Difference Between Additive and Non Additive Gene Action
Table of Contents
Key Difference – Additive vs Non Additive Gene Action
The interactions of the alleles at different gene loci can give rise to different gene actions or phenotypes. Quantitative genetic methods allow these gene actions to be measured in different selected populations. Thus, gene action can be categorized into three main types namely, Additive Gene Action, Dominance Gene action or Non Additive gene action and Epistasis. Additive Gene Action is referred to as the phenomenon in which the two alleles contribute equally to the production of the phenotype. Non additive or dominance gene action refers to the phenomenon in which one allele is expressed stronger than the other allele. The key difference between the additive and the non additive gene action is based upon its allelic expressions. In additive gene action, both alleles are expressed whereas in non-additive gene action one allele is expressed stronger than the other allele.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Additive Gene Action
3. What is Non Additive Gene Action
4. Similarities Between Additive and Non Additive Gene Action
5. Side by Side Comparison – Additive vs Non Additive Gene Action in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Additive Gene Action?
Additive gene action refers to the occurrence where both the alleles in the gene are expressed equally and do not show dominance over each other. Each allele has an equal opportunity to be expressed to give rise to the phenotype. The resultant phenotype is a combination of the two homozygous (homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive) types. Therefore, additive gene action is shown under heterozygous conditions.
The gene action is also said to be additive if they show the following characteristics;
- When substitution of one allele for another produces same plus or minus effect regardless of another gene (s).
- When the effect is the same replacement occurs in a homozygote or heterozygote condition.
The following example shows the additive gene action model;
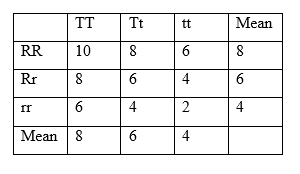
Figure 01: Additive Gene Action Model
In this model, any allelic combination would give the same mean if substituted with each other. According to this, Tt = [TT + tt] / 2 = 8. This shows that there is no dominance shown by either allele. It is similar to the R gene as well.
What is Non Additive Gene Action?
Non additive gene action is also referred to as the Dominance gene action as it deals with the characteristic of dominance. In non – additive gene action, one allele of the gene is expressed stronger than the other allele. Therefore, if the genotype is substituted the action or the phenotype of the gene will vary. Therefore, this quantitative genetic model is also known as the dominance gene action.
The dominance can be further categorized as complete and incomplete dominance depending on the means obtained. If it’s a heterozygous condition, it can lead to incomplete dominance whereas in the homozygous condition it results in complete dominance.
Non additive gene action model is illustrated in the following example.
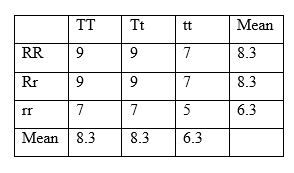
Figure 02: Non Additive Gene Action Model
This model shows that the combination TT is equal to RR and same as with the heterozygous condition that is tt and rr respectively. Therefore, there is complete dominance, and there is no interaction between the T and R genes.
Therefore, in non additive gene action, one allele masks the expression of the allele. This is also expressed in Mendelian genetics where the heterozygote showed the dominant form during its phenotypic expression when homozygous parents cross with each other.
What are the Similarities Between Additive and Non Additive Gene Action?
- Both types result in the quantitative measurement of gene action.
- Both are involved in predicting the allelic expression under homozygous or heterozygous conditions.
What is the Difference Between Additive and Non Additive Gene Action?
Additive vs Non Additive Gene | |
| Additive Gene Action is referred to as the phenomenon in which the two alleles of the gene contribute equally to the production of the phenotype. | Non additive or dominance gene action refers to the phenomenon in which one allele is expressed stronger than the other allele. |
| Dominance | |
| Does not show any dominance, both alleles are expressed equally in additive gene action. | May show complete dominance or incomplete dominance in non additive gene action. |
Summary – Additive vs Non Additive Gene Action
Additive and non additive gene actions belong to the category of quantitative genetics where the allelic expressions are analyzed. In additive gene action, each allele of the gene contributes equally towards its expression, whereas in non – additive gene action, one allele is expressed stronger in comparison with the other leading to a dominance situation. These allelic expressions are measured, and the frequencies are obtained to characterize the genetics of an individual or a plant. This data is mostly used in plant breeding techniques to choose the most potent genetic varieties of crops. This is the difference between additive and non additive gene action.
Download the PDF of Additive vs Non Additive Gene Action
You can download the PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation note. Please download the PDF version here: Difference Between Additive and Non – Additive Gene Action
Reference:
1.“3 Main Types of Gene Action | Vegetable Breeding.” Biology Discussion, 12 Dec. 2016. Available here
2.Study.com, Study.com. Available here
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26tw52graGmmnqiusNmraxlnqS7bq3DnaCtoaaaeqixzZ5kmpuknryvew%3D%3D