Difference Between Cloud Point and Pour Point
Table of Contents
The key difference between cloud point and pour point is that the cloud point refers to the temperature at which there is a presence of a wax cloud in the fuel whereas the pour point is the lowest temperature below which the fuel loses its flow characteristics.
Cloud point and pour point are important physical properties of any liquid fuel. Cloud point, as the name suggests is the temperature at which a cloud of wax crystals first appear in a liquid fuel when we cool it under special testing conditions. The cloud point of any petroleum product is an indicator of how well the fuel will perform under cold weather conditions. Pour point is just the opposite of cloud point as it refers to the lowest temperature at which we can observe the movement of oil and also we can pump the fuel easily. As such, there is only a slight difference in these two temperatures on the temperature scale, but the difference between cloud point and pour point is significant in the use of any fuel.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Cloud Point
3. What is Pour Point
4. Side by Side Comparison – Cloud Point vs Pour Point in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Cloud Point?
In the industry, cloud point is the temperature below which wax in fuel tends to form a cloudy appearance. Which means, it is the temperature at which a fuel forms a wax cloud. This is a condition which is detrimental for any engine as solidified wax makes the fuel thick and it clogs the fuel filters and injectors. This wax also gets applied on the pipeline and has a tendency to form an emulsion with water. This is a property that holds great significance in cold weathers. Usually, we name this parameter as Wax Appearance Temperature (WAT) when we refer to crude oil or heavy oil.

Figure 01: Appearance of Cloudiness in Olive Oil
For instance, olive oil stored in cold weather begins to solidify at around 4 °C. However, the temperature at winter in temperate countries is often below 0 °C. There, the olive oil begins to form a waxy or cloudy appearance in white colour, which sinks to the bottom of the oil container. There are two major methods that we can use to measure the cloud point of a fuel; manual method and automatic method.
What is Pour Point?
On the other hand, pour point is the lowest temperature at which the fuel continues to flow or the lowest temperature below which the fuel loses its flow characteristics. Pour point of a fuel is an indication of the temperature at which we can easily pump the fuel. Hence, alternatively we can describe the pour point as the lowest temperature at which a fuel performs satisfactorily, and beyond this temperature, the fuel stops flowing and starts to freeze.

Figure 02: The Pour Point is important regarding Lubricants
Typically, in crude oil, a high pour point can be observed with a high paraffin content. Mainly, this associates with the crude oil that we derive from plant materials. To measure this temperature, we can use two methods, same as in cloud point measuring; manual and automated methods.
What is the Difference Between Cloud Point and Pour Point?
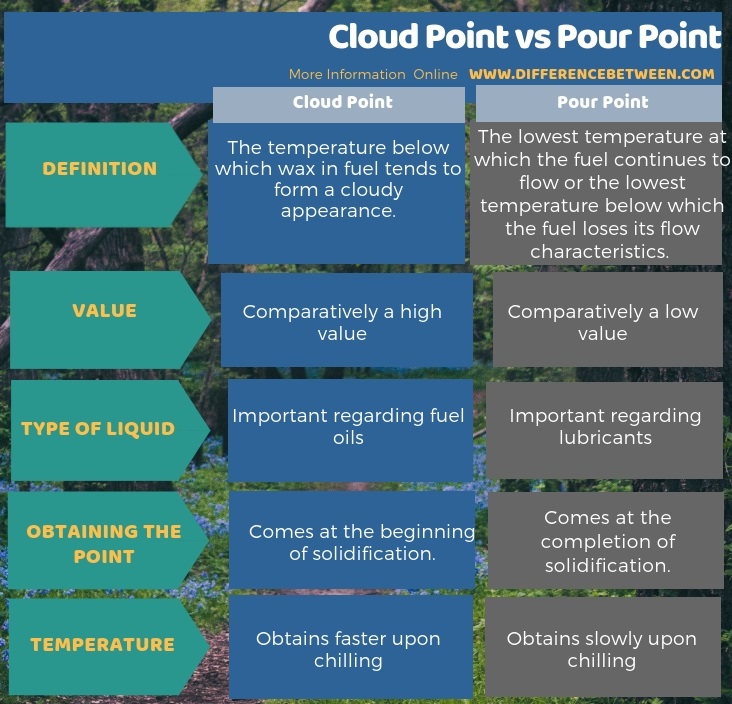
Cloud point and pour point is that cloud point refers to the temperature at which there is a presence of a wax cloud in the fuel whereas pour point is the lowest temperature below which the fuel loses its flow characteristics. Therefore, this is the key difference between cloud point and pour point. Comparatively, cloud point is of a high value (high temperature) but, pour point is of a low value (a low temperature). Therefore, upon chilling, cloud point comes faster and pour point comes later. Hence, this is also difference between cloud point and pour point.
Furthermore, the cloud point is important regarding fuel oils whereas the pour point is important regarding lubricants. The below infographic provides further information on the difference between cloud point and pour point.
Summary – Cloud Point vs Pour Point
Pour point and cloud point are two important physical properties of any fuel or lubricant. The key difference between cloud point and pour point is that the cloud point refers to the temperature at which there is a presence of a wax cloud in the fuel whereas the pour point is the lowest temperature below which the fuel loses its flow characteristics. In cold weather conditions, people add some certain additives to the fuel to keep its pour point and cloud point higher.
Reference:
1. “Cloud Point.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 5 Oct. 2017. Available here
2. “Pour Point.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 22 Dec. 2017. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Olive oil from Oneglia”By Lemone – Own work, (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”P-80 Temporary Rubber Assembly Lubricants”By Ipcol – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vy6isnWWgpLavwIyapZ1lpqh6sbvUq2Spp5mjwXA%3D