Difference Between Credit Crunch and Recession
Table of Contents
Key Difference – Credit Crunch vs Recession
Credit crunch and recession are two major aspects of macroeconomics, meaning that they affect the economy as a whole – not specifically a group of individuals or businesses. Both result in negative consequences by slowing down investor and consumer confidence. The key difference between credit crunch and recession is that credit crunch is a situation where the burrowing ability weakens due to the lack of funds available in the financial market whereas recession is the reduction in the level of business activity in the economy. The relationship between the two is that a recession is often followed by a credit crunch.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Credit Crunch
3. What is Recession
4. Side by Side Comparison – Credit Crunch vs Recession
5. Summary
What is Credit Crunch?
A credit crunch is a situation where the borrowing ability weakens due to the lack of funds available in the financial market. This happens when lenders have limited funds available to lend or are unwilling to lend additional funds. Another reason that can cause the same is that the cost of borrowing may be too high, making it unaffordable to many borrowers. Following are the main causes of a credit crunch.
When financial institutions have suffered losses from previous loans, they are generally unwilling or unable to lend. In most cases, mortgages are kept as loan collaterals and in the case of defaults, banks attempt to sell the properties in order to recover the funds. If home prices fall, the bank is unable to cover the value of the loan, thus it incurs a loss.
- Minimum threshold for commercial banks
The commercial banks have a minimum reserve amount of funds they have to maintain and when the bank reaches this minimal threshold level, they borrow from the central bank. This is usually done in the form of short-term loans. Determining the bank rate is usually done quarterly to control the money supply in the economy.
A credit crunch can do severe damage to the economy by diminishing economic growth through decreased capital liquidity.
E.g. The most recent credit crunch started in 2007, also known as the ‘global financial crisis’, is considered to be the worst economic downturn in recent times. It began in the mortgage market in the USA and continued to affect a large number of developed as well as developing nations.
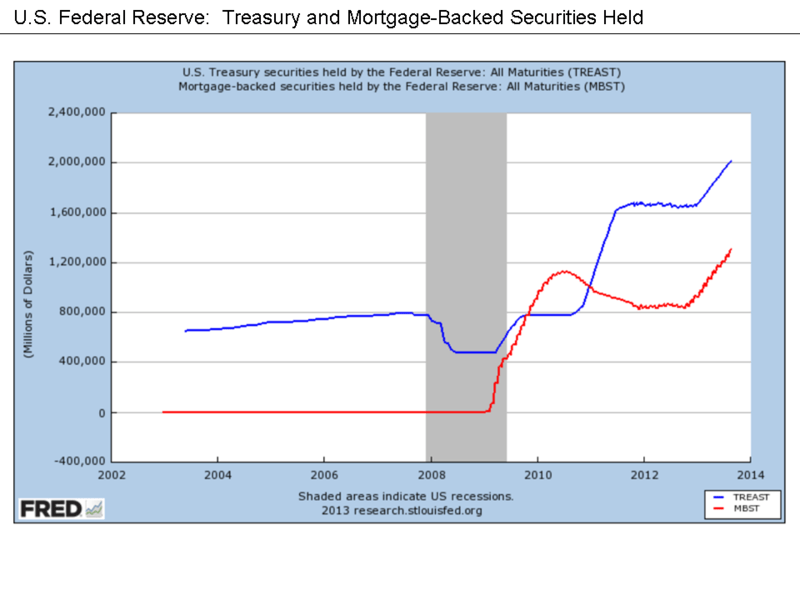
Figure 01: 2007 credit crunch started in the subprime mortgage market in the USA
What is Recession?
Recession is defined as the reduction in the level of business activity in the economy. If an economy experiences a negative economic growth rate as per country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for two consecutive quarters; then the economy is said to be a recession.
Causes for Recession
A recession is caused by the following factors.
Inflation
Inflation can be mentioned as the most significant contributor for recession as illustrated below.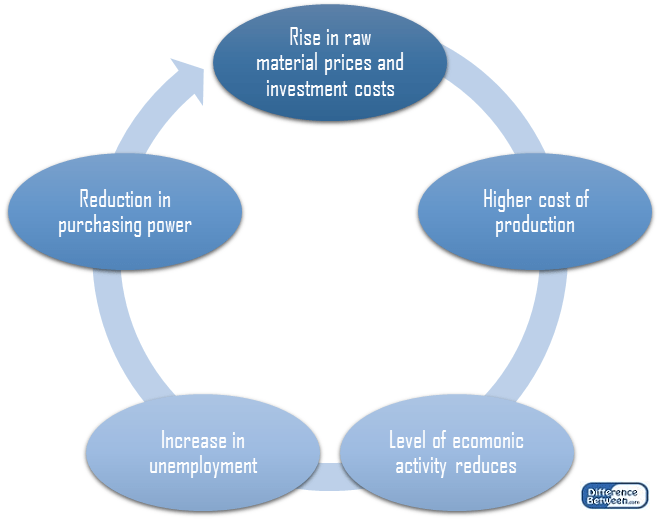
War, Natural Disasters and Similar Forms of Destruction
Resources of an economy are eradicated and wasted due to war and natural disasters and the GDP can be severely affected in case of significant scale of destruction.
