Difference Between Alpha Beta and Gamma Proteobacteria
Table of Contents
The key difference between alpha beta and gamma proteobacteria is that alpha proteobacteria and beta proteobacteria are monophyletic while gamma proteobacteria are paraphyletic.
Proteobacteria belong to a phylum of gram-negative bacteria with an outer membrane composed of lipopolysaccharides. This division of proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogens, such as Escherichia, Salmonella, Vibrio, Helicobacter and many other notable genera. There are six classes of proteobacteria based on the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences. Alpha, beta, and gamma are three such classes of proteobacteria. The classes of alpha, beta, delta and epsilon classes are always monophyletic while the class of gamma proteobacteria is paraphyletic due to the Acidithiobacillus genus. Multigenome alignment studies have revealed the above observations.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Alpha Proteobacteria
3. What are Beta Proteobacteria
4. What are Gamma Proteobacteria
5. Similarities Between Alpha Beta and Gamma Proteobacteria
6. Side by Side Comparison – Alpha Beta vs Gamma Proteobacteria in Tabular Form
7. Summary
What are Alpha Proteobacteria?
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of proteobacteria that are always monophyletic. They are oligotrophic organisms living in low nutrient environments such as deep oceanic sediments, glacial ice, and deep undersurface soil. In this class, there are two taxa as chlamydias and rickettsias. These taxa are obligate intracellular organisms. They cannot produce ATP on their own. Therefore, often rely on host cells for energy needs.
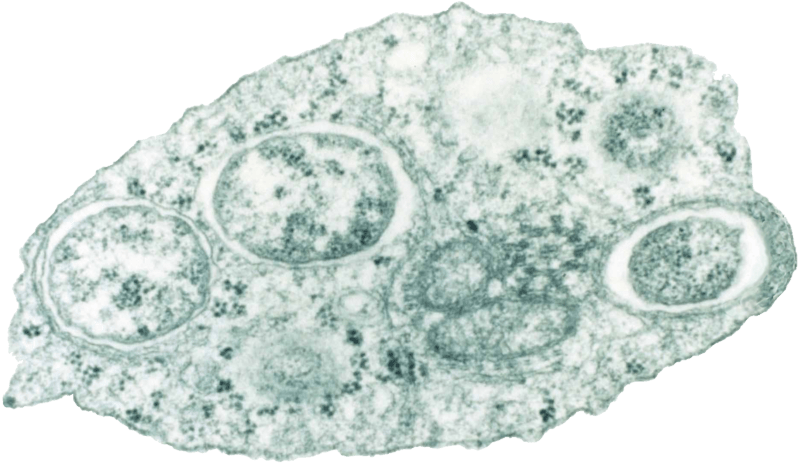
Figure 01: Alpha Proteobacteria
There are several Rickettsia spp, which are human pathogens. R. rickettsii causes rocky mountain spotted fever (meningoencephalitis) while R. prowazekii causes epidemic typhus. In contrast, Chlamydia (C. trachomatis) causes eye disease like trachoma, often leading to blindness.
What are Beta Proteobacteria?
Beta proteobacteria are another class of proteobacteria that are eutrophic, meaning that they require a copious amount of organic nutrients. They frequently grow between aerobic and anaerobic areas such as mammalian intestines. Some genera of beta proteobacteria are human pathogens. For example, the genus; Neisseria are lethal bacteria.
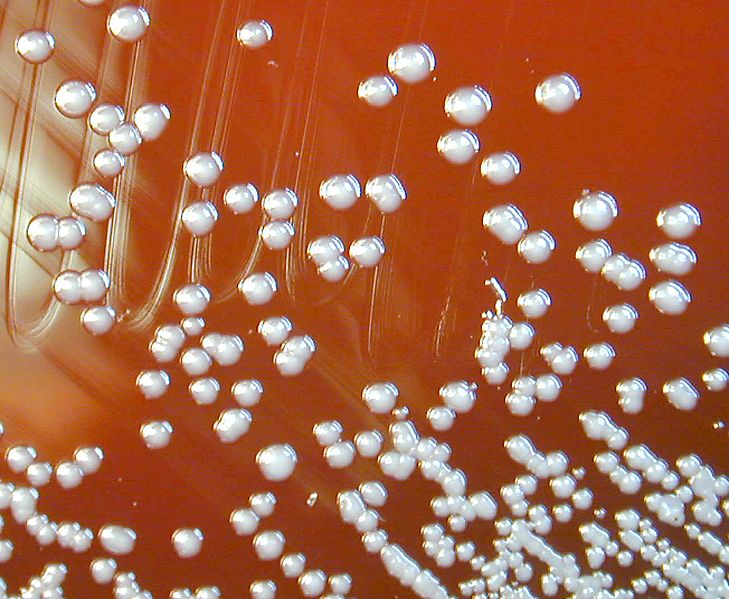

Figure 01: Beta Proteobacteria
The species N. gonorrhoeae causes sexually transmitted infections called gonorrhoea. N. Meningitides causes bacterial meningitis. Neisseria are cocci that live on the mucosal surface of the human body. The pathogen Bordetella pertussis, which causes pertussis (whooping cough) is also a member of beta proteobacteria. It is from the order of Burkholderiales.
What is Gamma Proteobacteria?
Gammaproteobacteria are the most diverse class of proteobacteria. They are paraphyletic. This class includes a number of human pathogens. For example, a large number of the family Pseudomonaceae, which includes the genus Pseudomonas come under this class. P. aeruginosa is a species within the above genus. They are gram-negative, strictly aerobic, nonfermenting, highly motile human pathogens. P. Aeruginosa causes urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, dermatitis, soft tissue infections, bacteraemia, bone and joint infections, gastrointestinal tart infections, and a variety of systematic infections.
