Difference Between Complete and Partial Mole
Table of Contents
Key Difference – Complete vs Partial Mole
Molar pregnancy is a rare complication of pregnancy in which two types can be seen as complete and partial mole. In complete mole, the placental tissue develops abnormally with swollen fluid filled cysts, and no fetal tissue formation takes place. In partial mole, normal development of the placental tissue takes place but no fetal tissue development. This is the key difference between complete mole and partial mole.
Molar pregnancy is also referred to as a hydatidiform mole. It is defined as a rare complication that develops during pregnancy and where abnormal growth of trophoblasts takes place. Trophoblasts are cells that normally grow in the placenta. Molar pregnancy is of two components, partial mole and complete mole.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Complete Mole
3. What is Partial Mole
4. Similarities Between Complete and Partial Mole
5. Side by Side Comparison – Complete vs Partial Mole in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Complete Mole?
Complete mole is one types of molar pregnancy. During complete mole, the placenta develops in an abnormal way. It is also referred to as complete hydatidiform mole (CHM). It is considered as the most common type of trophoblasts disease. It becomes hostile to the growing fetus where the placenta develops cysts. These cysts eventually get filled with fluids and are swollen. Abnormal placental tissue development leads to the destruction of the placenta. Due to this, no fetal tissue development will take place. Even though the zygote is developed into later stages of fetal tissue development, the process will be stalled due to the abnormal placenta.
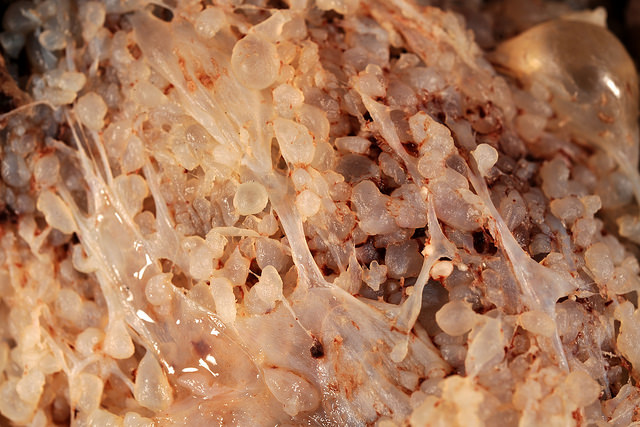
Figure 01: Complete Mole
During this disease condition, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) levels are elevated. CHM is normally diagnosed with the onset of completion of the first trimester and typically during the mid of second trimester.
What is Partial Mole?
Partial mole is defined as a type of abnormal pregnancy where normal placental development takes place, but no fetal tissue growth occurs. It is also referred to as partial hydatidiform mole (PHM). In other terms, it is defined as incomplete or non-development of the fertilized egg. Similar to complete hydatidiform mole, the partial version also develops cysts that are swollen due to the filling of fluids.
But these cysts are non-invasive and does not cause the destruction of the placenta. The placenta will grow normally unlike in complete hydatidiform mole. Partial molar pregnancy could also result in an incomplete embryo and a placenta where it may initiate development. But most of the time the fetus does not grow in partial mole.
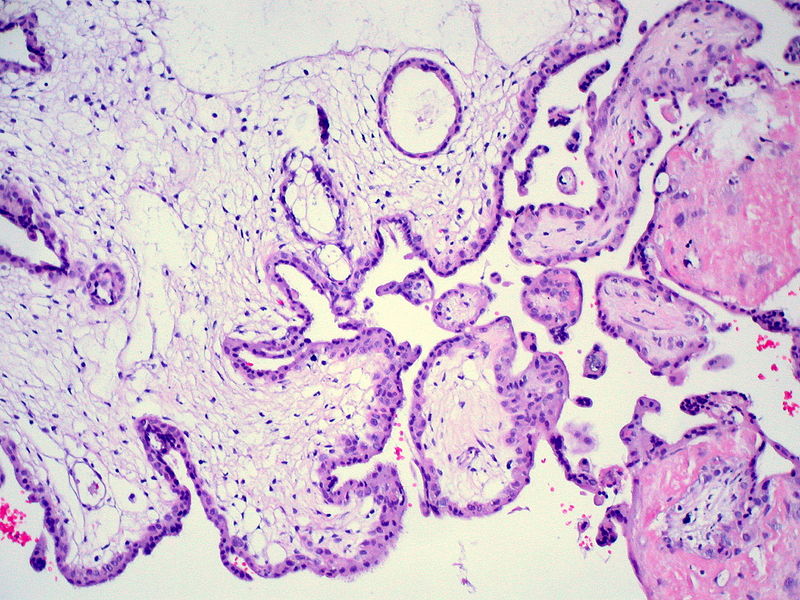
Figure 02: Partial Mole
A partial mole occurs due to a genetical disorder where the egg is fertilized with two sperms, and therefore it receives two sets of chromosomes from the father. Instead of normal 46 chromosomes (23 from mother and 23 from father), this fertilized egg contains 69 chromosomes (23 from mother and 46 from father). This is the reason behind the abnormal development of the fetus in partial mole.
What are the Similarities Between Complete and Partial mole?
- In both Complete and Partial mole, development of cysts occurs.
- The cysts fill with fluids in both complete and partial mole.
- During both conditions, the fetal tissue does not develop.
- Elevated HCG levels are present in both moles.
What is the Difference Between Complete and Partial Mole?
Complete vs Partial Mole | |
| Complete mole is a disease condition that relates with pregnancy where it stalls the developments of the placental and fetal tissue. | Partial mole is defined as a similar type of gestational disease where the placenta develops normally, but no development of fetal tissue takes place. |
| Development of the Placenta Tissue | |
| No placental tissue development in complete mole. | The placental tissue will be developed under normal conditions in partial mole. |
| Development of the Fetal Tissue | |
| No fetal tissue development takes place in complete mole. | Partial or no fetal tissue development takes place in partial mole. |
| HCG Levels | |
| Extremely high HCG levels occur during complete mole. | Comparatively low elevated levels of HCG occur in partial mole. |
| Development of Cysts | |
| Invasive fluid filled cysts are developed that disrupt the placenta in complete mole. | Similar types of cysts may develop but are non-invasive and do not harm the placenta in partial mole. |
| Diagnosis | |
| Complete mole can be diagnosed after the first trimester. | Partial mole can be diagnosed during the first trimester. |
Summary – Complete vs Partial Mole
Molar pregnancy is a common gestational disease condition. It is of two types: complete hydatidiform mole and partial hydatidiform mole. During complete mole, the development of both placenta and fetus do not take place. But during partial mole, the placenta develops but no fetal development takes place. During both conditions, HCG levels get elevated. This is the difference between complete and partial mole.
Reference :
1.“Partial Molar Pregnancy.” Cleveland Clinic. Available here
2.“Molar Pregnancy.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 14 Dec. 2017. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’Complete Hydatidiform Mole’ by Ed Uthman (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
2.’Partial Hydatidiform Mole 2 (571278649)’By Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA (CC BY 2.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vzqanpZ2kmnqiusNmraxloJa%2FtbXApWSmp5yafA%3D%3D