and complex organisms. Their reproduction could be either sexual or asexual. The sexual reproduction is present only among the eukaryotes, and that involves the important step of meiosis in cell division. By that means the sexual reproduction has allowed the gene exchange to create new traits as adaptations for the changing world. However, the diversity of eukaryotic organisms is very low; e.g. in the human body, there are ten times more prokaryotes than body cells.
What is Prokaryotic?
“Pro” means before, and “karyone” means a case in Greek, giving rise to the term prokaryote. The best example to introduce the prokaryotes is the bacteria. Prokaryotic organisms are more often unicellular and very rarely multi-cellular. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. Also, they do not have organelles bound with membranes. However, they have 70S small ribosomes in the cytoplasm. They have a nucleoid with strands of irregular DNA complex in the cytoplasm. There is only one loop of chromosomal DNA in the nucleoid. However, they have a primitive cytoskeleton for the maintenance of the shape of the cell.
The surface-area-to-volume ratio is very high in prokaryotes that results in a high metabolic rate, which leads to an increased growth rate. Therefore, the generation time of prokaryotes is very short. They can form aggregate communities, called colonies that suggest social bonding among prokaryotic organisms. Biofilms are prime examples of their social living, and scientists believe that antibiotic resistance is higher in biofilms.
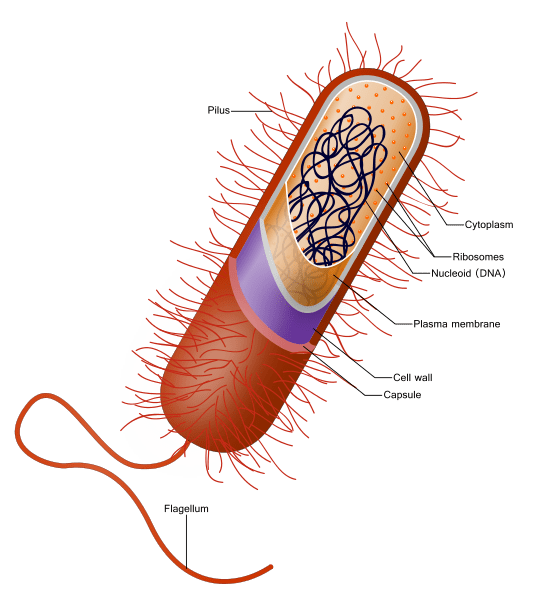
Figure 02: Prokaryotes
Moreover, prokaryotic shapes are mainly of four known as Coccus, Bacillus, Spirocheate, and Vibrio. They reproduce via asexual means such as binary fission and budding. However, gene exchange takes place through bacterial conjugation. People could never stop studying the prokaryotes, as it is almost impossible to measure the diversity at any scale.
What are the Similarities Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic?
- Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms are living organisms.
- They are composed of cells.
- Also, both reproduce, grow and die.
- Besides, both carry out many different metabolic processes.
What is the Difference Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles while prokaryotic cells do not contain both nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. We can consider this as the key difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. Furthermore, another difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms is that the eukaryotes can be either unicellular or multicellular while all prokaryotes are unicellular.
Moreover, eukaryotes contain 80S ribosomes while prokaryotes contain 70S ribosomes. Hence, it is another difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Also, a further difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms is that the eukaryotes contain many chromosomes while the prokaryotes have a single chromosome.
Below infographic on the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic shows more differences between both organisms.
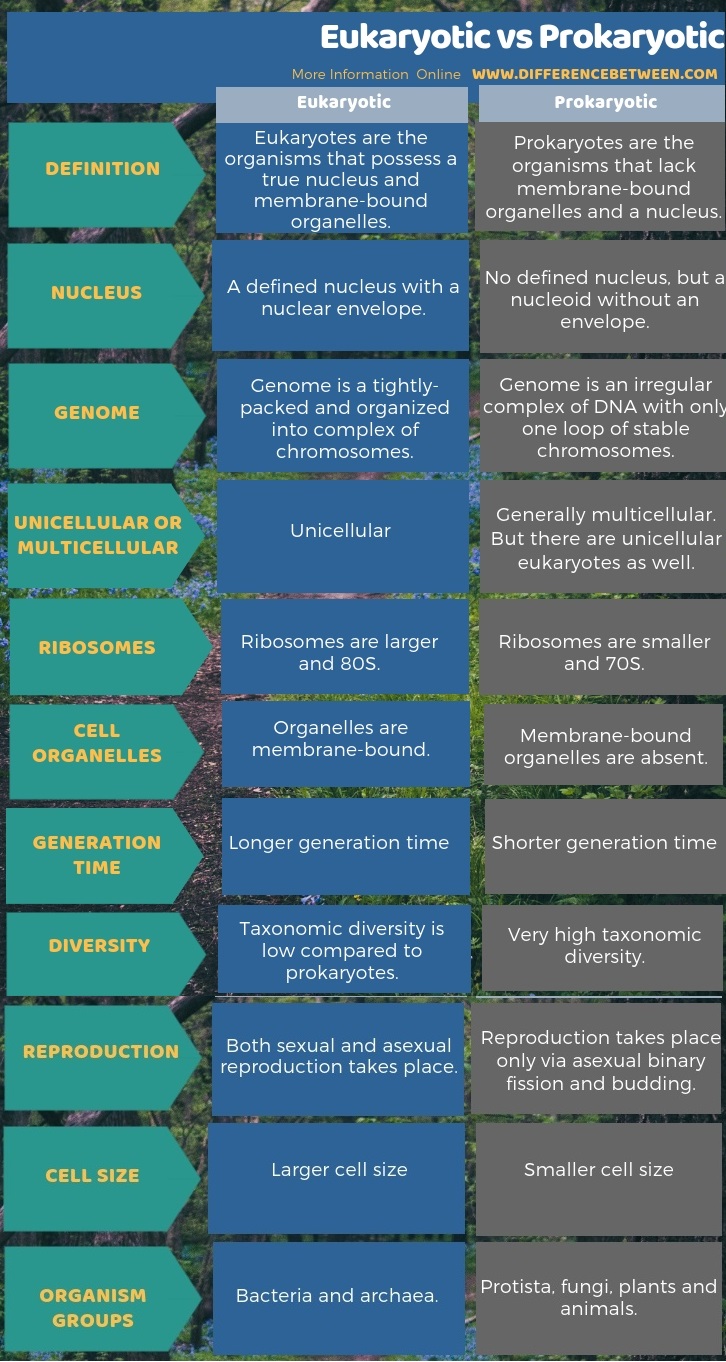
Summary – Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic
Living organisms can be either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are simple and tiny organisms while eukaryotes are large, complex organisms. The key difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms is the presence and absence of a nucleus in their cells. Eukaryotes have a true membrane-bound nucleus while prokaryotic lack a nucleus. Furthermore, eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles while prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles. Also, eukaryotes have 80S ribosomes while prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms.
Reference:
1. “Prokaryotic Cells.” Khan Academy, Khan Academy. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”11820433176″ by AJC1 (CC BY-SA 2.0) via Flickr
2.”Prokaryote cell” By Ali Zifan – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26x1KSYq7GfqbakecCnm2auo2K9s7vKmqmyp6SesHA%3D