Difference Between Bacteriocin and Antibiotic
Table of Contents
The key difference between bacteriocin and antibiotic is that bacteriocin is a proteinaceous toxin produced by bacteria against a closely related bacterial strain while the antibiotic is an antibacterial substance and a secondary metabolite that kills or inhibits the growth of bacteria.
Antimicrobial substances have the ability to kill pathogenic microorganisms or retard their growth and reproduction. Antimicrobials can be antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral. Antibacterial substances or antibiotics work against bacteria while antifungal substances work against pathogenic fungi. Antiviral drugs kill viruses. Therefore, antibiotics are a type of most effective antibacterial substances that can be used to combat bacterial infections. Bacteriocin is a proteinaceous toxin produced by bacteria. It works against closely related bacterial strains. Thus, both antibiotic and bacteriocin possess antibacterial activity.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Bacteriocin
3. What is Antibiotic
4. Similarities Between Bacteriocin and Antibiotic
5. Side by Side Comparison – Bacteriocin vs Antibiotic in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Bacteriocin?
Bacteriocin is a proteinaceous toxin produced by bacteria to inhibit another closely related bacterium. In fact, they are antibacterial peptides produced by the translation process occurring in ribosomes. Hence, they are ribosomally originated substances. Since bacteriocins can pose antimicrobial activity only against closely related bacterial strains, their antibacterial activity is a narrow spectrum.
Figure 01: Bacteriocin
Furthermore, bacteriocins are high molecular weight peptides. Lactic acid bacteria produce a range of bacteriocins. Moreover, bacteriocin producing bacteria are insusceptible for bactericidal agents, unlike antibiotic-producing bacteria. Bacteriocins can be used as narrow-spectrum antibiotics to treat bacterial diseases.
What is an Antibiotic?
An antibiotic is an antibacterial substance that either kills or inhibits the growth of bacteria. Therefore, an antibiotic works against bacteria. Bactericidal antibiotics kill bacteria, while bacteriostatic antibiotics inhibit the growth of bacteria. They cannot kill viruses. Antibiotics are popular drugs used today in treating many types of bacterial diseases. Alexander Fleming discovered the first natural antibiotic ‘penicillin’ in 1928 through his experiments. Ampicillin, amoxicillin, and penicillin G are several penicillin-based antibiotics. Soil bacteria and fungi produce antibiotics naturally. These antibiotics are able to differentiate host cells and bacterial cells. Hence, they specifically act only against bacterial cells.

Figure 02: Antibiotics
Mechanism of action differs among the different types of antibiotics. Some antibiotics such as polymixins and polyenes, etc. target the cell membrane of bacteria and disrupt the cell membrane or phospholipid bilayer. Similarly, some antibiotics such as penicillin, cephalosporin, etc., target the peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall and inhibit cell wall synthesis. Furthermore, antibiotics such as rifamycin and quinolones inhibit DNA synthesis or RNA synthesis and prevent the multiplication of bacteria. Other groups of antibiotics, including erythromycin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, gentamycin, etc., inhibit protein synthesis by targeting ribosomes.
What are the Similarities Between Bacteriocin and Antibiotic?
- Bacteriocin and antibiotic are antibacterial substances.
- Bacteria produce bacteriocins and antibiotics.
- Since they have antimicrobial activity, they can be used as drugs to treat bacterial diseases.
What is the Difference Between Bacteriocin and Antibiotic?
Bacteriocin and antibiotic are antibacterial substances. Bacteriocins are proteinaceous antibacterial substances that work against closely related bacterial strains. In contrast, antibiotics are antibacterial substances that kill and inhibit the growth of many types of bacteria. So, this is the key difference between bacteriocin and antibiotic. Furthermore, bacteriocins are narrow-spectrum antibacterial agents, while antibiotics are broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. Thus, this is also a difference between bacteriocin and antibiotic.
The below infographic summarizes the difference between bacteriocin and antibiotic.
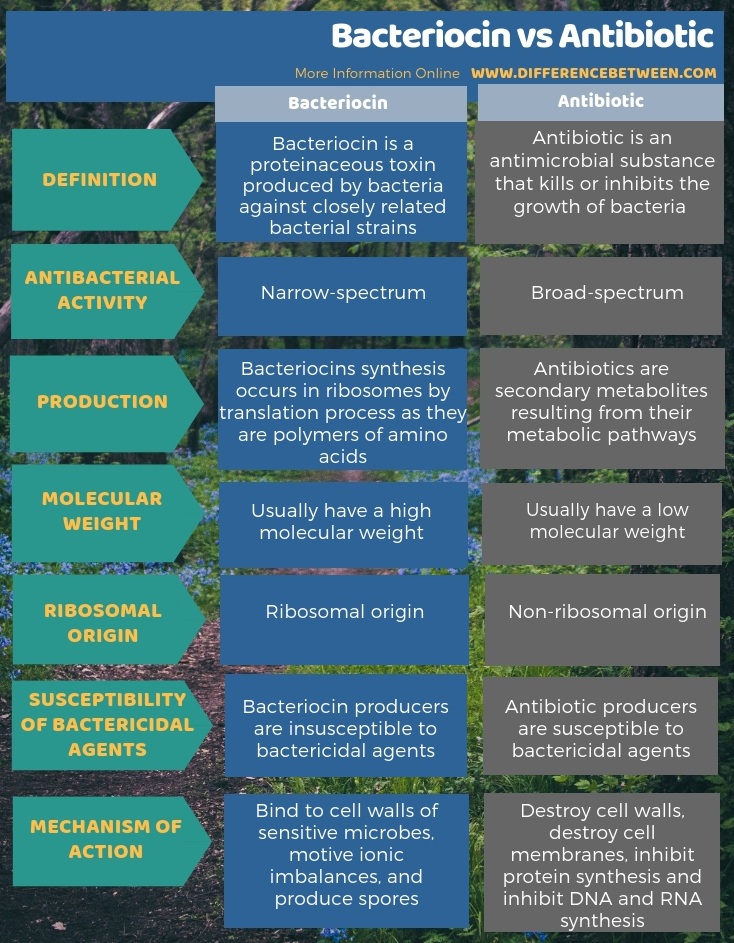
Summary – Bacteriocin vs Antibiotic
Bacteriocins are proteinaceous toxins produced by bacteria against closely related bacterial strains while antibiotics are antibacterial agents that destroy or slow down the growth of bacteria. Therefore, both bacteriocins and antibiotics have antibacterial activity. But, bacteriocins have a narrow spectrum antibacterial activity while antibiotics have a broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Furthermore, bacteriocins are high molecular weight peptides produced by the translation process, while antibiotics are low molecular weight secondary metabolites. So, this is the summary of the difference between bacteriocin and antibiotic.
Reference:
1. Cleveland, J, et al. “Bacteriocins: Safe, Natural Antimicrobials for Food Preservation.” International Journal of Food Microbiology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 4 Dec. 2001, Available here.
2. “Antibiotics.” MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 18 Apr. 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “PDB 1o82 EBI” By Jawahar Swaminathan and MSD staff at the European Bioinformatics Institute – (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Antibiotics” By Sheep purple (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26uwJyrnqqZpLCquoyapZ1lkaPBqq7IqKuim18%3D