Difference Between Acetonitrile and Acetone
Table of Contents
The key difference between acetonitrile and acetone is that acetonitrile is a nitrile compound, whereas acetone is a ketone.
Both acetonitrile and acetone are organic compounds. That means; both these compounds have carbon and hydrogen atoms with C-H bonds and C-C bonds. These compounds fall into two categories depending on the chemical structure; they have different functional groups.
CONTENT
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Acetonitrile
3. What is Acetone
4. Side by Side Comparison – Acetonitrile vs Acetone in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Acetonitrile?
Acetonitrile is an organic compound having the chemical formula CH3CN. It occurs as a colorless liquid, and it has a faint, distinct odor. It is the simplest organic nitrile compound. The compound is mainly formed as a byproduct during the production of acrylonitrile.
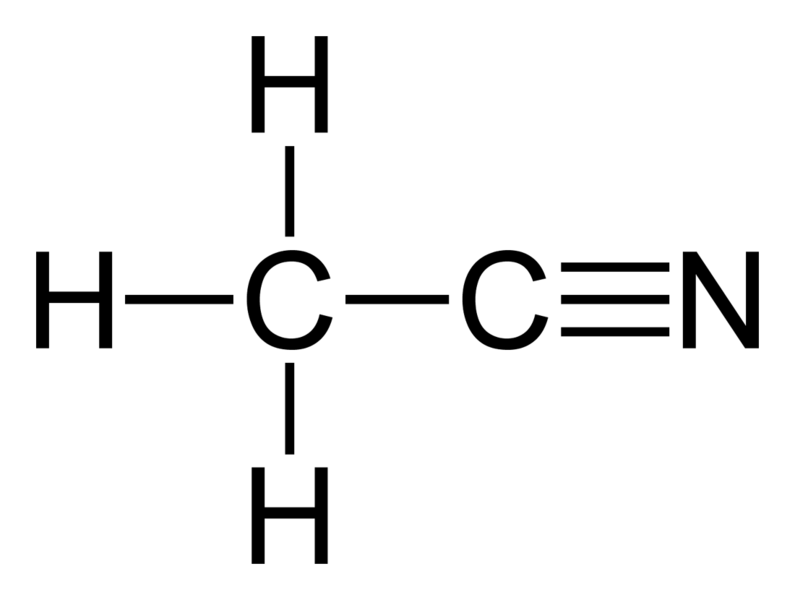
Figure 01: Structure of Acetonitrile
The molar mass of this compound is 41 g/mol. It is miscible with water and some other organic solvents as well. Acetonitrile has moderate toxicity at small doses, but inside our body, acetonitrile can undergo different metabolic processes, which leads to the production of hydrogen cyanide, which is a highly toxic compound.
When considering the applications of acetonitrile, we mainly use it as a solvent. During the purification of butadiene in refineries, acetonitrile is the solvent we use. Since this compound has a high dielectric constant, and it has the ability to dissolve electrolytes, acetonitrile is important in the manufacture of batteries as well. Furthermore, it is useful as a solvent in pharmaceutical applications as well.
What is Acetone?
Acetone is an organic compound having the chemical formula (CH3)2CO. It occurs as a colorless and flammable liquid that is highly volatile. It is the simplest and smallest ketone. Its molar mass is 58 g/mol. It has a pungent, irritating odor, and is miscible with water. The compound is common as a polar solvent. The polarity is due to the high electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen atoms of the carbonyl group. However, it is not that much polar; thus, it can dissolve both lipophilic and hydrophilic substances.
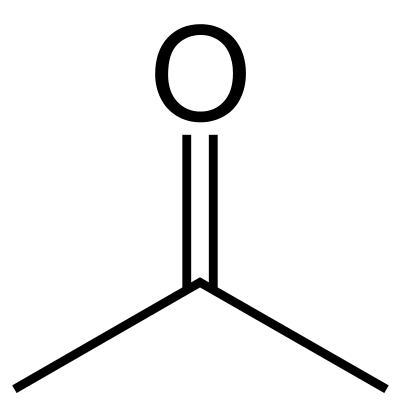
Figure 02: Chemical Structure of Acetone
Our body can produce acetone in normal metabolic processes, and it is eliminated from the body through different mechanisms. In the industrial scale, the production method includes direct or indirect production from propylene. The common process is the cumene process.