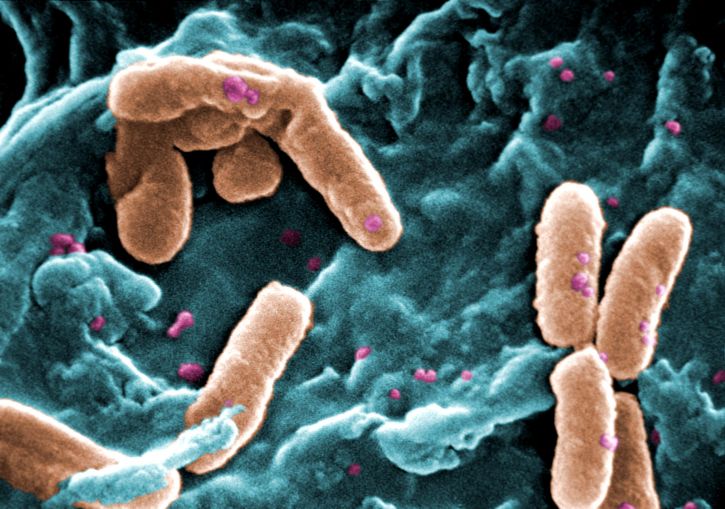
Figure 03: Gamma Proteobacteria
Pasteurella haemolytica, which causes severe pneumonia in sheep and goats, also belongs to gamma proteobacteria. Moreover, the genus Haemophilus which contains two human pathogens, H. influenzae and H. ducreyi, also come under this class. Another popular example for gamma proteobacteria is order Vibrionales, which includes the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Vibrio cholera is the causative agent of cholera. This is due to a toxin produced by Vibrio choleraet that causes hypersecretion of electrolytes and water in the large intestine. It ultimately leads to profuse watery diarrhoea and dehydration.
What are the Similarities Between Alpha Beta and Gamma Proteobacteria?
- They are gram-negative proteobacteria.
- All these classes contain human pathogens.
- They all contain an outer membrane mainly composed of lipopolysaccharides.
What is the Difference Between Alpha Beta and Gamma Proteobacteria?
Alpha proteobacteria and beta proteobacteria are monophyletic, while gamma proteobacteria are paraphyletic. So, this is the key difference between alpha beta and gamma proteobacteria. Moreover, alpha beta proteobacteria classes contain all descendants of the common ancestor as they are monophyletic. However, since gamma proteobacteria are paraphyletic, they do not include all the descendants of their common ancestor. Thus, this is another important difference between alpha beta and gamma proteobacteria.
Below is a summary of the differences between alpha beta and gamma proteobacteria in tabular form.
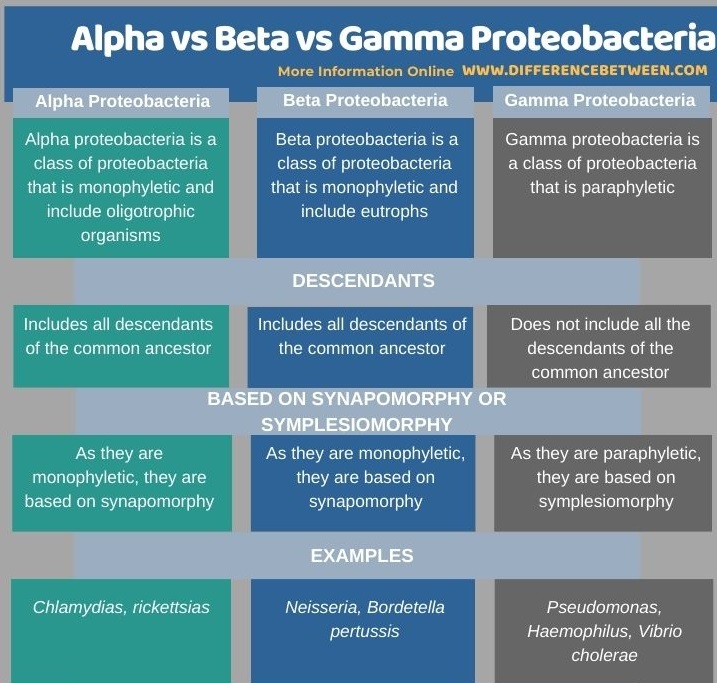
Summary – Alpha Beta vs Gamma Proteobacteria
Proteobacteria are divided into different classes, which are referred to by the Greek letters from alpha to epsilon. The alpha, beta, delta, epsilon sections are monophyletic, but gamma proteobacteria are paraphyletic due to the Acidithiobacillus genus. This has been confirmed by multigenome alignment studies. Thus, this is the key difference between alpha beta and gamma proteobacteria.
Reference:
1. “Microbiology.” Lumen, Available here.
2. “8.7A: Overview of Proteobacteria.” Biology LibreTexts, Libretexts, 3 Jan. 2021, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Wolbachia” By Scott O'Neill – Genome Sequence of the Intracellular Bacterium Wolbachia. PLoS Biol 2/3/2004: e76. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020076 (CC BY 2.5) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Burkholderia pseudomallei 01” (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
3. “Scanning, electron micrograph, pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacteria” (CC0) via Pixino
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26ty6mfmmWSmsGiecCnm2afkaK6onnPq6atnZ%2BXrqTAxKugmmc%3D