Government Policies
Governments implement different policies such as wage and price controls in order to control the money supply in the economy. These may be regarded as unfavorable for investors and businesses, thus the economic activity will diminish.
Unemployment
Due to high inflation and increase in the cost of production, corporations have to lay off employees. This causes a reduction in the amount of goods and services produced.
Recession is a part of the business cycle, any economy cannot grow continuously without experiencing any negative effects at all. Therefore, recessions are somewhat inevitable. However, the negative effects of the recession can be controlled to reduce its destructive effects by controlling the causes of recession such as inflation and unemployment. The government has a significant role to play in such economic situations since recession affects the economy.
E.g. the major recession followed by the credit crunch in 2007 is named as the ‘great recession’ and many countries in the world were affected by the same in various degrees.
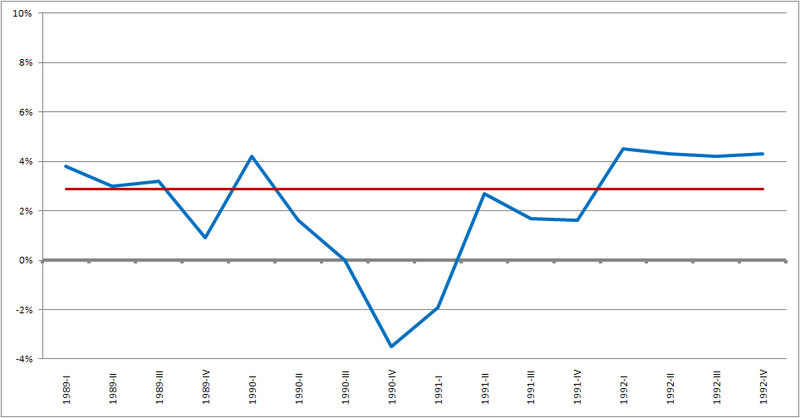
Figure 02: GDP growth in the United States between 1989 and 1992, showing the 1990-1991 recession
What is the difference between Credit Crunch and Recession?
Credit Crunch vs Recession | |
| Credit crunch is a situation where the borrowing ability weakens due to the lack of funds available in the financial market. | Recession is defined as the reduction in the level of business activity economy. |
| Cause | |
| Credit crunch often results in the reduction in the borrowing ability. | Recession can be caused by many factors, primary one been inflation. |
| Measure | |
| There are no distinct criteria to conclude whether an economy is experiencing a credit crunch, it is an outcome of many factors. | If an economy experiences a negative economic growth rate as per country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for two consecutive quarters; then the economy is said to be a recession. |
Summary – Credit Crunch vs Recession
The difference between credit crunch and recession mainly depends on the causes that result in the beginning of each. Credit crunch is a result of financial institutions reducing the lending limit of funds to individuals and firms while recession can result from diminishing economic activity caused by factors such as inflation and unemployment. Recessions caused by war and natural disasters are almost unavoidable and it may take many years to recover from such negative conditions. For example, the world’s most severe economic recession to date lasted from 1929 to 1939 which is named as the ‘great depression’.
Reference:
1.”Recession.” Investopedia. N.p., 25 Nov. 2003. Web. 27 Apr. 2017.
2. Pettinger, Tejvan. “Can Inflation Cause a Recession?” Economics Help. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Apr. 2017.
3.”Credit Crunch.” Investopedia. N.p., 19 Nov. 2003. Web. 27 Apr. 2017.
4. Amadeo, Kimberly. “What Happened During the Great Depression of 1929?” The Balance. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Apr. 2017.
Image Courtesy:
1. “U.S. Federal Reserve – Treasury and Mortgage-Backed Securities Held” By Farcaster at English Wikipedia (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “1990-91recessionb” By FrankieG123 – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26v0Z6boqxdmL%2B2usKhZJqmlGLDtHnRnpqeq6OevK97