What is the Difference Between Acetonitrile and Acetone?
Both acetonitrile and acetone are organic compounds. The key difference between acetonitrile and acetone is that acetonitrile is a nitrile compound, whereas acetone is a ketone. Acetonitrile is an organic compound having the chemical formula CH3CN while Acetone is an organic compound having the chemical formula (CH3)2CO. Moreover, the molar mass of acetonitrile is 41 g/mol, while the molar mass of acetone is 8 g/mol.
When considering the atomic composition of each compound, acetonitrile contains carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen atoms whereas acetone contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Furthermore, acetonitrile is important as a solvent during the purification of butadiene in refineries, as a solvent in the pharmaceutical industry, and is useful in manufacturing batteries, etc. Acetone is important as a polar solvent. Furthermore, Acetonitrile is moderately toxic at small doses and highly toxic after metabolism while acetone is mild toxicity at high doses.
The below infographic summarizes the difference between acetonitrile and acetone.
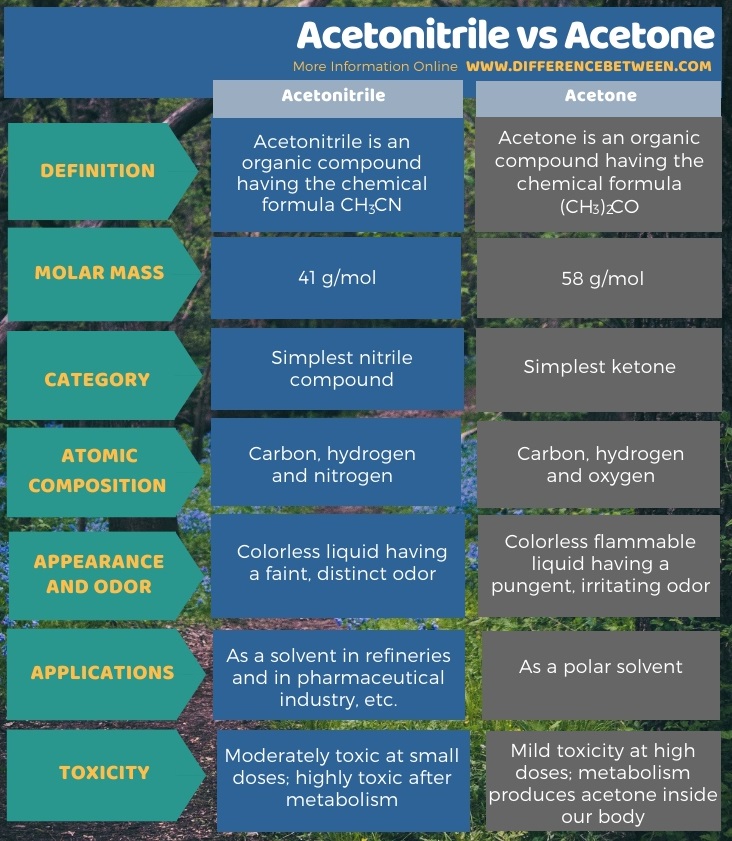
Summary – Acetonitrile vs Acetone
Both acetonitrile and acetone are organic compounds, but they have different chemical structures and different chemical and physical properties. The key difference between acetonitrile and acetone is that acetonitrile is a nitrile compound, whereas acetone is a ketone.
Reference:
1. Udovich, Carl A. “Ceramic Membrane Reactors for the Conversion of Natural Gas to Syngas.” Natural Gas Conversion V, Proceedings Ofthe 5th International Natural Gas Conversion Symposium, Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 1998, pp. 417–422., doi:10.1016/s0167-2991(98)80467-9.
2. “Acetone.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Acetonitrile-2D-flat” By Benjah-bmm27 – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Acetone-2D-skeletal” By Fvasconcellos – Vector version of File:Acetone-2D-skeletal.png by Ben Mills (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26twp6rqKaZqb%2BquMRmmKecXZawpsDOp5xo